Method for producing alginate lyase through fermentation by using marine bacteria
A technology of alginate lyase and marine bacteria, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of lack of high-value processing of brown algae and alginic acid, limit the popularization and application of alginate lyase, and poor enzyme stability, and achieve remarkable fermentation effect and increase Bacterial biomass and the effect of prolonging the enzyme production period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A method for producing alginic acid lyase by fermenting marine bacteria, comprising the steps of:
[0035] S1, preparation of seed solution: Flavobacterium aquaticus ( Flavobacterium mizutaii ) comes from the Marine Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center MCCC, with the preservation number 1A08665. After thawing the frozen and preserved strains, they were streaked and inoculated on 2216E solid medium (recipe: peptone 5g / L, yeast extract powder 1g / L, lemon Ferric acid 0.01g / L, agar 20g / L, aged sea water 1000mL, pH 7.4), cultured at 28°C for 24 hours; put the activated strain into the seed medium, and the liquid volume in the 500mL Erlenmeyer flask was 100mL. The temperature is 28°C, the rotation speed is 180r / min, and the shaker is shaken for 12 hours; the culture is taken for microscopic examination, and it is confirmed that the bacteria grow well without any bacterial contamination, and then they can be inoculated into the seed tank; the formula of the s...
Embodiment 2
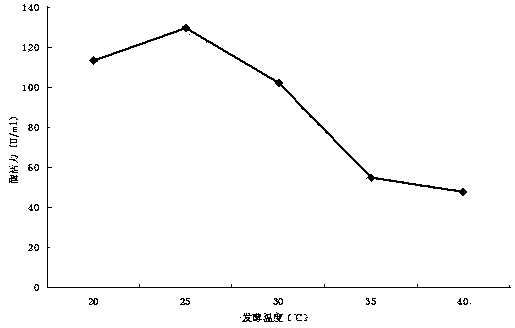
[0041] Example 2 Optimization of fermentation conditions
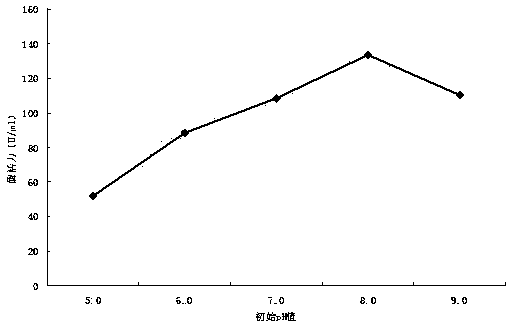
[0042] 1. Optimization of the initial pH value of the fermentation medium
[0043] According to the method provided in Example 1, during fermentation and enzyme production, the initial pH value of the fermentation medium was adjusted to 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, and 9.0 respectively. After the fermentation, the crude enzyme liquid was prepared and the alginate lyase activity was measured. Determine the optimal initial pH.
[0044] The initial pH value of the fermentation medium causes the difference in the oxidation-reduction potential of the bacterial cell membrane, which directly affects the progress of the oxidation-reduction reaction and the generation of free energy, thereby affecting the activity of the cell membrane, so the absorption of nutrients in the medium and the secretion of enzymes make an impact. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that when the pH value is 5.0, the enzyme production ability of Flavobacteri...
Embodiment 3
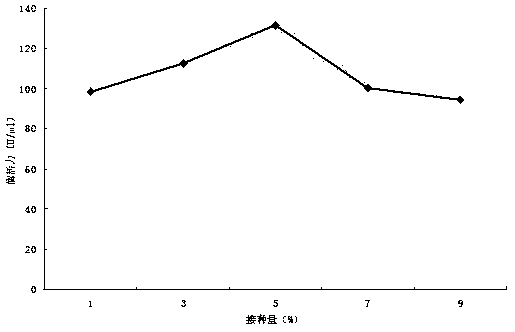
[0051] Example 3 Optimization of fermentation medium
[0052] 1. Optimization of the amount of bean cake powder added
[0053] According to the method provided in Example 1, when fermenting and producing enzyme culture, the addition amount of bean cake powder in the fermentation medium is respectively set to 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 g / L, and other components remain unchanged. The crude enzyme solution was prepared and the activity of alginate lyase was determined to determine the amount of bean cake powder added.
[0054] Nitrogen source is one of the main components of fermentation medium, which has an important influence on the growth and metabolism of microorganisms. Studies have shown that organic nitrogen sources are easier to be decomposed and utilized by bacteria than inorganic nitrogen sources, and organic nitrogen sources can also provide certain growth factors to enable bacteria to grow efficiently and rapidly. Compared with peptone and yeast extract powder, bean cake...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com