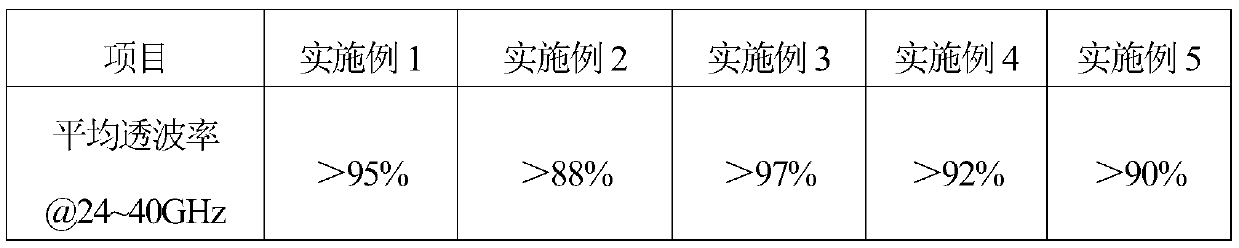
Wave-transmitting material for millimeter-wave radome and forming method thereof
A technology of millimeter-wave antennas and wave-transparent materials, which is applied to antennas, antenna components, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as low production efficiency, high dielectric constant and loss, poor weather resistance and flame retardancy, and achieve simplification Effects of production and processing steps, reduction of manufacturing costs, and excellent flame retardant properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
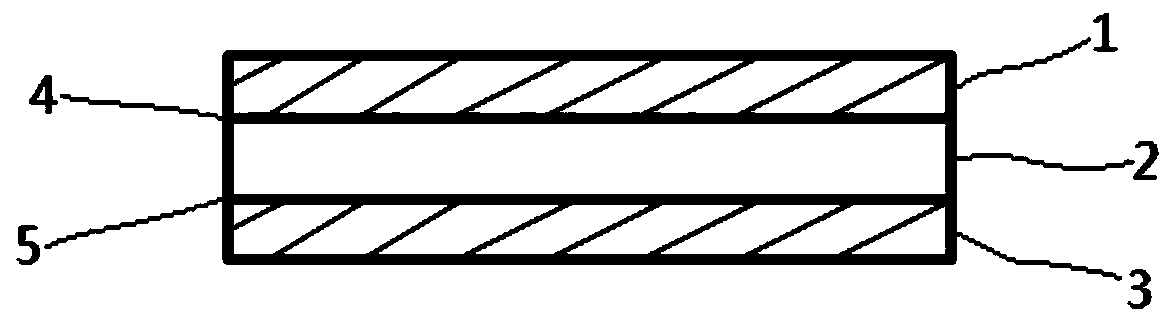
[0037] A wave-transparent material for a millimeter-wave radome, which consists of an upper skin 1, a core layer 2, and a lower skin 3, wherein the upper and lower skins are respectively bonded to the core layer by a first adhesive 4 and a second adhesive 5 tied together. Its preparation method is:
[0038] Step (1). Lay polyethersulfone film, continuous glass fiber woven cloth, and polyethersulfone film in the mold of the hot press in sequence, and control the mass percentage of fiber and polyethersulfone resin to 20:80. Hot pressing within the temperature range to obtain a 0.1mm thick fiber-reinforced polyethersulfone resin composite material as the upper and lower skin layers;
[0039] Step (2). Lay the lower skin, acrylic resin adhesive, 3mm thick core layer, acrylic resin adhesive, and upper skin in sequence in the mold, and preheat to 200-240°C; the adhesive Thickness 0.05mm, core layer density is 30kg / m 3 Polyethersulfone closed-cell micro-foaming material;
[0040]...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A wave-transparent material for a millimeter-wave radome, which consists of an upper skin 1, a core layer 2, and a lower skin 3, wherein the upper and lower skins are respectively bonded to the core layer by a first adhesive 4 and a second adhesive 5 tied together. Its preparation method is:
[0043] Step (1). Add polyethersulfone resin and continuous quartz fiber to the sheet extruder, melt and extrude the sheet in the temperature range of 300-390°C, and control the content of fiber and polyethersulfone resin to 70% by mass: 30. Obtain a 2mm thick fiber-reinforced polyethersulfone resin composite material as the upper and lower skin layers;
[0044] Step (2). Lay the lower skin, polyurethane resin adhesive, 2mm thick core layer, polyurethane resin adhesive, and upper skin in the mold in sequence, and preheat to 200-240°C; the adhesive Thickness 0.2mm, core layer density is 40kg / m 3 Polyethersulfone closed-cell micro-foaming material;
[0045] Step (3). Hot-press mo...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A wave-transparent material for a millimeter-wave radome, which consists of an upper skin 1, a core layer 2, and a lower skin 3, wherein the upper and lower skins are respectively bonded to the core layer by a first adhesive 4 and a second adhesive 5 tied together. Its preparation method is:
[0048]Step (1). Add the polyethersulfone resin to the casting machine, melt and cast the resin to form a film in the temperature range of 340-390 ° C, and introduce the aramid fiber mat into the die head of the casting machine, and the die head The extruded molten polyethersulfone resin is infiltrated, rolled, cooled, and the mass percentage of the fiber and polyethersulfone resin is controlled to be 60:40 to obtain a 0.3mm thick fiber-reinforced polyethersulfone resin composite material as the upper and lower skin layers;
[0049] Step (2). Lay the lower skin, epoxy resin adhesive, 1mm thick core layer, polyurethane resin adhesive, and upper skin in the mold in sequence, and pre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com