a wear-resistant cloth
A fabric and raw material technology, applied in textiles and papermaking, conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filament, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., can solve problems such as yellowing and light degradation of polyamide fibers, and achieve improved wear resistance and increased Effect of low interface bonding force and friction coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
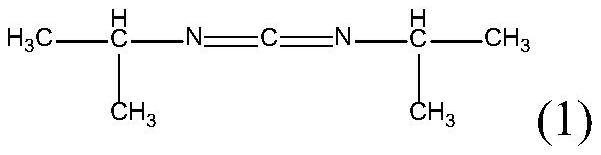
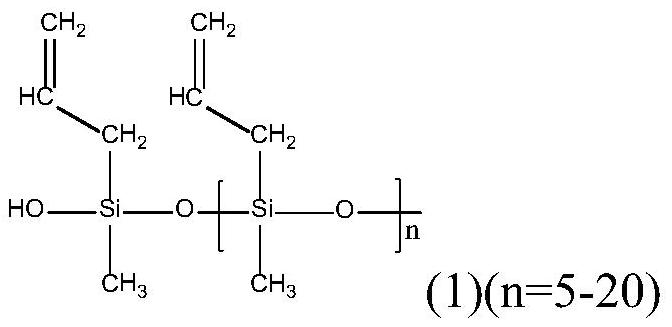
[0075] The base polymer was commercially available poly(trimethylene terephthalate) (component a)) to which 12 wt. % of thermoplastic elastomer polyurethane TPE was gravimetrically added to 80 wt. U (component b)), 6% by weight of a copolymer of polysiloxane of formula (1-1) and acrylate monomer (component c)), and 2% by weight of N,N'-di isopropylcarbodiimide (component d)).
[0076]
[0077] The polymer mixture is melted at 250°C to 270°C in the extruder, pressed into the spinning assembly by a gear pump, and then spun in a water bath at 68°C. Multiple stretches are performed under heat while heat setting and then the monofilament is wound.
[0078] Thus monofilaments obtained with a nominal diameter of 1.18 mm have the following textile values:
[0079] Diameter: 1.194mm
[0080] Linear density: 20000dtex
[0081] Free heat shrinkage 180°: 20.2%
[0082] Line strength: 35.4cN / tex
[0083] Nodule strength: 30.6cN / tex
[0084] Interlocking strength: 33.9cN / tex
[0...
Embodiment 2
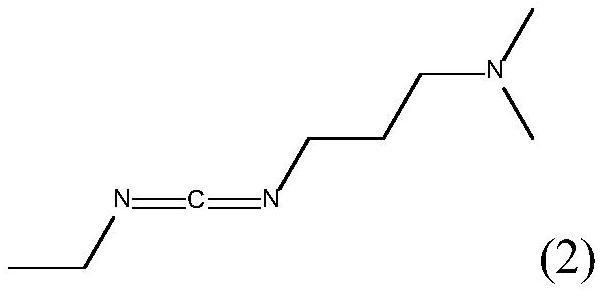
[0087] The base polymer is a commercially available 4:1 blend of polytrimethylene terephthalate and polytrimethylene naphthalate (component a)) gravimetrically to 85% by weight before the extruder Add 10% by weight of thermoplastic elastomer styrene block copolymer (TPE-S) (component b)) in the raw material, 2.5% by weight of polysiloxane and acrylate monomer of structural formula such as (2-1) copolymer (component c)), and 2.5% by weight of N,N'-diisopropylcarbodiimide (component d)).
[0088]
[0089] The polymer mixture is melted at 250°C to 270°C in the extruder, pressed into the spinning assembly by a gear pump, and then spun in a water bath at 68°C. Multiple stretches are performed under heat while heat setting and then the monofilament is wound.
[0090] The performance qualities of the monofilaments obtained are listed in Table 1 below.
Embodiment 3
[0092] Repeat Example 2, the base polymer is commercially available polytrimethylene naphthalate raw material (component a)), thermoplastic elastomer polyurethane (TPE-U) (component b)), polysiloxane with hydroxyl (formula (3-1)) and hydroxyl-containing acrylate generate graft copolymer (component c) through condensation reaction), 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide salt salt (component d)). The amount of each component is the same as in Examples.
[0093]
[0094]The performance qualities of the monofilaments obtained are listed in Table 1 below.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com