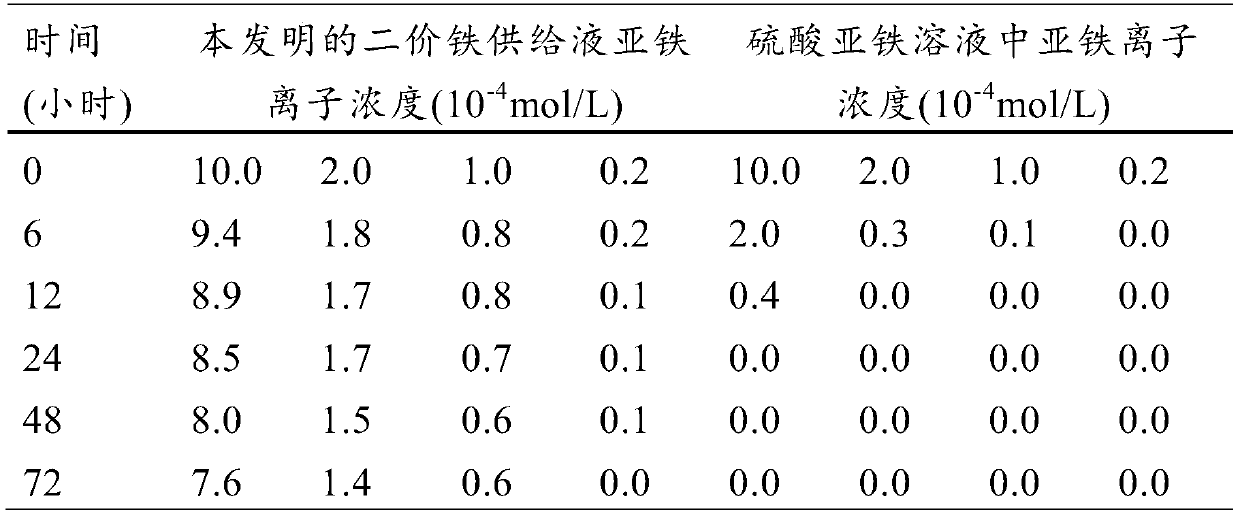
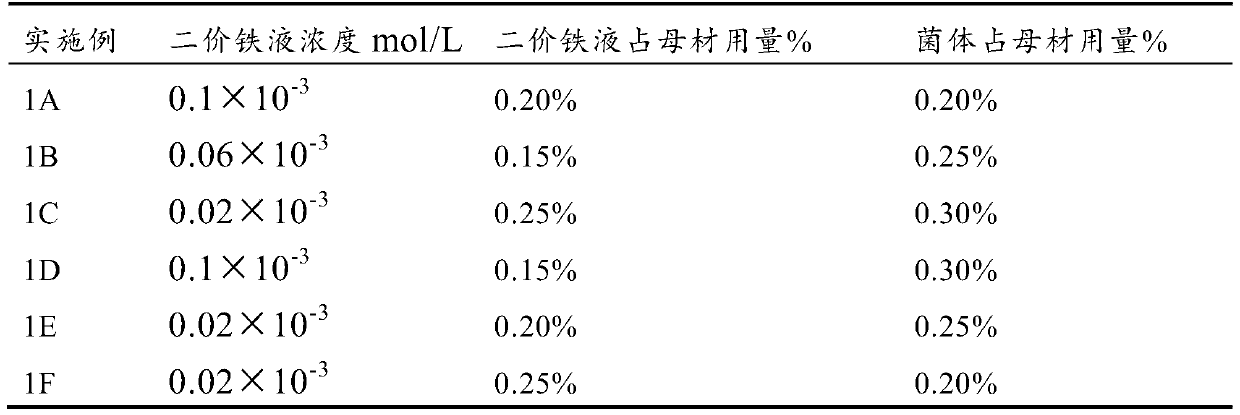
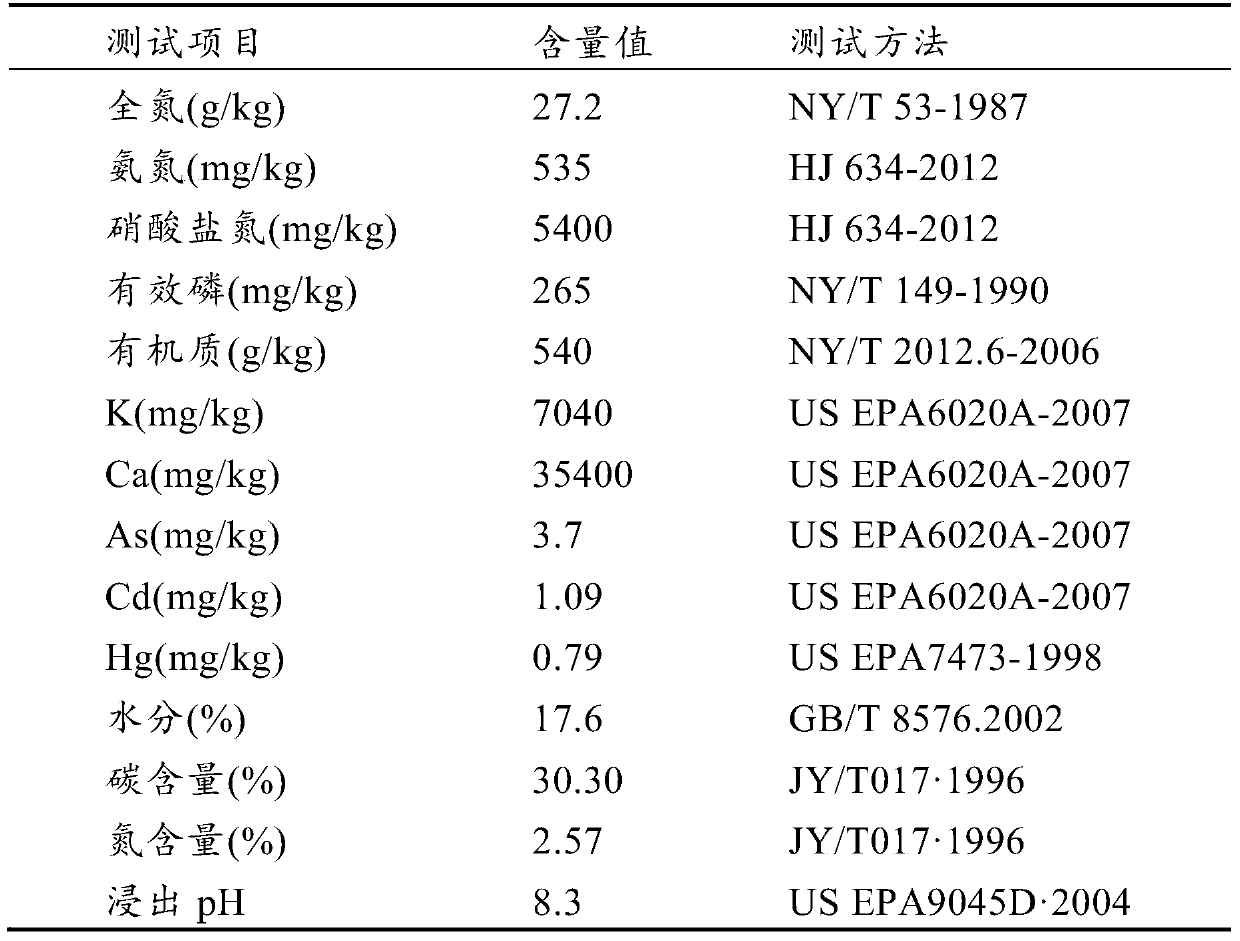
Application of ferrous iron supply liquid to aspect of promoting flora fermentation for petroleum residue treatment
A technology for supplying liquid and ferrous iron, applied in the direction of solid waste removal, etc., can solve problems such as hindering the effective use of resources, achieve the effects of shortening the fermentation cycle, increasing the volume reduction rate, and better degrading organic phosphorus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 2
[0016] The preparation of embodiment 1 ferrous iron supply liquid
[0017] Put citric acid monohydrate powder (2.5mol) with a purity of ≥99% into a reactor with 10L of water, heat up to 60°C, and slowly add a total of 3mol of carbonic acid with a purity of ≥97% in 10 batches under stirring. Sodium, stir for 6 minutes after each batch is added and heat up to 80°C, use nitrogen to isolate the air, add 1 mol of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate with a purity of ≥95% at one time, finally heat up to 92°C, and keep stirring at 92°C to react 2 hours. Cool down to room temperature in the absence of air. Finally, a ferrous iron supply liquid is obtained.
[0018] After inspection, in the ferrous iron supply liquid of the present embodiment, the total concentration of ferrous ions (ferrous iron) in the mixed solution is 0.095mol / L, and the moles of ferrous sodium citrate, ferrous sulfate, and ferrous citrate The mass ratio is 1:0.28:0.23.
Embodiment 2 2
[0019] Embodiment 2 Preparation of ferrous iron supply liquid
[0020] Put citric acid monohydrate powder (2.5mol) with a purity of ≥99% into a reactor with 10L of water, heat up to 50°C, and slowly add a total of 3mol of carbonic acid with a purity of ≥97% in 8 batches under stirring. Sodium, after each batch is added, stir for 8 minutes and heat up to 70°C, use nitrogen to isolate the air, add 1 mol of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate with a purity of ≥95% at one time, finally heat up to 88°C, and keep stirring at 88°C for 5 Hour. Cool down to room temperature in the absence of air. Finally, a ferrous iron supply liquid is obtained.
[0021] After inspection, in the ferrous iron supply liquid of the present embodiment, the total concentration of ferrous ions (ferrous iron) in the mixed solution is 0.095mol / L, and the moles of ferrous sodium citrate, ferrous sulfate, and ferrous citrate The mass ratio is 1:0.38:0.17.
Embodiment 3 2
[0022] Embodiment 3 Preparation of ferrous iron supply liquid
[0023] Put citric acid monohydrate powder (2.5mol) with a purity of ≥99% into a reaction kettle with 10L of water, raise the temperature to 55°C, and slowly add a total of 3mol of sodium carbonate with a purity of ≥97% in 12 batches under stirring After each batch is added, stir for 4 minutes and raise the temperature to 75°C, use nitrogen to isolate the air, add 1 mol of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate with a purity of ≥95% at one time, and finally raise the temperature to 90°C, and keep stirring at 90°C for 2 Hour. Cool down to room temperature in the absence of air. Finally, a ferrous iron supply liquid is obtained.
[0024] After inspection, in the ferrous iron supply liquid of the present embodiment, the total concentration of ferrous ions (ferrous iron) in the mixed solution is 0.095mol / L, and the moles of ferrous sodium citrate, ferrous sulfate, and ferrous citrate The mass ratio is: 1:0.35:0.2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com