Method for evaluating soil acid-buffer ability by utilizing surface hydroxyl hydrogen ion adsorption capacity
A technology of adsorption capacity and hydrogen ions, applied in the field of soil chemistry, to achieve the effect of stable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1 method construction
[0053] (1) Soil acid-base buffer reaction system
[0054] The acid-base buffering reaction of soil is mainly carried out by many active substances, mainly composed of calcium carbonate, oxygen-containing functional groups, exchangeable cations, and oxides of iron and aluminum. The following is a brief analysis of the main components involved in the buffer reaction system.
[0055] Calcium carbonate can dissolve under acidic conditions and produce carbon dioxide volatilization. As shown in formula (1).
[0056]
[0057] Surface functional groups can accept hydrogen ions under acidic conditions and donate hydrogen ions under basic conditions. As shown in formula (2).
[0058]
[0059] Exchangeable cations mainly include base ions and acid-causing ions (hydrogen ions, aluminum ions), and exchangeable base ions can exchange with acid-causing ions under acidic conditions. Under alkaline conditions, acid-causing ions can exchange ...
Embodiment 2
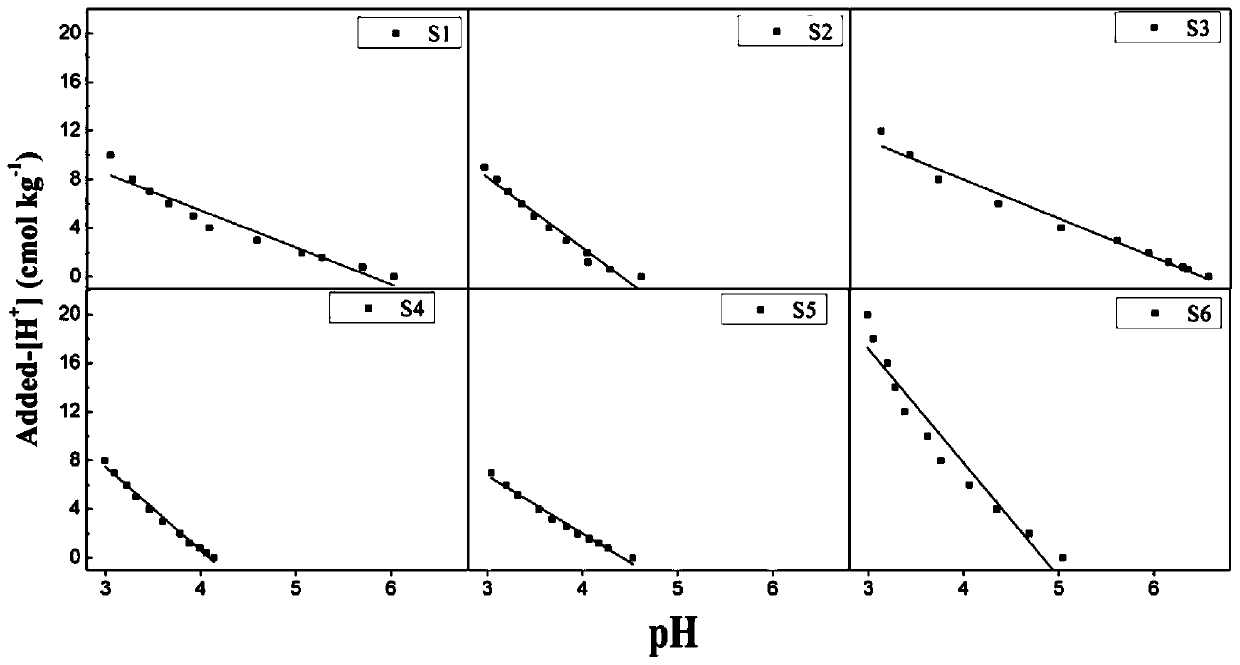
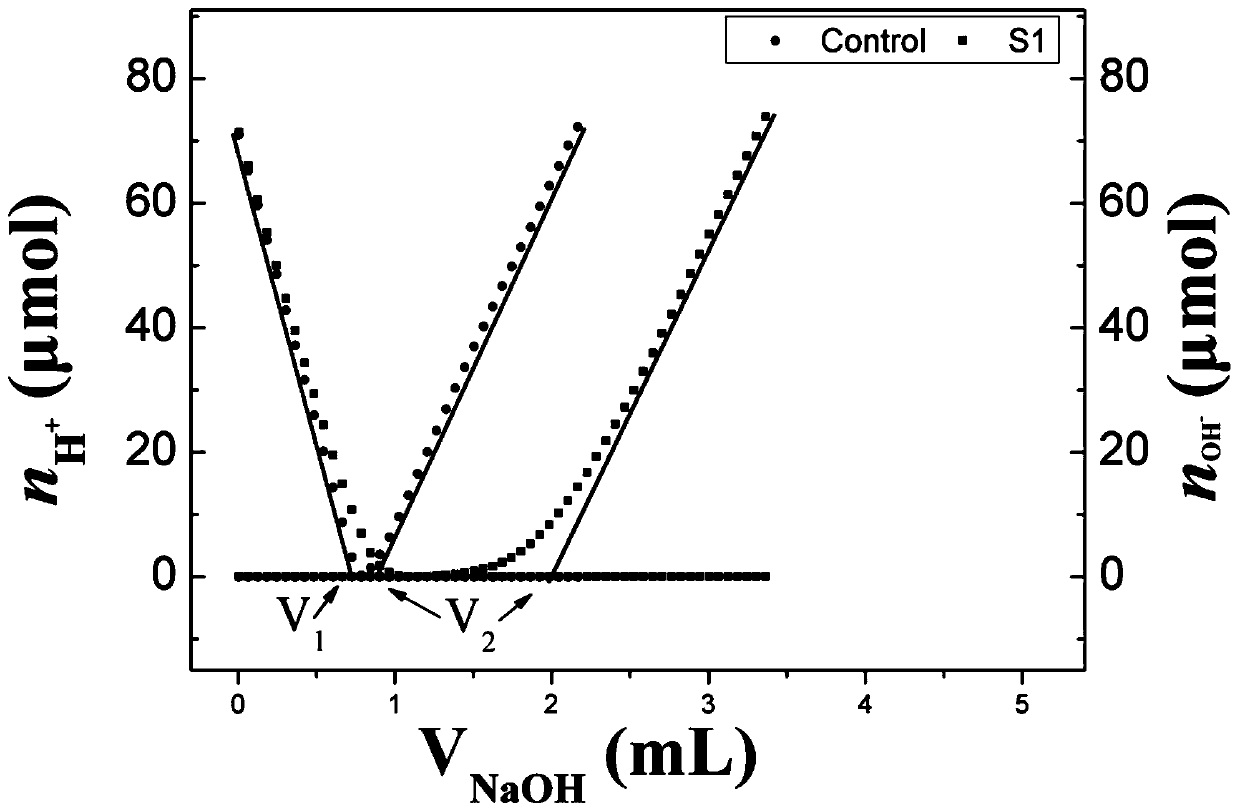
[0073] (1) Selection and pretreatment of soil
[0074] The calcium carbonate content of the collected Hainan brick red soil (S1) is less than 1%. After natural air drying, it is ground through a 0.15mm nylon sieve.
[0075] (2) Preparation and calibration of strong acid and strong base standard solutions
[0076] 0.1M hydrochloric acid: Take 8.3mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid (12M), dilute to 1L with ultrapure water (18MΩ·cm), and accurately weigh 0.02g of sodium carbonate for calibration.
[0077] 0.1M sodium hydroxide: Weigh 4g of sodium hydroxide, dissolve it with ultrapure water and dilute to 1L, accurately weigh 0.05g of potassium hydrogen phthalate for calibration.
[0078] (3) Preparation of ionic strength solution
[0079] Weigh 5.844g of sodium chloride, dissolve it in ultrapure water and dilute to 1L to make a 0.1M sodium chloride solution.
[0080] (4) Acid-base titration process
[0081] In this method, a Metrohm 905 automatic potentiometric titrator (Metr...
Embodiment 3
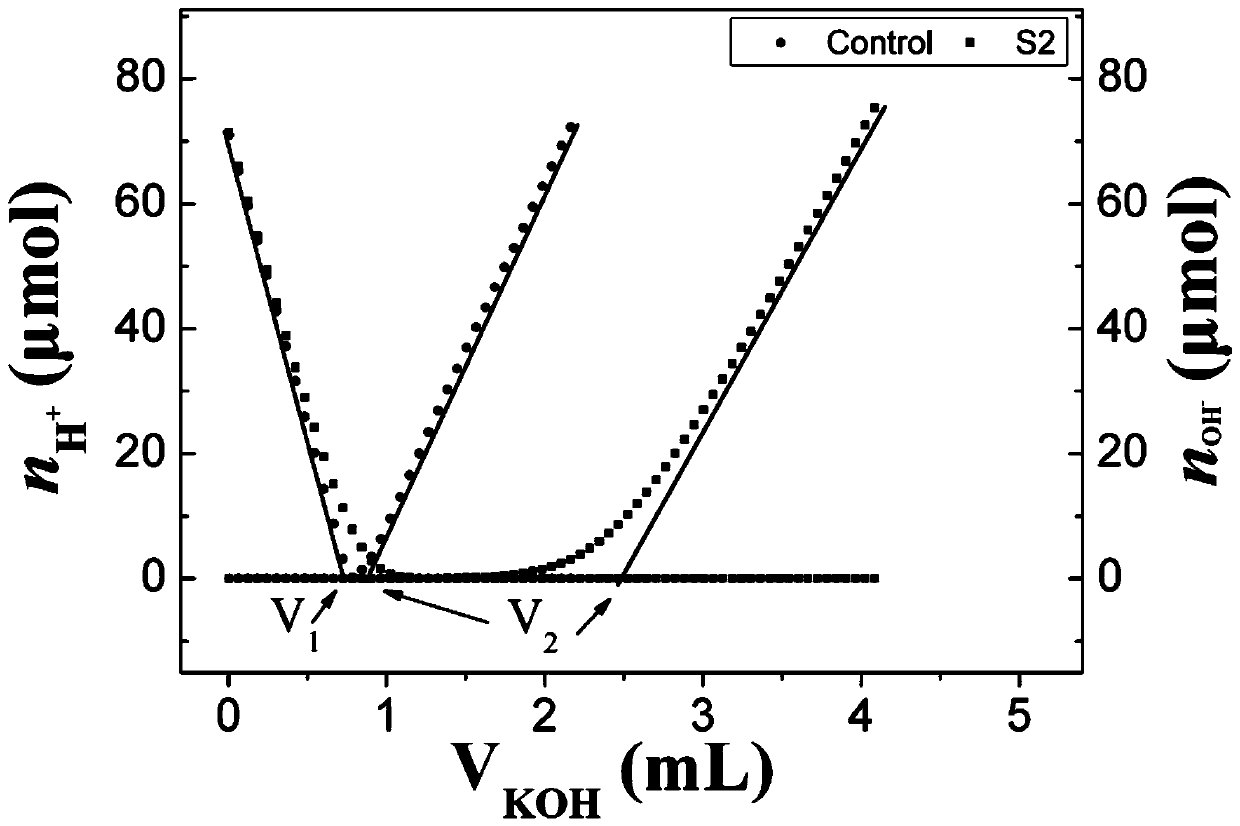
[0101] (1) Selection and pretreatment of soil
[0102] The collected Guangdong paddy soil (S2) has a calcium carbonate content of less than 1%, and is ground through a 0.15mm nylon sieve after natural air drying.
[0103] (2) Preparation and calibration of strong acid and strong base standard solutions.
[0104] 0.1M nitric acid: take 6.97mL of concentrated nitric acid (14M), dilute to 1L with ultrapure water (18MΩ·cm), and accurately weigh 0.02g of sodium carbonate for calibration.
[0105] 0.1M Potassium Hydroxide: Weigh 5.61g of Potassium Hydroxide, dissolve it in ultrapure water and dilute to 1L, accurately weigh 0.05g of Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate for calibration.
[0106] (3) Weigh 10.11 g of potassium nitrate, dissolve it in ultrapure water and dilute to 1 L to prepare a 0.1 M potassium nitrate solution.
[0107] (4) Acid-base titration process
[0108] Using the Metrohm 905 automatic potentiometric titrator, the pH electrode was calibrated in standard buffer solut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com