A gel bionic artificial muscle 3D printing device and preparation method
An artificial muscle and 3D printing technology, applied in the field of artificial muscles, can solve problems such as low efficiency, poor surface contact, and high cost, and achieve the effects of simplifying process steps, avoiding poor contact, and high production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
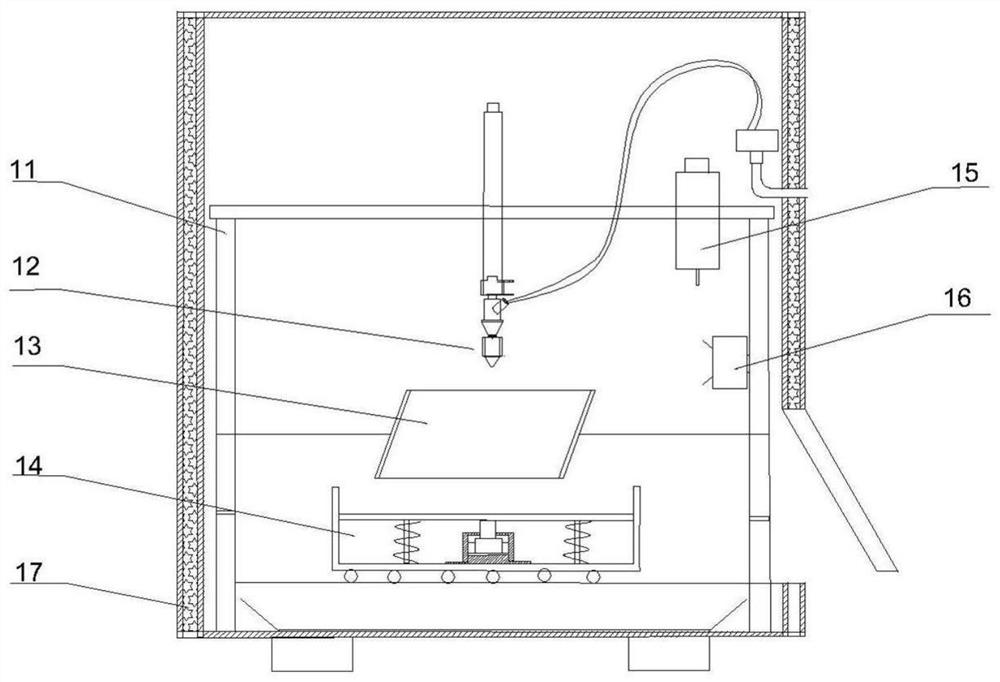
[0029] The present invention provides a technical solution: a 3D printing preparation method for gel-like bionic artificial muscles, comprising the following steps:
[0030](1) 3D modeling and program programming: use the drawing software SolidWorks to design the model and upload and process the simple program of the single-chip microcomputer.
[0031] (2) Basic settings of the 3D printer: set the accuracy of the thickness of the 3D printing driver layer between 0.5mm-0.8mm, and the printing thickness between 2mm-5mm. Set the drying temperature to 75°C and work for 30 minutes each time. Set the artificial muscle electrolyte layer water phase separation soaking time to 10 minutes.
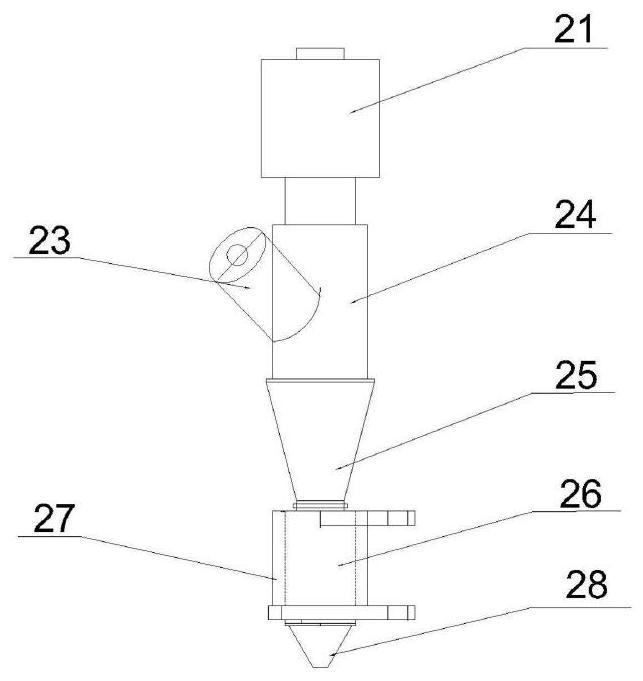
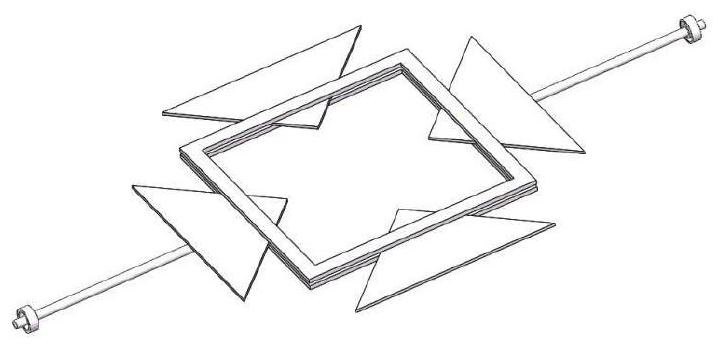
[0032] (3) Artificial muscle driver layer printing: the nozzle works, and the pre-configured cellulose hydrogel is sprayed on the printing platform through the nozzle; then the first temperature control device works, the first heater starts heating, and the internal temperature of the printer is ra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com