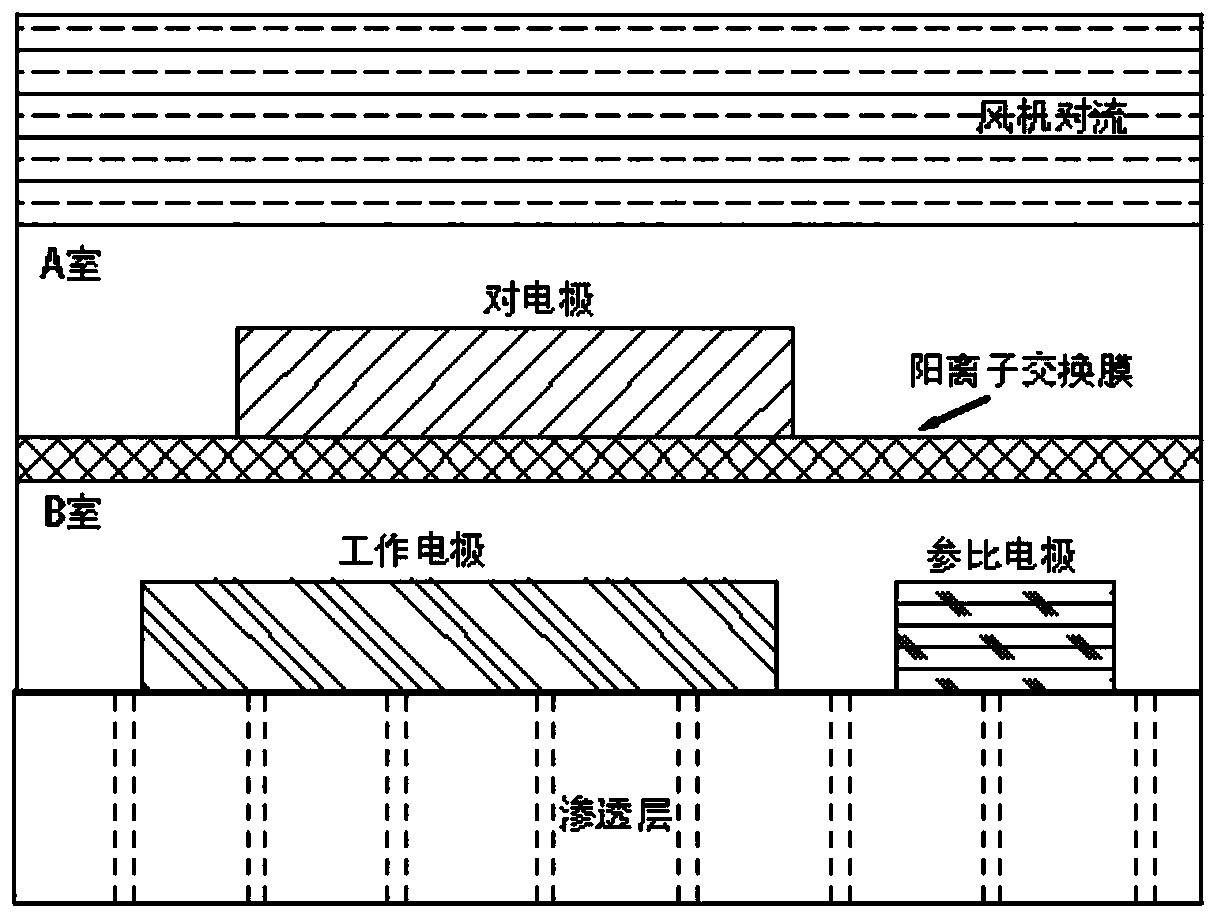
Enzyme-free glucose electrochemical sensor and detection method thereof
A glucose and electrochemical technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, scientific instruments, laboratory containers, etc., can solve the problems of large deviation, low sensitivity, inability to facilitate real-time detection, etc., to improve the electrocatalytic efficiency, realize the The effect of real-time detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Preparation of working electrode, i.e., preparation of homojunction copper oxide nanofiber arrays with P-N junction properties:
[0029] (1) Print particle-free copper conductive ink to the electrode position;
[0030] (2) Porous copper conductive films were obtained by heat treatment at 80 °C for 60 min;
[0031] (3) After heat treatment at 250 °C for 120 min, a P-type copper oxide fiber array was constructed on the porous copper surface;
[0032] (4) Using oxalic acid as the electrolyte, the electrode is anodized by adding halogen (Cl - ) and adjust the pH value to 1.5 to promote the adsorption of halide ions on the surface of the copper oxide, and achieve doping with the growth of the crystal. The trapping of holes by the halogen ions is used to modify the copper oxide into an N-type semiconductor to obtain the obtained described homojunction copper oxide nanofiber arrays with P-N junction properties.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Preparation of working electrode, i.e., preparation of homojunction copper oxide nanofiber arrays with P-N junction properties:
[0035] (1) Print particle-free copper conductive ink to the electrode position;
[0036] (2) Porous copper conductive films were obtained by heat treatment at 200 °C for 1 min;
[0037] (3) After heat treatment at 400 °C for 5 min, a P-type copper oxide fiber array was constructed on the porous copper surface;
[0038] (4) Using sulfuric acid as the electrolyte, the electrode is anodized by adding halogen (Br - ) and adjust the pH value to 4, to promote the adsorption of halogen ions on the surface of copper oxide, and to achieve doping with the growth of crystals, using the trapping of holes by halogen ions, the copper oxide is modified into an N-type semiconductor to obtain the obtained described homojunction copper oxide nanofiber arrays with P-N junction properties.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Preparation of working electrode, i.e., preparation of homojunction copper oxide nanofiber arrays with P-N junction properties:
[0041] (1) Print particle-free copper conductive ink to the electrode position;
[0042] (2) Porous copper conductive films were obtained by heat treatment at 150 °C for 30 min;
[0043] (3) After heat treatment at 300 °C for 60 min, a P-type copper oxide fiber array was constructed on the porous copper surface;
[0044] (4) Using citric acid as the electrolyte, the electrode is anodized by adding halogen (F -) and adjust the pH value to 5, to promote the adsorption of halogen ions on the surface of copper oxide, and to achieve doping with the growth of crystals, using the trapping of holes by halogen ions, the copper oxide is modified into an N-type semiconductor to obtain the obtained described homojunction copper oxide nanofiber arrays with P-N junction properties.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com