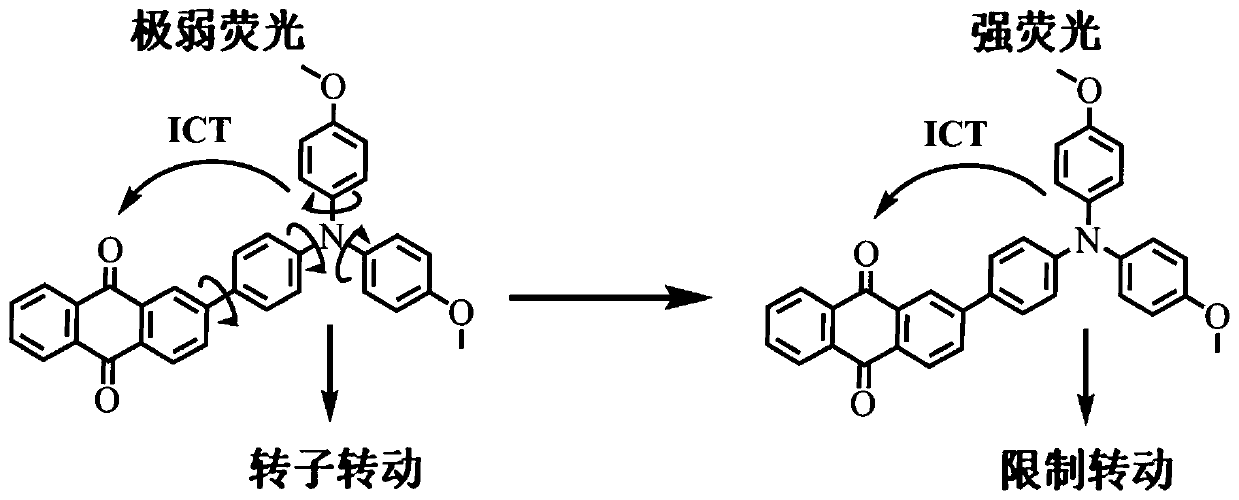
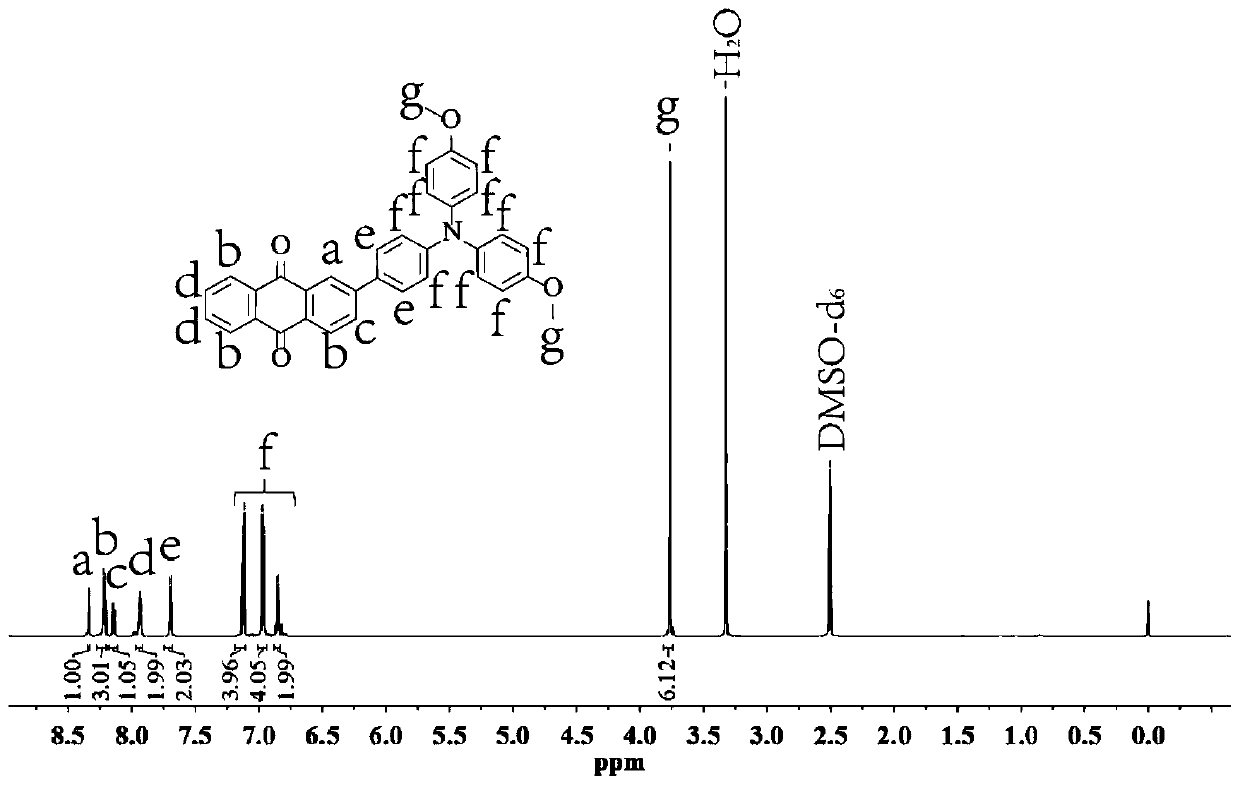
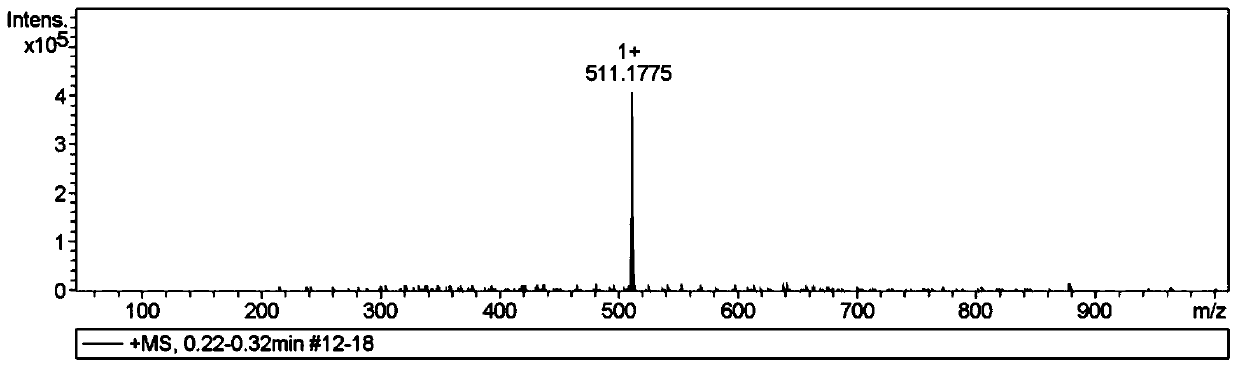
Fluorescent compound for detecting viscosity of oil displacement of tertiary oil recovery, and preparation method and application of fluorescent compound
A fluorescent compound and viscosity technology, applied in the preparation of organic compounds, chemical instruments and methods, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of shrinking final yield, poor anti-interference effect, hindering solute diffusion, etc., and achieve good detection and analysis results. , Improve the final oil recovery rate, the effect of high recognizable degree
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A method for preparing a fluorescent compound used for tertiary oil recovery chemical flooding viscosity detection, comprising the steps of:
[0054] (1) Dissolve 286 mg of 2-bromoanthracene-9,10-dione in 10 mL of dry THF and stir it evenly with ultrasonic to obtain solution 1;
[0055] (2) 349mg of (4-(bis(4-methoxyphenyl)amino)phenyl)boronic acid was dissolved in 10mL of dry and dehydrated DMF, and stirred evenly by ultrasonic to obtain solution 2;
[0056] (3) Dissolve 326mg of cesium carbonate in deionized water at the same time, and stir evenly with ultrasonic to obtain 1mol / L of Cs 2 CO 3 Aqueous solution (Solution 3);
[0057] (4) Mix the solution 1 described in step (1) with the solution 2 described in step (2), mix well, and add 1.06 mg of palladium catalyst therein, vacuumize, then carry out a heating reaction, control the reaction temperature to be 40 ℃, after reacting for 30min, to which the 1mol / L Cs prepared in step (3) was added dropwise 2 CO 3 aqueo...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A method for preparing a fluorescent compound used for tertiary oil recovery chemical flooding viscosity detection, comprising the steps of:
[0061] (1) Dissolve 286 mg of 2-bromoanthracene-9,10-dione in 50 mL of dry THF and stir it evenly with ultrasonic to obtain solution 1;
[0062] (2) Dissolve 872.5 mg of (4-(bis(4-methoxyphenyl)amino)phenyl)boronic acid in 50 mL of dry and dehydrated DMF, and stir evenly with ultrasonic to obtain solution 2;
[0063] (3) At the same time, 1.63g of cesium carbonate was dissolved in deionized water, and stirred evenly by ultrasonic to obtain 3mol / L of Cs 2 CO 3 Aqueous solution (Solution 3);
[0064] (4) Mix the solution 1 described in step (1) with the solution 2 described in step (2), mix evenly, and add 10.6 mg of palladium catalyst therein, vacuumize, perform a heating reaction, and control the reaction temperature to 70°C , after reacting for 3h, the Cs of 3mol / L prepared in step (3) was added dropwise thereto 2 CO 3Aqueo...
Embodiment 3
[0066] A method for preparing a fluorescent compound used for tertiary oil recovery chemical flooding viscosity detection, comprising the steps of:
[0067] (1) Dissolve 286 mg of 2-bromoanthracene-9,10-dione in 100 mL of dry THF and stir it evenly to obtain solution 1;
[0068] (2) Dissolve 1745mg of (4-(bis(4-methoxyphenyl)amino)phenyl)boronic acid in 500mL of dry and dehydrated DMF, and stir evenly with ultrasonic to obtain solution 2
[0069] (3) At the same time, 3.26g of cesium carbonate was dissolved in deionized water, and ultrasonically stirred evenly to obtain 5mol / L of Cs 2 CO 3 Aqueous solution (Solution 3);
[0070] (4) Mix the solution 1 described in step (1) with the solution 2 described in step (2), mix uniformly, and add 106 mg of palladium catalyst therein, vacuumize, carry out a heating reaction, control the reaction temperature to be 100 ° C, After reacting for 5h, the Cs of 5mol / L prepared in step (3) was added dropwise therein 2 CO 3 Aqueous solution...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com