High-Z-element-natural leather composite X-ray shielding material and preparation method thereof
A technology of natural leather and shielding materials, applied in special leather manufacturing, leather impregnation, small raw hide/big raw hide/leather/fur treatment, etc., can solve problems such as hazards, poor water and gas permeability, and poor compatibility, and achieve a wide range of applications , strong universal applicability, large load effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Weigh 1 part of SrCl 2 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in 15 parts of deionized water, and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 3.0 with HCl. One part of chrome-tanned cowhide with a thickness of 1.0 mm was placed in the prepared salt solution, and ultrasonically assisted for 0.5 h at 20 °C, and then The samples were dried in an oven at 60 °C to obtain nano-strontium chloride-cowhide composites.
[0047] The obtained composite material was tested and found that the shielding efficiency of the composite material for X-rays with an average energy of 16 keV and a half-value layer of 0.32 mm Al reached 95%, and for X-rays with an average energy of 48 keV and a half-value layer of 0.32 mm The X-ray shielding efficiency of 0.24 mm Cu reaches 36%. Then its tear strength is tested, and it is obtained as Figure 12 Stress–elongation images of the nanostrontium chloride–pigskin composite shown. It can be seen from the figure that the prepared composite has excellent tear strength.
Embodiment 2
[0049] Weigh 2 parts of AgNO 3 Dissolve in 198 parts of deionized water, use HCl to adjust the pH of the solution to 4.0, take 1 part of chrome-tanned sheepskin with a thickness of 0.7 mm in the prepared salt solution, shake and react at 35 °C for 1 h, and then soak the sample Dehydration in excess acetone can get nano-silver nitrate-sheepskin composite material.
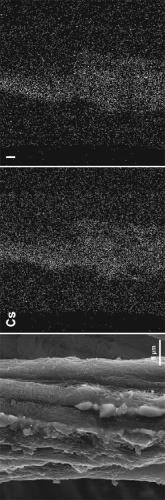
[0050] The obtained composite material was tested and found that the shielding efficiency of the composite material for X-rays with an average energy of 16 keV and a half-value layer of 0.32 mm Al reached 68%, and for X-rays with an average energy of 48 keV and a half-value layer of The X-ray shielding efficiency of 0.24 mm Cu reaches 17%. Then the material was scanned by electron microscope, and the figure 1 SEM image of the nanosilver nitrate–sheepskin composite shown. It can be seen from the figure that a large number of silver nitrate nanoparticles are loaded on the sheepskin fiber, and the distribution is r...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Weigh 36 parts of SnCl 4 Dissolve 84 parts of acetone, take 1 part of chrome-tanned pigskin with a thickness of 1.5 mm in the prepared salt solution, shake the reaction at 10 °C for 2 h, and then place the sample in a vacuum drying oven to dry, that is Nanoscale tin chloride-pigskin composites are available.
[0053] According to the test of the prepared composite material, the composite material has a shielding efficiency of 73% for X-rays with an average energy of 16 keV and a half-value layer of 0.32 mm Al. The X-ray shielding efficiency of 0.24 mm Cu reaches 24%. After testing, the tear strength of the material is 53 N mm –1 , it can be seen that the prepared composites have excellent tear strength.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com