Method for recovering nitrate nitrogen in wastewater by electrochemical ammoniation of microorganisms
A technology of microbial electrochemistry and nitrate nitrogen, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, electrochemical and biological combined treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of low cost, strong environmental adaptability, and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: A method for the ammonization of nitrate using a bioelectrochemical system with an external resistance of 10Ω and a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio of 8
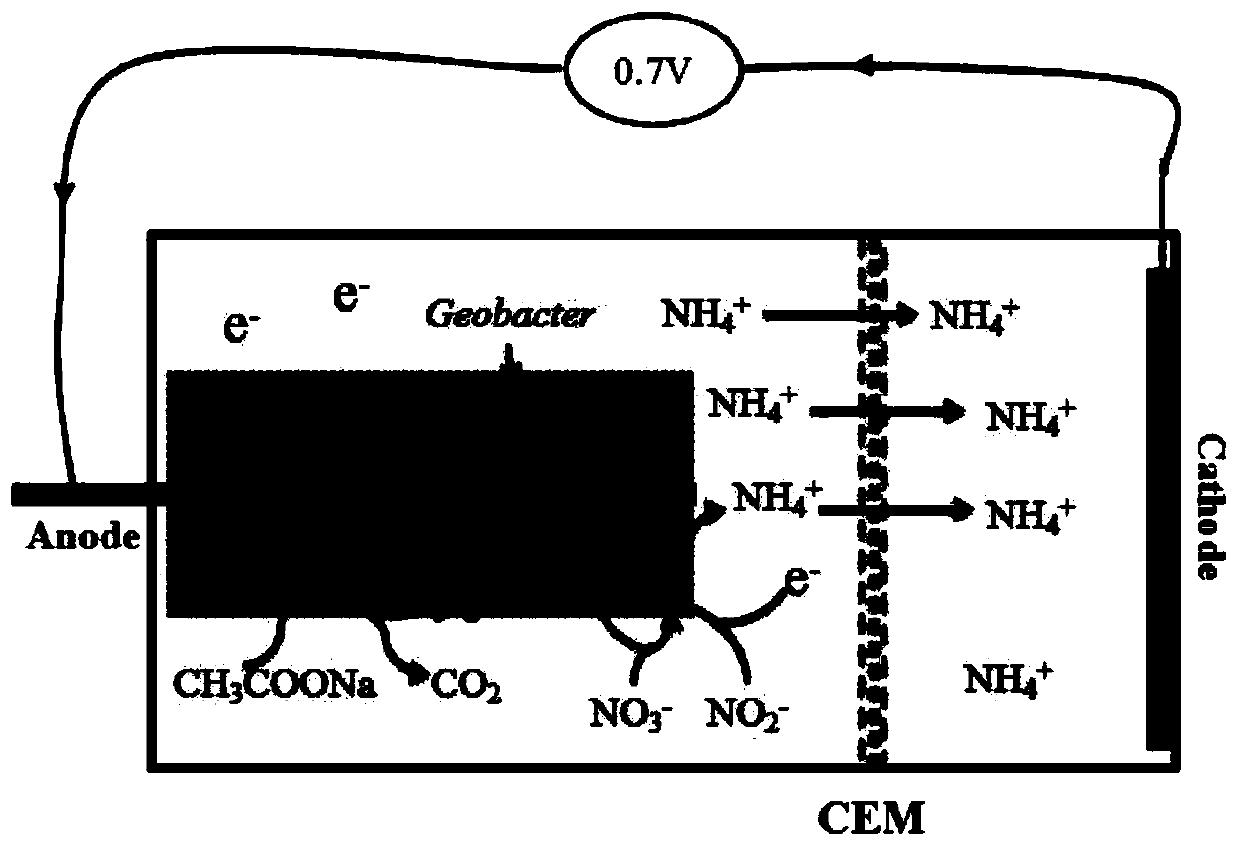
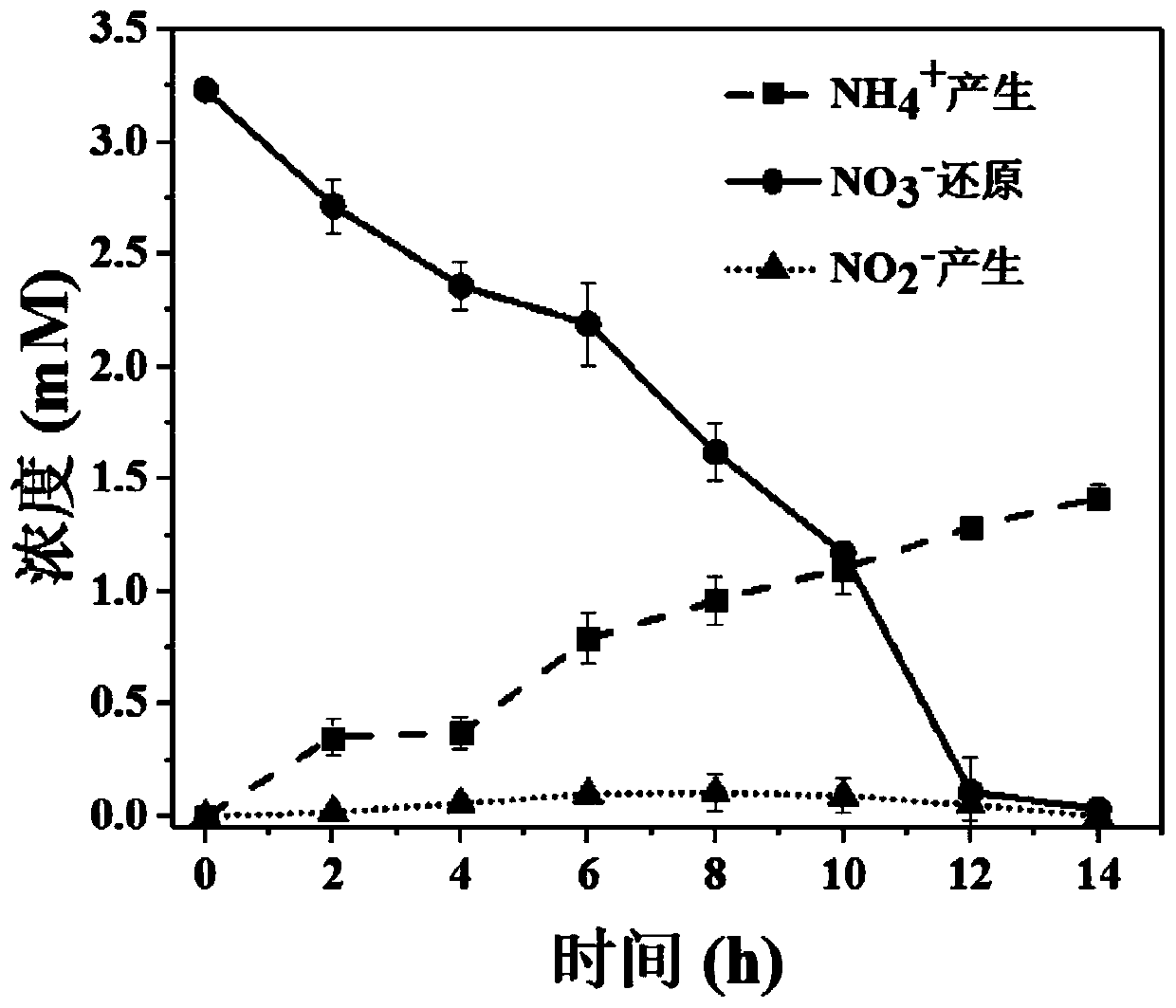
[0027] The invention provides a method for recovering nitrogen from nitrate wastewater by combining microbial electrochemical ammonification with microbial electrolysis. Since the bioelectrochemical system can enrich and domesticate more electroactive microorganisms with DNRA function, applying the DNRA process to the bioelectrochemical system can significantly improve its DNRA efficiency. The reactor was started and acclimated under the condition of 10Ω external resistance, and the DNRA process under this condition was explored by adding wastewater containing 3.2mM nitrate. The specific steps are as follows:
[0028] A bioelectrochemical system is constructed in sewage, and the domestication method is a microbial fuel cell method. The carbon fiber brush is used as the anode, the activated carbon air cathode is u...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: A method for the ammonization of nitrate using a bioelectrochemical system with an external resistance of 100Ω and a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio of 8
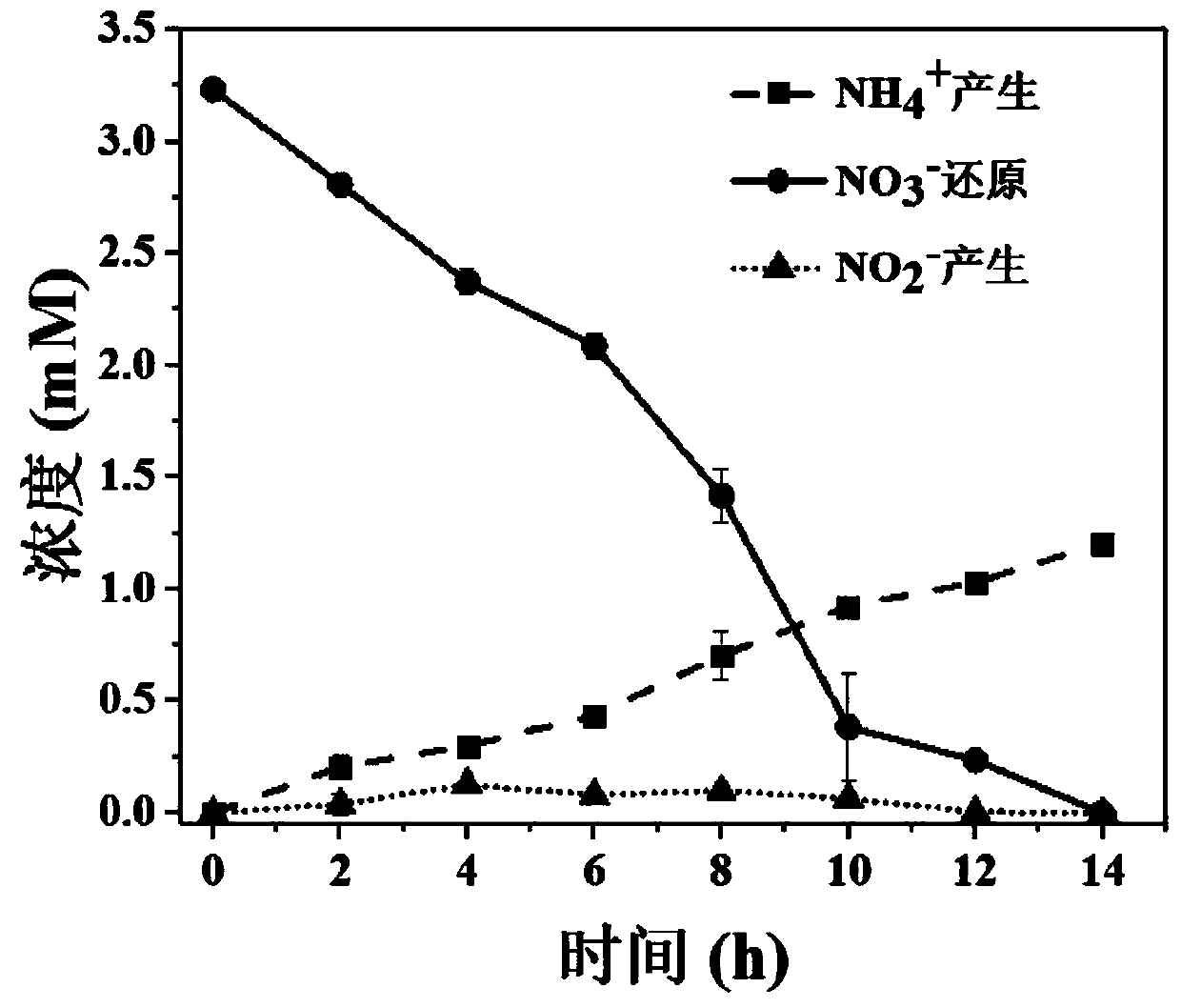
[0030] As the external resistance increases, the electrical activity of the biofilm gradually decreases, the content of electrogenic bacteria gradually decreases, the DNRA process will gradually weaken, and the denitrification process will gradually increase. Add 3.2mM nitrate to explore the DNRA process under this condition, the specific steps are as follows:
[0031] A kind of utilization bioelectrochemical system described in embodiment 1 is the method for nitrate ammonification under 10Ω external resistance and carbon-nitrogen ratio is 8 conditions, and difference is:
[0032] The fixed value resistor connected between the two poles is 100Ω. Its ammonization efficiency is as image 3 shown. image 3 The results show that the nitrate is completely degraded within 8-14 hours, and its ammonium conversion effi...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3: A method for ammonizing nitrate using a bioelectrochemical system with an external resistance of 10Ω and a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio of 0.5
[0034] As the nitrate content increases, the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio gradually decreases. Since denitrifying bacteria are more sensitive to nitrate than DNRA bacteria, they grow faster at low carbon-nitrogen ratios, resulting in the proportion of DNRA bacteria in the microbial community. Decrease gradually, denitrifying bacteria gradually increase, thus reducing the reactor DNRA efficiency. The reactor was started and acclimatized under the condition of 10Ω external resistance, and the DNRA process under this condition was explored by adding 44.2mM nitrate. The specific steps are as follows:
[0035] A kind of method utilizing bioelectrochemical system described in Example 1 to ammonify nitrate under 10Ω external resistance condition, difference is:
[0036] The carbon-to-nitrogen ratio of the wastewater is 0.5, and th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com