Gene methylation analysis method and product and application
An analysis method, a methylation technology, applied in the field of gene analysis, can solve the problems of increasing nucleic acid loss, high DNA loss, and high probability of contamination, and achieve the effects of reducing degradation and loss, simplifying the operation process, and facilitating automatic operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
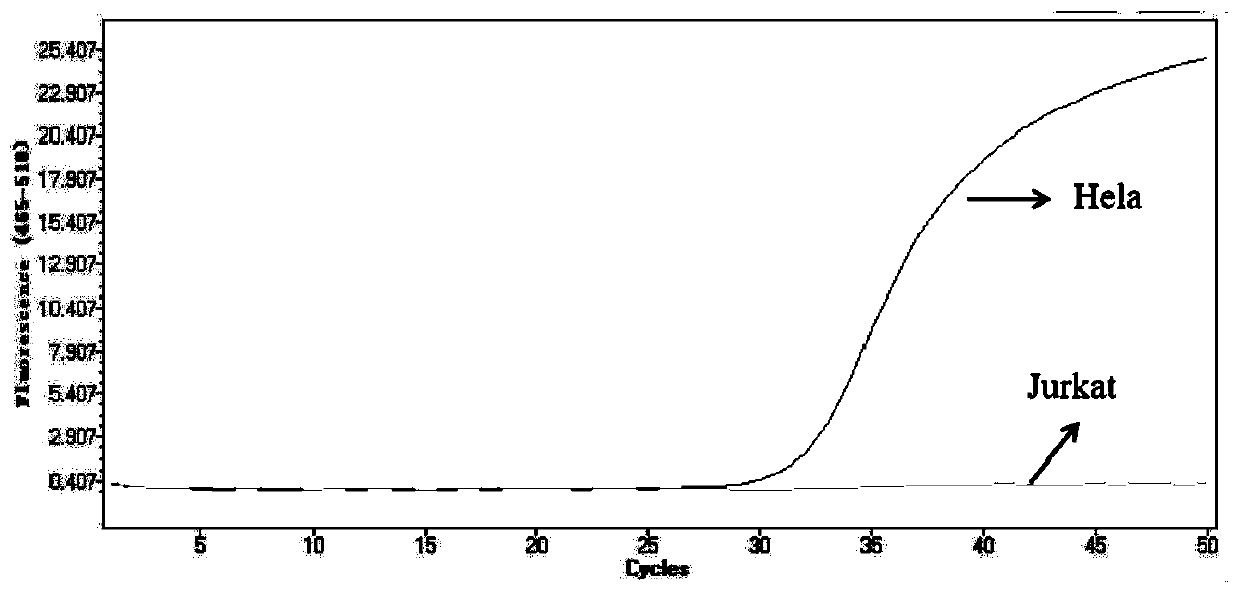
[0062] Detection of methylation of septin9 gene
[0063] Sample pretreatment: Put equal amounts of interrupted Hela and Jurkat cell DNA into 2 ml of healthy human plasma samples;
[0064] Concentration: Add 4 ml of lysate (the lysate consists of 5.22M guanidine isothiocyanate, 0.42M TE buffer and 17% triton) and 40 microliters of magnetic beads (beaver, hydroxyl magnetic beads), Shake at room temperature for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant after absorbing the magnetic beads on the magnetic stand.
[0065] Conversion: add 320 microliters of conversion reagent (the conversion reagent is 5.34M ammonium bisulfite, 0.53M sodium sulfite, 0.05M protective agent (protective agent component 6-hydroxyl-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl The magnetic beads were resuspended in a mixture of tetrahydrofuran solution of chroman-2-carboxylic acid)), and the above mixture was incubated at 85° C. for 40 minutes.
[0066] Re-concentration: 1 ml of binding solution (7M guanidine hydrochloride) was added t...
Embodiment 2
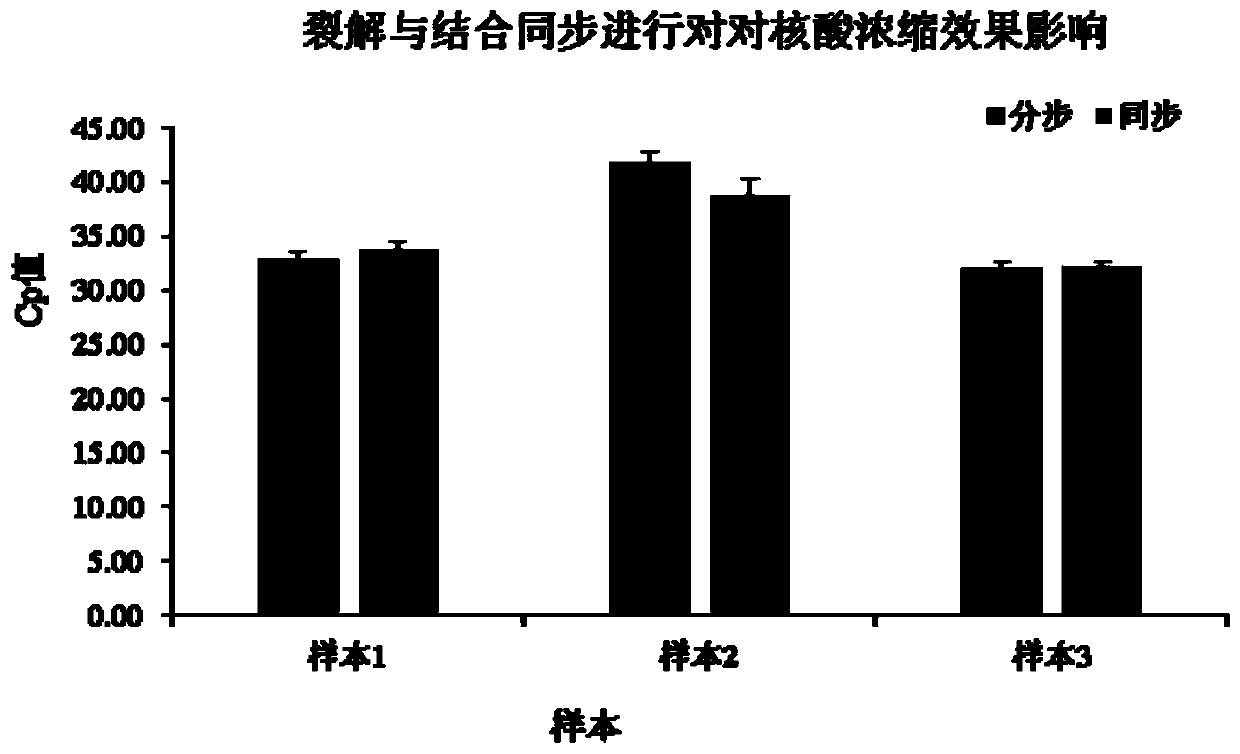
[0070] In this example, the effects of synchronous addition of lysate and magnetic beads and sequential addition of lysate and magnetic beads were compared. The remaining steps of the method of sequentially adding magnetic beads are the same as those in Example 1, and nucleic acid concentration is performed on the same batch of samples. The obtained DNA was detected by real-time fluorescent PCR for methylation, and the detection results are shown in figure 2 . The results show that magnetic beads can be added simultaneously with the lysate in the sample, which will not affect the effect of lysis and binding, so that the binding step and lysis step can be completed at the same time, thereby greatly simplifying the nucleic acid extraction step. figure 2 It shows that the cleavage and binding are carried out synchronously on the effect of nucleic acid concentration.
Embodiment 3
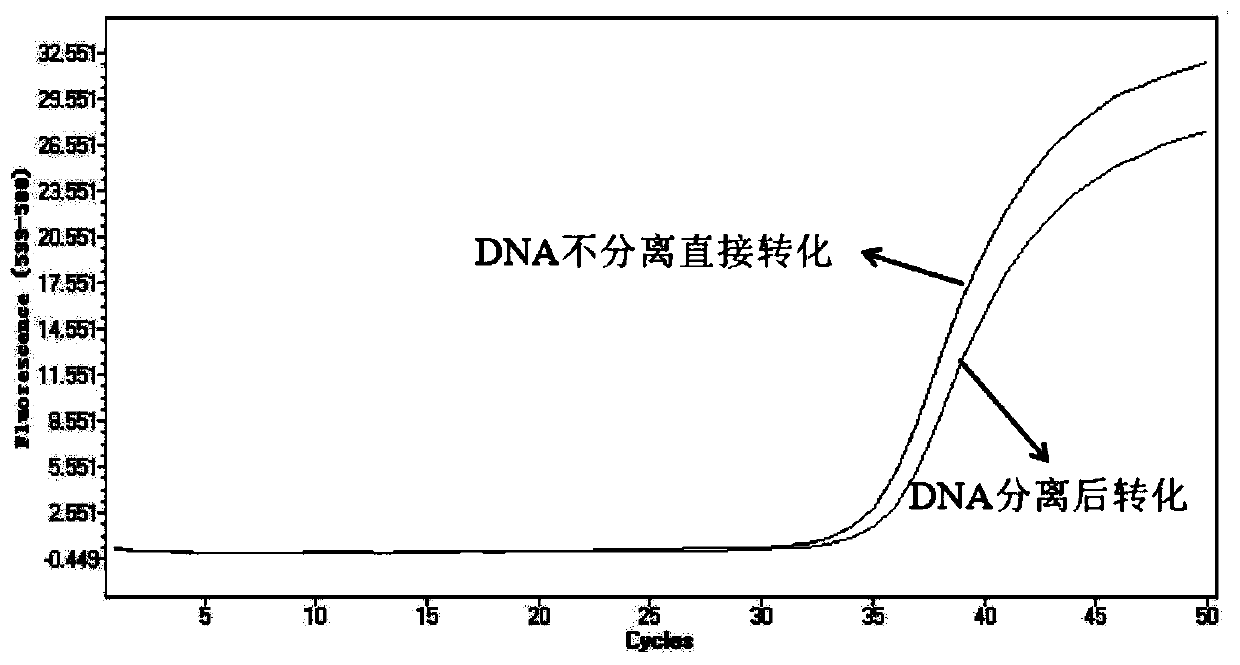
[0072] DNA is directly transformed after enrichment by magnetic beads
[0073] Into 2mL of healthy human plasma samples into the interrupted Hela cell DNA. 1 part is processed completely according to embodiment 1, and 1 part of step (1) is processed according to the following steps:
[0074] Concentration: add 4 ml of lysate and 40 μl of magnetic beads, shake at room temperature for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant after the magnetic frame absorbs the magnetic beads, and then wash with 100 μl of buffer (TE buffer, pH=8.0) take off.
[0075] Transformation: Add 220 microliters of transformation reagent (the transformation reagent is ammonium bisulfite of 7.8M, sodium sulfite of 0.78M, DNA protectant of 0.07M (protectant component 6-hydroxyl-2,5,7,8 - a mixture of tetramethylchroman-2-carboxylic acid in diethylene glycol dimethyl ether solution), the above mixture was incubated at 85° C. for 40 minutes.
[0076] Re-concentration: add 1 ml of binding solution (7M guanidine ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com