Perovskite solar cell device and method for manufacturing same
A solar cell and perovskite technology, applied in the direction of final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of limited commercial applications, high production costs, low mobility, etc., and achieve high energy conversion efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
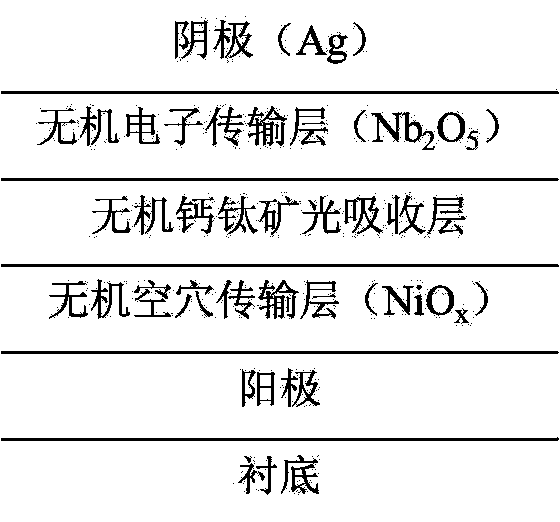
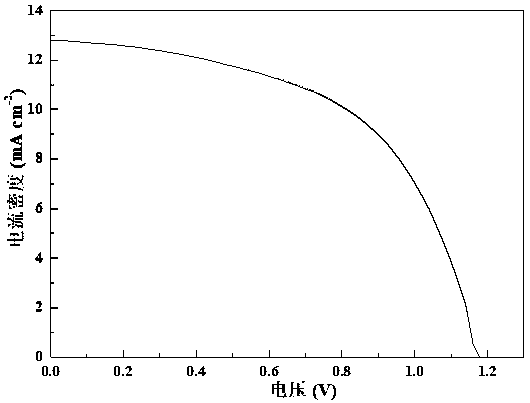
[0065] Take several ITO conductive glass substrates with the same batch number, the thickness of ITO is about 200 nanometers, and its square resistance is about 20 ohms / square. Sequentially use micron semiconductor special detergent, deionized water, acetone, and isopropanol to ultrasonically clean for 15 minutes to remove dirt on the substrate surface. Then put it into an incubator to dry at 80 degrees Celsius. Subsequently, inorganic nickel oxide (NiO x ) as the hole transport layer, by adjusting the thickness of the inorganic hole transport layer to 20-50 nanometers and then optimizing the energy conversion efficiency of the all-inorganic perovskite battery device, the evaporated nickel oxide substrate is transferred to the anhydrous In an oxygen-free glove box filled with high-purity nitrogen. In this glove box, the component prepared by spin coating is CsPbI 2 The hybrid inorganic perovskite photoactive layer of Br was then heated using a two-step heating method, first...
example 2
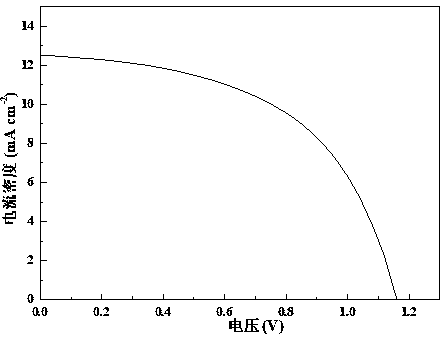
[0071] The preparation process is the same as that in Example 1. A number of ITO conductive glass substrates with the same batch number are taken. The thickness of the ITO is about 200 nanometers, and its sheet resistance is about 20 ohms / square. Sequentially use micron semiconductor special detergent, deionized water, acetone, and isopropanol to ultrasonically clean for 15 minutes to remove dirt on the substrate surface. Then put it into an incubator to dry at 80 degrees Celsius. Subsequently, inorganic nickel oxide (NiO x ) as the hole transport layer, the evaporated nickel oxide substrate was annealed in the air at 200 degrees Celsius for 1 hour, and then transferred to a glove box filled with high-purity nitrogen gas without water and oxygen. In this glove box, the component prepared by spin coating is CsPbI 2 The hybrid inorganic perovskite photoactive layer of Br was then heated using a two-step heating method, first on a heating stage at 40 °C for 4 min, then at 160 °...
example 3
[0075] The preparation process is the same as that in Example 1. A number of ITO conductive glass substrates with the same batch number are taken. The thickness of the ITO is about 200 nanometers, and its sheet resistance is about 20 ohms / square. Sequentially use micron semiconductor special detergent, deionized water, acetone, and isopropanol to ultrasonically clean for 15 minutes to remove dirt on the substrate surface. Then put it into an incubator to dry at 80 degrees Celsius. Subsequently, inorganic nickel oxide (NiO x ) as the hole transport layer, the evaporated nickel oxide substrate was annealed in the air at 300 degrees Celsius for 1 hour, and then transferred to a glove box filled with high-purity nitrogen gas without water and oxygen. In this glove box, the component prepared by spin coating is CsPbI 2 The hybrid inorganic perovskite photoactive layer of Br was then heated using a two-step heating method, first on a heating stage at 40 °C for 4 min, then at 160 °...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com