Low-pressure wireless hair dryer
A hair dryer, wireless technology, applied in the field of low-voltage wireless hair dryer, can solve the problems of metal heating wire temperature rise, easy to cause local burns, no antibacterial, etc., to reduce power loss, avoid winding and knotting problems, and easy to use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
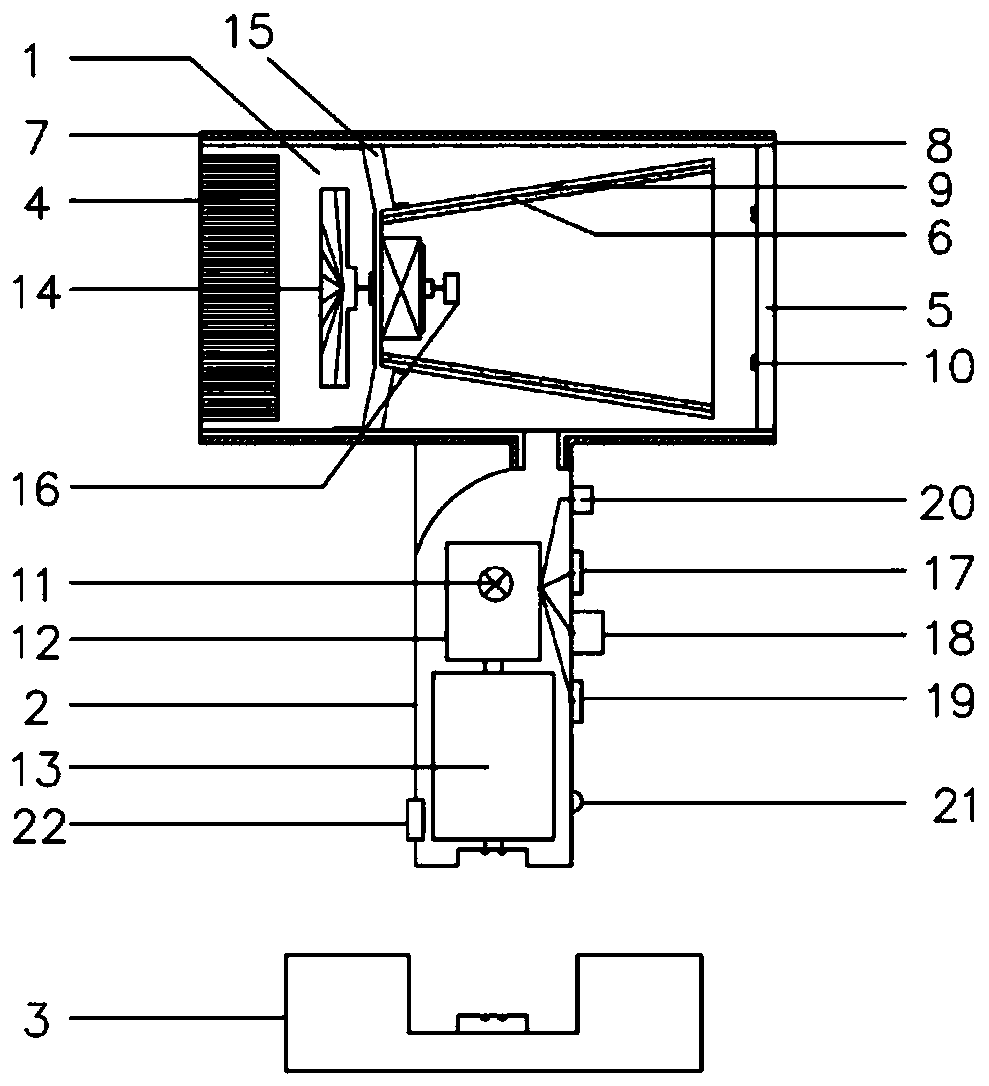
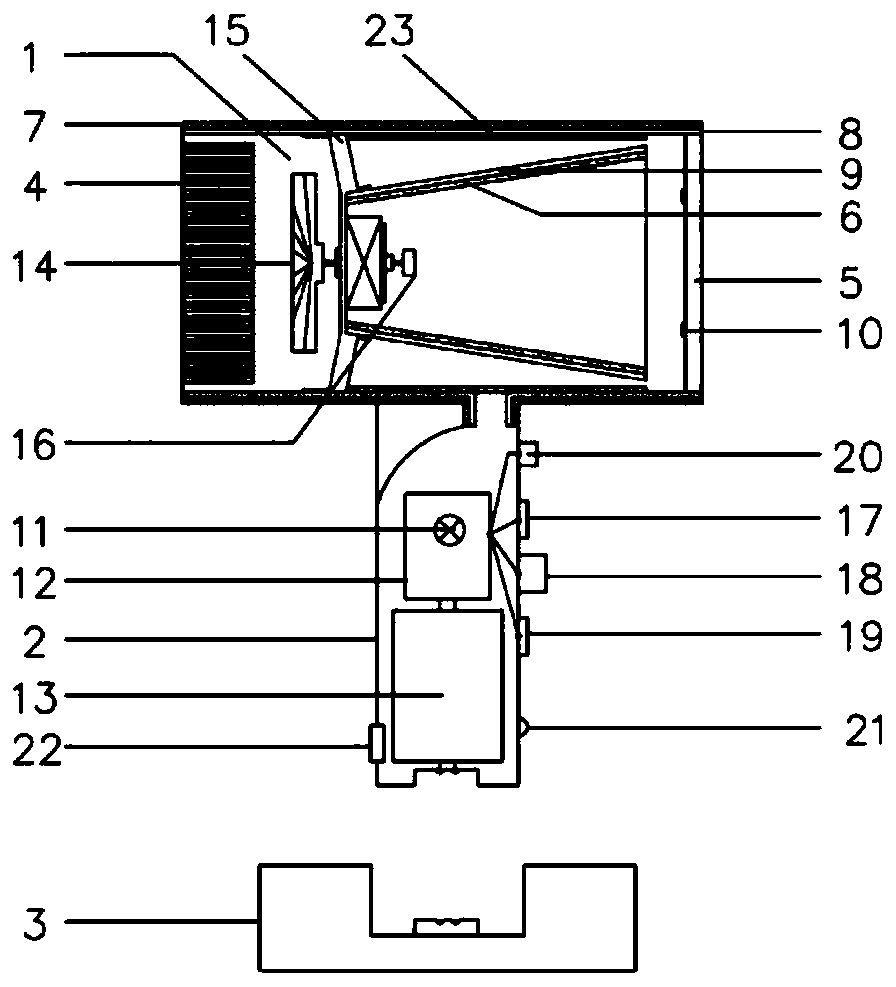
[0029] This embodiment describes a low-voltage wireless hair dryer, such as figure 1 As shown, the hair dryer includes a blower 1 , a handle 2 and a base 3 , the lower part of the blower 1 is connected to the handle 2 , and the inner cavity communicates, and the blower can be placed on the base 3 through the handle 2 .
[0030] The air duct 1 can be a straight cylindrical structure, and the air duct 1 can be made of high temperature resistant ABS (acrylonitrile-styrene-butadiene copolymer), PPS (polyphenylene sulfide), PC (polycarbonate), PA (polyethylene sulfide) Amide), PP (polypropylene), HDPE (high-density polyethylene) and a series of polymer composite materials or imitation metal texture materials. An air inlet cover 4 and an air outlet cover 5 are respectively provided at the left and right ends of the air cylinder 1 to form an air circulation channel in the air cylinder 1 .
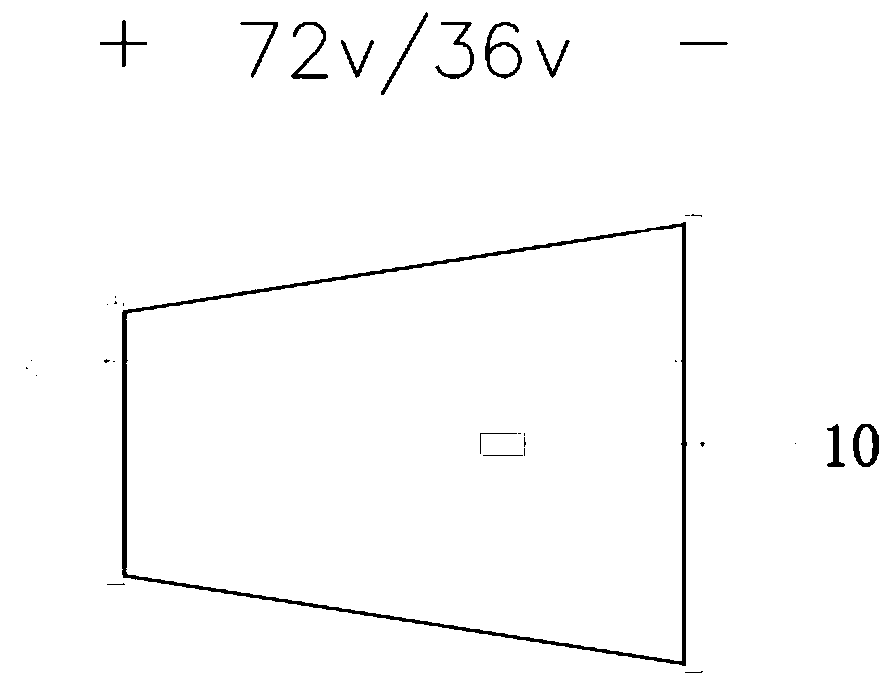
[0031] The heating part is installed on the side close to the air outlet cover 5 in the inner...
Embodiment 2
[0049] In a preferred embodiment, the heating element 6 adopts the self-made new heating element of the present invention, which is made of high-performance electric heating material obtained from microcrystalline graphite directly grown on high-temperature-resistant fibers. Specifically, the novel heating element of the present invention includes a high temperature resistant fiber layer and a microcrystalline graphite layer coated outside the high temperature resistant fiber layer.
[0050] The preparation method of electrothermal material usually includes the following steps:
[0051] Step 1: Prepare the cleaned fiber material;
[0052] Step 2: Carry out surface coating treatment on the fiber material, and the coated film layer contains a carbon source cracking catalytic material;
[0053] Step 3: Place the coated fiber material in a vacuum reaction chamber;
[0054] Step 4: feeding protective gas and reducing gas into the vacuum reaction chamber, and then feeding carbon s...
example
[0057] Specifically, taking the growth of microcrystalline graphite after copper-clad treatment on quartz fiber cloth as an example, the preparation method is specifically described, and the specific process is as follows:
[0058] Step 1: Prepare a clean quartz fiber cloth, and clean the quartz fiber cloth by ultrasonic cleaning;
[0059] Step 2: Coating copper (nano-copper particles) on the surface of the quartz fiber cloth by spraying copper at room temperature, completing the coating treatment on the surface of the quartz fiber cloth, and controlling the thickness of the copper film to 50 μm. The normal temperature copper spraying mentioned here refers to the technology of using a metal solvent to dissolve copper nanoparticles into one, and using an ordinary paint spray gun to directly spray the metal coating, which is a prior art and will not be described in detail here.
[0060] Step 3: Put the copper-clad quartz fiber cloth into a 1100°C high-temperature tube furnace wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com