Cellulose solvent, and preparation method and application thereof
A cellulose solvent and cellulose technology, applied in the production of bulk chemicals, etc., can solve problems such as hindering large-scale industrial production, high requirements for cellulose raw materials, and difficulty in realizing industrial application, etc. Dissolution effect, effect of shortening dissolving time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
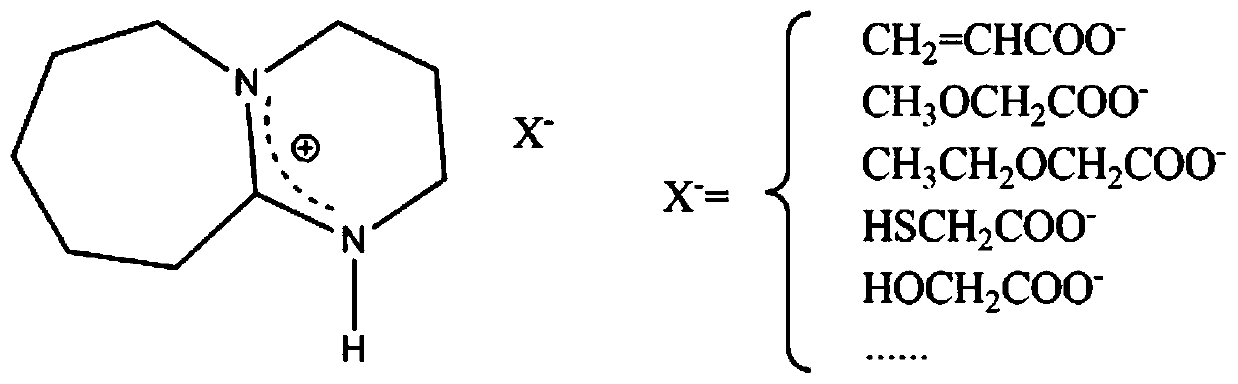
[0047] Take 15.224g of organic base DBU and 45mL of n-hexane in a three-necked flask, pass nitrogen, and slowly add 7.206g of acrylic acid to the reaction system at a rate of 30 drops / min under magnetic stirring at 200rpm. During the addition, the temperature of the reaction system Control at 25°C, after the acrylic acid is completely added, continue to stir at 200rpm at room temperature for 8h, the non-imidazole ionic liquid is precipitated from n-hexane, after separation, the obtained high-purity non-imidazole ionic liquid is under the protection of argon, at 80°C After heating for 2h, the dry cellulose solvent [DBUH][CH 2 =CHCOO] (its structural formula sees figure 1 ). Weigh microcrystalline cellulose and add it to the above cellulose solvent, and continue to stir at 80° C. and 200 rpm until it cannot be dissolved, and a homogeneous solution in which microcrystalline cellulose is dissolved is obtained. After analysis, it can be obtained that the maximum solubility of Avi...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Take 13.702g of organic base DBU and 50mL of n-hexane in a three-necked flask, pass nitrogen gas, and slowly add 9.008g of methoxyacetic acid dropwise to the reaction system at a rate of 40 drops / min under magnetic stirring at 400rpm. The temperature of the system was controlled at 30°C. After the methoxyacetic acid was completely added, the stirring was continued at 400 rpm for 10 h at room temperature. The non-imidazole ionic liquid was precipitated from n-hexane. After separation, the obtained high-purity non-imidazole ionic liquid was Under protection, heating at 80°C for 2h, the dry cellulose solvent [DBUH][CH 3 OCH 2 COO] (its structural formula sees figure 1 ). Weigh microcrystalline cellulose and add it to the above cellulose solvent, and continue to stir at 80° C. and 200 rpm until it cannot be dissolved, and a homogeneous solution in which microcrystalline cellulose is dissolved is obtained. After analysis, the maximum solubility of microcrystalline cellulo...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Take 15.224g of organic base DBU and 50mL of ether in a three-necked flask, pass nitrogen gas, and slowly add 9.212g of thioglycolic acid dropwise to the reaction system at a rate of 40 drops / min under magnetic stirring at 300rpm. During the dropwise addition, the reaction system The temperature was controlled at 28°C. After the thioglycolic acid was completely added, the stirring was continued at 300 rpm at room temperature for 11 hours. The non-imidazole ionic liquid was precipitated from ether. After separation, the obtained high-purity non-imidazole ionic liquid was protected by nitrogen. Heating at 80°C for 2h, the dry cellulose solvent [DBUH][HSCH 2 COO] (its structural formula sees figure 1 ). Weigh microcrystalline cellulose and add it to the above cellulose solvent, and continue to stir at 80° C. and 200 rpm until it cannot be dissolved, and a homogeneous solution in which microcrystalline cellulose is dissolved is obtained. After analysis, the maximum solubi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Membrane strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Membrane strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com