Near-infrared II-region fluorescent quantum dot cytomembrane marking system and marking method and application
A fluorescent quantum dot and labeling system technology, applied in the field of nano-biological materials, can solve the problems of low tissue penetration depth, easy quenching of fluorescent probes, high spontaneous background fluorescence, etc., to achieve good tissue penetration depth, good labeling and The effect of related function research and simplified experimental operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
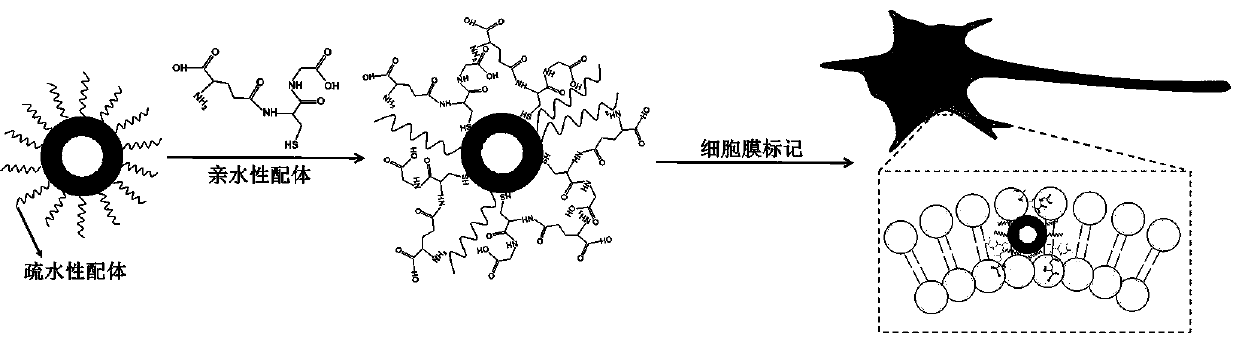
[0035] Another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention also provides a preparation method for the aforementioned near-infrared II region fluorescent quantum dot cell membrane labeling system, which includes: making hydrophobic ligands and hydrophilic ligands respectively modified and connected to the near-infrared II region fluorescent quantum dots Dot the surface to obtain the near-infrared II region fluorescent quantum dot cell membrane labeling system.
[0036]In some embodiments, the preparation method specifically includes:
[0037] The hydrophobic ligand is modified and connected to the surface of the fluorescent quantum dot in the near-infrared II region to form a hydrophobic ligand quantum dot;
[0038] The hydrophilic ligand, the hydrophobic ligand quantum dot and the solvent are uniformly mixed, stirred, and centrifuged to obtain the near-infrared II region fluorescent quantum dot cell membrane labeling system.
[0039] In some more specific implementatio...
Embodiment 1
[0056] Hydrophilic GSH-DT-Ag 2 The specific preparation method of S quantum dots:
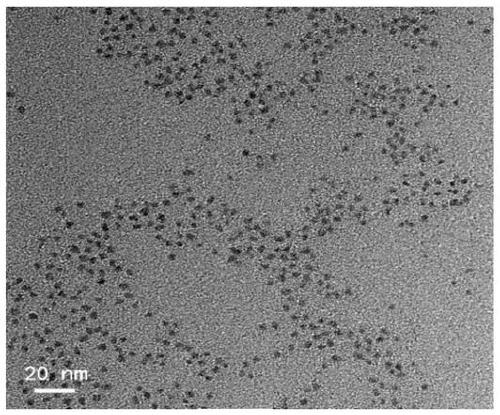
[0057] Take a clean and dry glass bottle, add chloroform and deionized water to it, and add DT-Ag according to a certain molar concentration ratio 2 S and glutathione (GSH), after mixing by magnetic stirring, continue to stir under the condition of avoiding light, and finally take the upper water phase and the liquid at the oil-water interface, discard the upper water phase by centrifugation, and wash once with deionized water Obtained GSH-DT-Ag after centrifugation and resuspension 2 S water-soluble quantum dots. GSH-DT-Ag prepared 2 The TEM characterization data of S hydrophilic quantum dots are as follows: figure 2 As shown, the average particle size is about 2 nm.
Embodiment 2
[0059] Hydrophilic DHLA-DT-Ag 2 The specific preparation method of S quantum dots:
[0060] Take a clean and dry glass bottle, add chloroform and deionized water to it, and add DT-Ag according to a certain molar concentration ratio 2 S and dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA), after mixing by magnetic stirring, continue to stir under the condition of avoiding light, and finally take the upper water phase and the liquid at the oil-water interface, discard the upper water phase by centrifugation, and wash once with deionized water DHLA-DT-Ag obtained after centrifugation and resuspension 2 S water-soluble quantum dots. The preparation method of other hydrophilic hydrophilic / phobic double ligand quantum dots is similar.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com