Preparation method for electronic glass substrate with low thermal shrinkage
A technology of electronic substrate and shrinkage rate, which is applied in the field of preparation of electronic substrate glass with low thermal shrinkage rate, to meet the requirements of high-resolution display, reduce thermal deformation, and reduce thermal shrinkage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] A method for preparing an electronic substrate glass with a low thermal shrinkage rate according to the present invention, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0025] The first step is to make silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, boron oxide, magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, strontium oxide, barium oxide, zirconium dioxide, zinc oxide, cerium oxide and tin oxide into glass according to a predetermined ratio. Batch materials, glass batch materials are melted at high temperature to form alkali-free boroaluminosilicate glass liquid, and then formed by float process. In the stretching zone with float forming tin bath, alkali-free boroaluminosilicate glass is continuously Feed to the surface of the molten metal tin liquid, and when the viscosity of the molten glass reaches 10 5 At Pa·s, it reaches the intermediate state of glass plasticity, and it is thinned by the pulling force of the edge pulling machine in the stretching direction to form a glass ribbon with...
specific Embodiment
[0056] First, the heat shrinkage test method is as follows:
[0057] Heat up at a heating rate of 5°C / min, and the temperature rises to 550°C. After keeping at this temperature for 5 minutes, cool down to room temperature at a cooling rate of 2°C / min. The lowest temperature record after exporting the data is 62.05°C. Choose this temperature The following six absolute shrinkage data, take the average value, according to the heat shrinkage formula: absolute expansion / length before heat treatment * 10 6 , the unit is ppm.
specific Embodiment 1
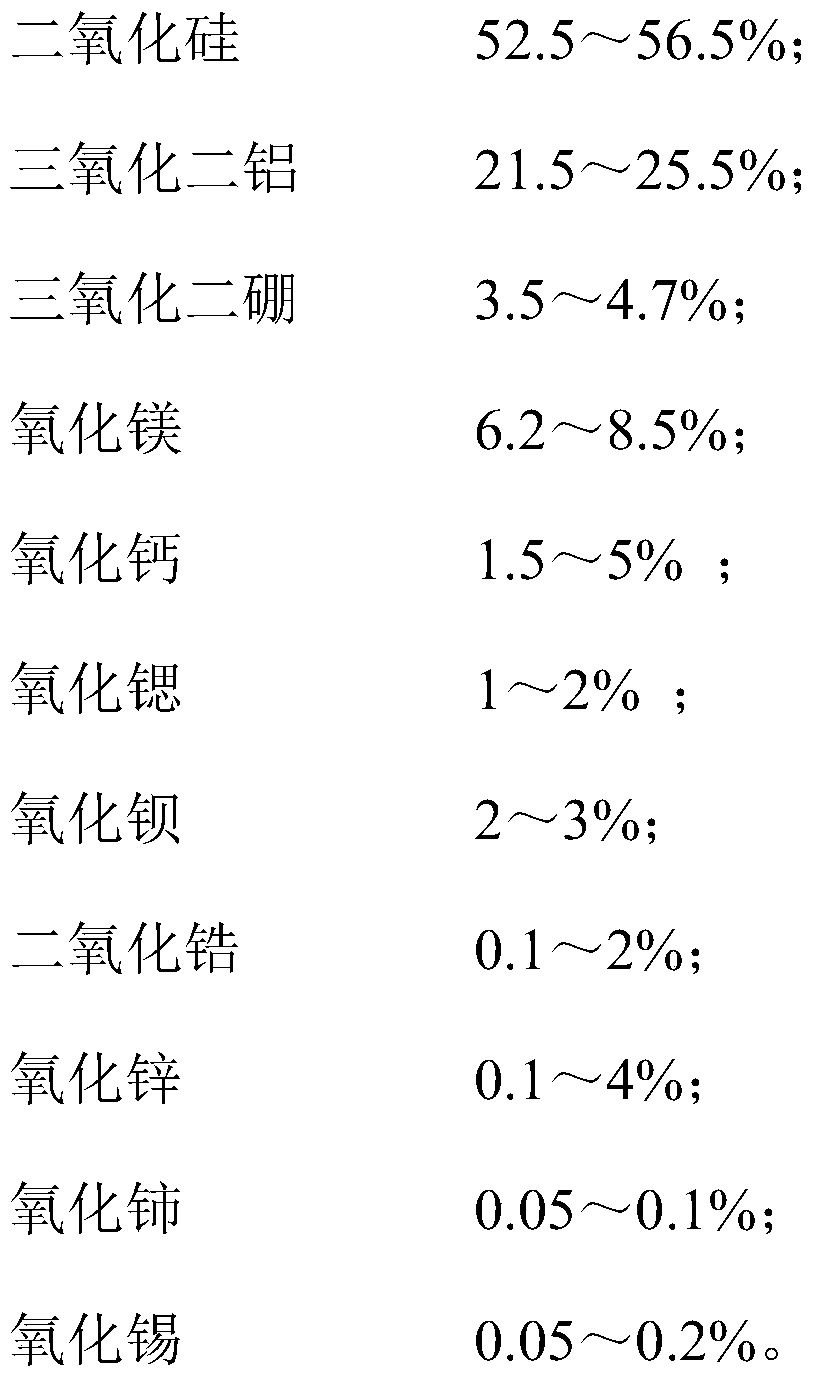
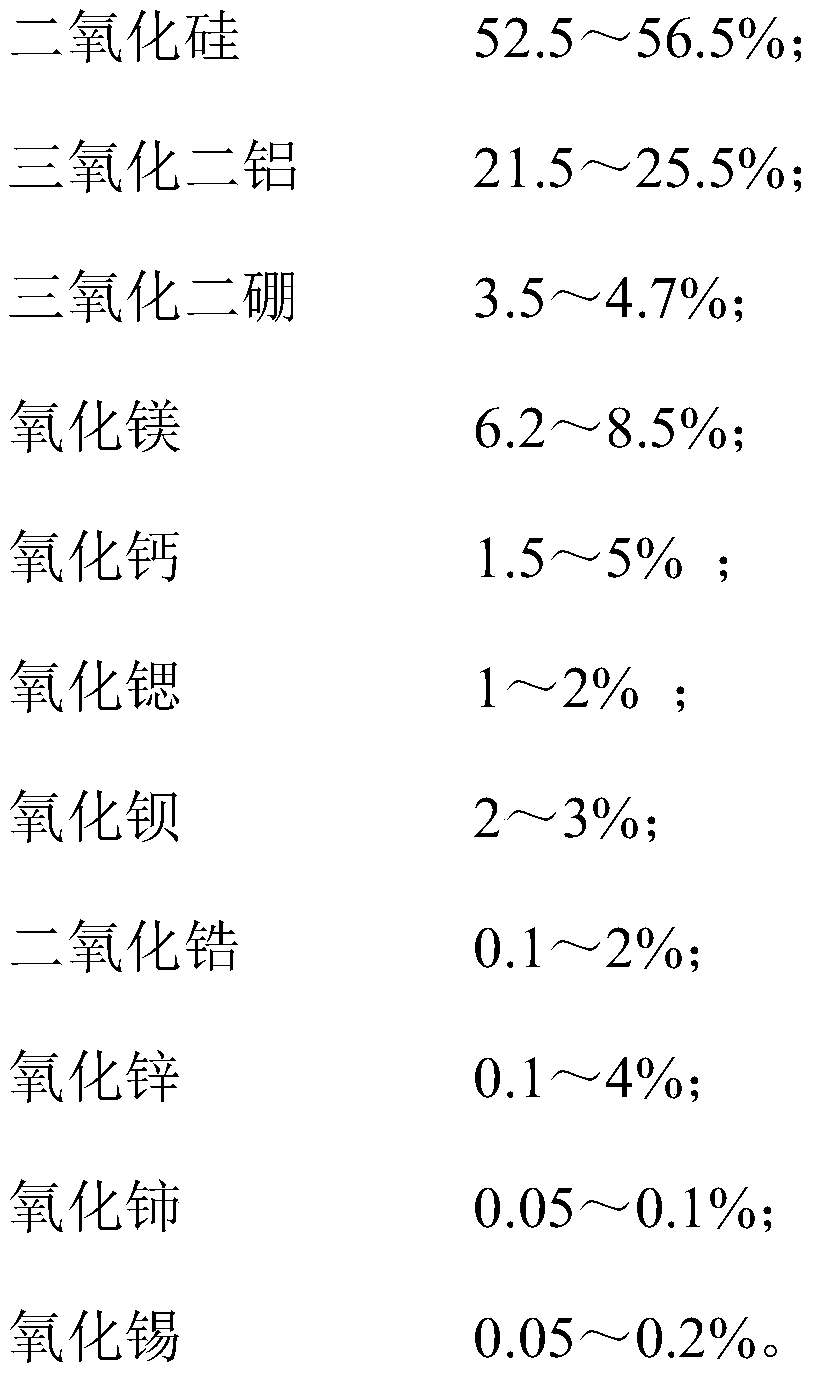
[0059] SiO 2 : 52.5%, Al 2 o 3 : 25.1%, B 2 o 3 : 3.8%, MgO: 8.11%, CaO: 2.3%, BaO: 2.6%, SrO: 1.1%, ZrO 2 : 1.2%, ZnO: 3.1%, CeO 2 : 0.07%, SnO 2 : 0.12%, the balance is impurities brought by mineral raw materials.
[0060] The above components are used to make glass batch materials, which are melted at a temperature of 1650-1660°C for three hours, and the working temperature is below 1320°C-1380°C. 8 Pa·s start, glass viscosity 10 8 Pa·s-10 11 Within this range of Pa·s, the temperature difference of the qualified plate area along the width direction of the glass plate, that is, the qualified plate area perpendicular to the drawing direction, shall not exceed 2°C, and the cooling rate shall be controlled at 10-15°C / min; Viscosity at 10 11 Pa·s-10 12 In the Pa·s process, the cooling rate in the corresponding temperature range is 15-20°C / min, and the glass viscosity reaches 10 12 At the time of Pa·s, heat preservation T=L / V (L is the width of the zone, V is the pull...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average coefficient of thermal expansion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com