Selective separation recovery technology of heavy metal in electroplating sludge containing chromium
A selective and heavy metal technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of large consumption of acid and alkali and various precipitants, lack of convenience for separation and recovery, poor selective separation effect, etc., and achieve considerable economic benefits, Realize the effects of harmlessness and low requirements for industrial equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
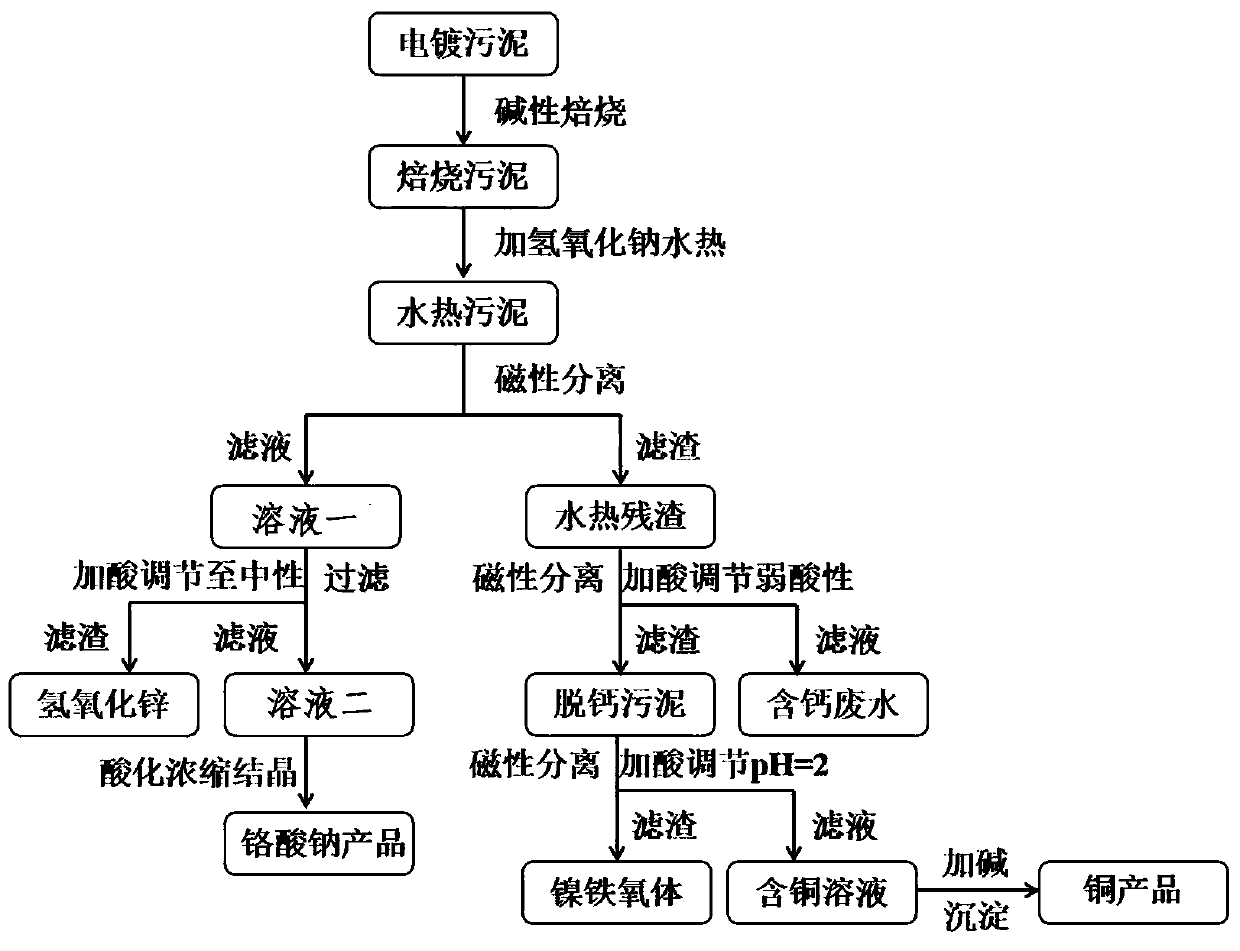
[0037]A process for selective separation and recovery of heavy metals in chromium-containing electroplating sludge, comprising the following steps:
[0038] (1) Mix 10g of electroplating sludge with 1g of ferric hydroxide and 2g of sodium carbonate, and place it in a muffle furnace for calcination at 550°C for 1.5 hours to obtain roasted sludge; the electroplating sludge is extracted from field sampling, and its elemental composition is mainly Cr(5.5%), Fe(7.8%), Ni(5.6%), Cu(6%), Zn(4.2%), Ca(10.2%), measured by ICP;
[0039] (2) Put the roasted sludge into a hydrothermal kettle, add 100mL of sodium hydroxide with a concentration of 5mol / L, and conduct a hydrothermal mineralization reaction at 180°C for 4 hours to obtain hydrothermal sludge;
[0040] (3) Separate the hydrothermal sludge by applying an external magnetic field. After separation, a 100mL solution containing Cr(VI) and Zn(II) (Zn concentration is 4.2g / L, Cr concentration is 4.5g / L) and a magnetic Hydrothermal re...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A process for selective separation and recovery of heavy metals in chromium-containing electroplating sludge, comprising the following steps:
[0045] (1) Take 20g of electroplating sludge (the electroplating sludge is extracted from field sampling, and the elemental composition determined by ICP is mainly Cr(6%), Fe(7.2%), Ni(5.5%), Cu(5.5%), Zn (4.3%), Ca (10.5%)) were mixed with 2.5g iron oxide and 5g sodium carbonate, and placed in a muffle furnace for calcination at 500°C for 2 hours to obtain roasted sludge;
[0046] (2) Put the roasted sludge into a hydrothermal kettle, add 200mL of potassium hydroxide with a concentration of 5mol / L, and conduct a hydrothermal mineralization reaction at 200°C for 3 hours to obtain hydrothermal sludge;
[0047] (3) Separate the hydrothermal sludge by applying an external magnetic field, and obtain a 200mL solution containing Cr(VI) and Zn(II) after separation (Zn concentration is 4.3g / L, Cr concentration is 4.3g / L) and a magnetic ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A process for selective separation and recovery of heavy metals in chromium-containing electroplating sludge, comprising the following steps:
[0052] (1) Take 15g of electroplating sludge (the electroplating sludge is extracted from field sampling, and the element composition determined by ICP is mainly Cr(5.8%), Fe(7.3%), Ni(5.6%), Cu(5.6%), Zn(4.1%), Ca(10%)) were mixed with 2.0g iron oxide and 3g sodium carbonate, and placed in a muffle furnace for calcination at 400°C for 2 hours to obtain roasted sludge;
[0053] (2) Put the roasted sludge into a hydrothermal kettle, add 150mL of potassium hydroxide with a concentration of 5mol / L, and conduct a hydrothermal mineralization reaction at 190°C for 10 hours to obtain hydrothermal sludge;
[0054] (3) Separate the hydrothermal sludge by applying an external magnetic field, and obtain a solution containing Cr(VI) and Zn(II) after separation—150mL (Zn concentration is 4.3g / L, Cr concentration is 4.5g / L) and a magnetic Hy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com