Slow-release antibacterial polyacrylonitrile fibers and preparing method and application thereof
A polyacrylonitrile fiber, slow-release technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, to achieve the effect of expanding the use, improving the slow-release ability, and improving the moisture absorption rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
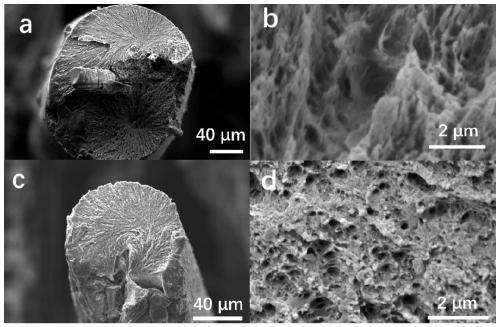
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
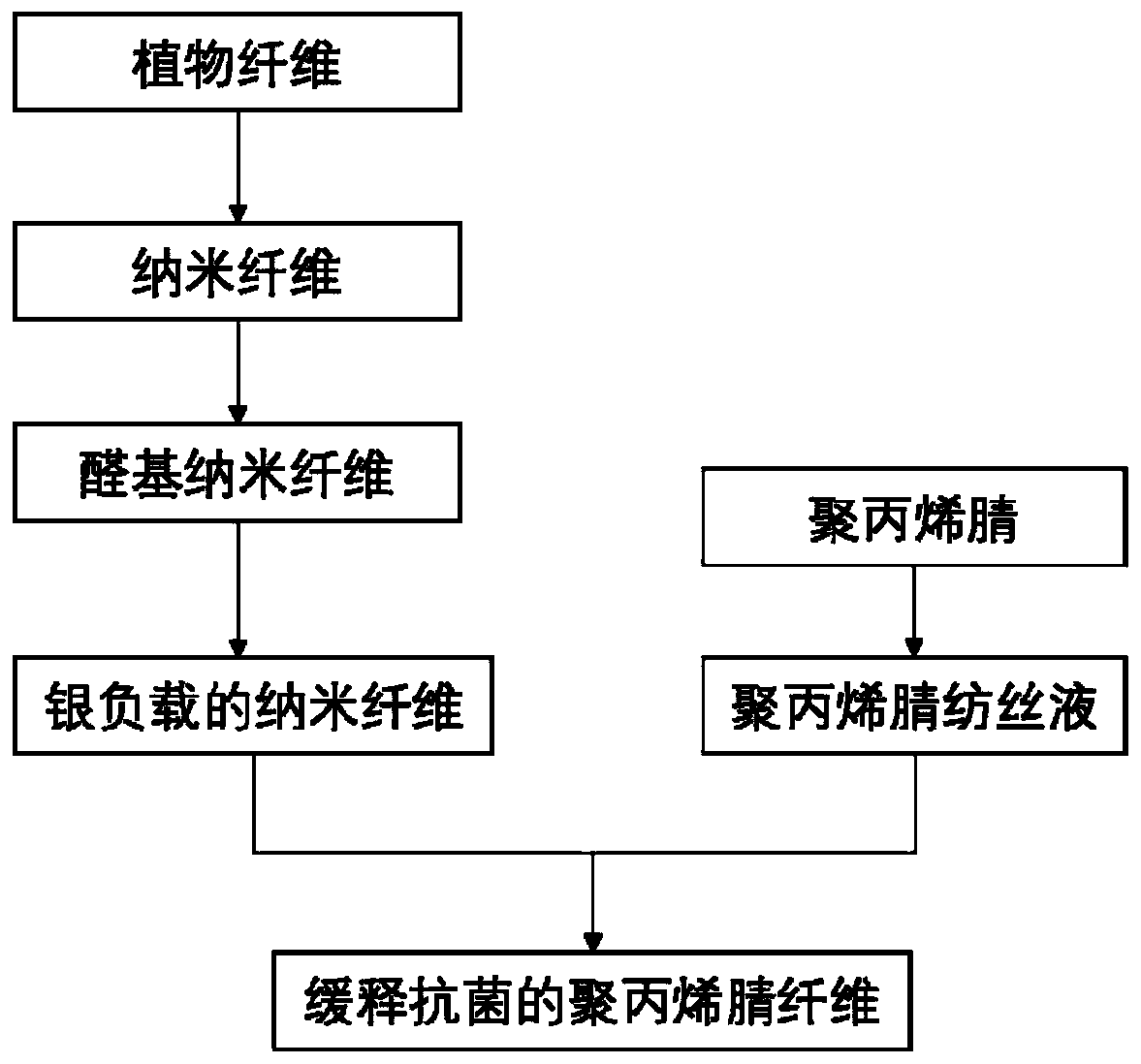
[0037] A slow-release antibacterial polyacrylonitrile fiber, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0038] (1) Take bamboo fiber as raw material, and obtain nanocellulose after being processed several times with an ultrafine particle pulverizer. The treatment conditions of ultrafine disc grinding are as follows: the slurry concentration is 0.1%, the disc grinding gap is -100 μm, and the treatment times are 10 times.
[0039] (2) Oxidizing the C2 and C3 positions of the glucopyranose structural unit in the nanocellulose prepared in the step (1) with sodium periodate to generate cellulose with a 2,3-dialdehyde structure. The sodium periodate oxidation condition is as follows: add 5 g of sodium periodate to each gram of nanocellulose, react at 80° C. in the dark for 1 hour, and stir at a speed of 500 r / min.
[0040] (3) reacting the aldehyde-based cellulose and the silver ammonia solution in the step (2) under a heating environment for a period of time to generate nano...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A slow-release antibacterial polyacrylonitrile fiber, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0045] (1) Take eucalyptus fiber as raw material, and obtain nanocellulose after being processed several times with an ultrafine pulverizer. The treatment conditions of ultrafine disc grinding are as follows: the slurry concentration is 20%, the disc grinding gap is 200 μm, and the treatment times are 100 times.
[0046] (2) Oxidizing the C2 and C3 positions of the glucopyranose structural unit in the nanocellulose prepared in the step (1) with sodium periodate to generate cellulose with a 2,3-dialdehyde structure. The sodium periodate oxidation condition is: adding 1 g of sodium periodate to each gram of nanocellulose, reacting at 80° C. in the dark for 3 hours, and stirring at a speed of 500 r / min.
[0047] (3) reacting the aldehyde-based cellulose and the silver ammonia solution in the step (2) under a heating environment for a period of time to generate nano-silve...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A slow-release antibacterial polyacrylonitrile fiber, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0052] (1) Using rice straw fiber as a raw material to obtain nanocellulose after being processed several times with an ultrafine pulverizer. The treatment conditions of ultrafine disc grinding are as follows: the slurry concentration is 10%, the disc grinding gap is -100 μm, and the number of treatments is 50 times.
[0053] (2) Oxidizing the C2 and C3 positions of the glucopyranose structural unit in the nanocellulose prepared in the step (1) with sodium periodate to generate cellulose with a 2,3-dialdehyde structure. The sodium periodate oxidation condition is as follows: add 2.5 g of sodium periodate per gram of nanocellulose, react at 60° C. in the dark for 2 hours, and stir at a speed of 500 r / min.
[0054] (3) reacting the aldehyde-based cellulose and the silver ammonia solution in the step (2) under a heating environment for a period of time to generate nano-s...
PUM
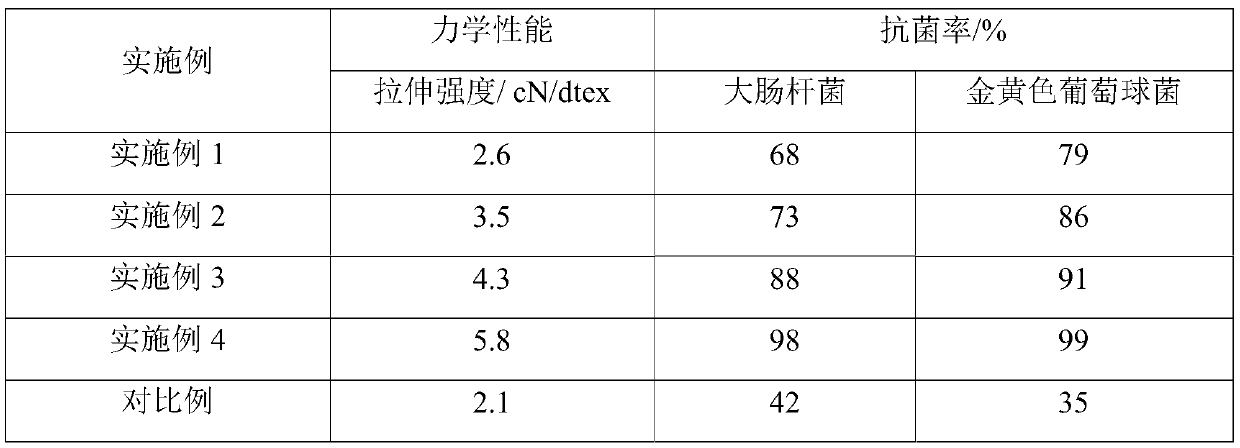
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com