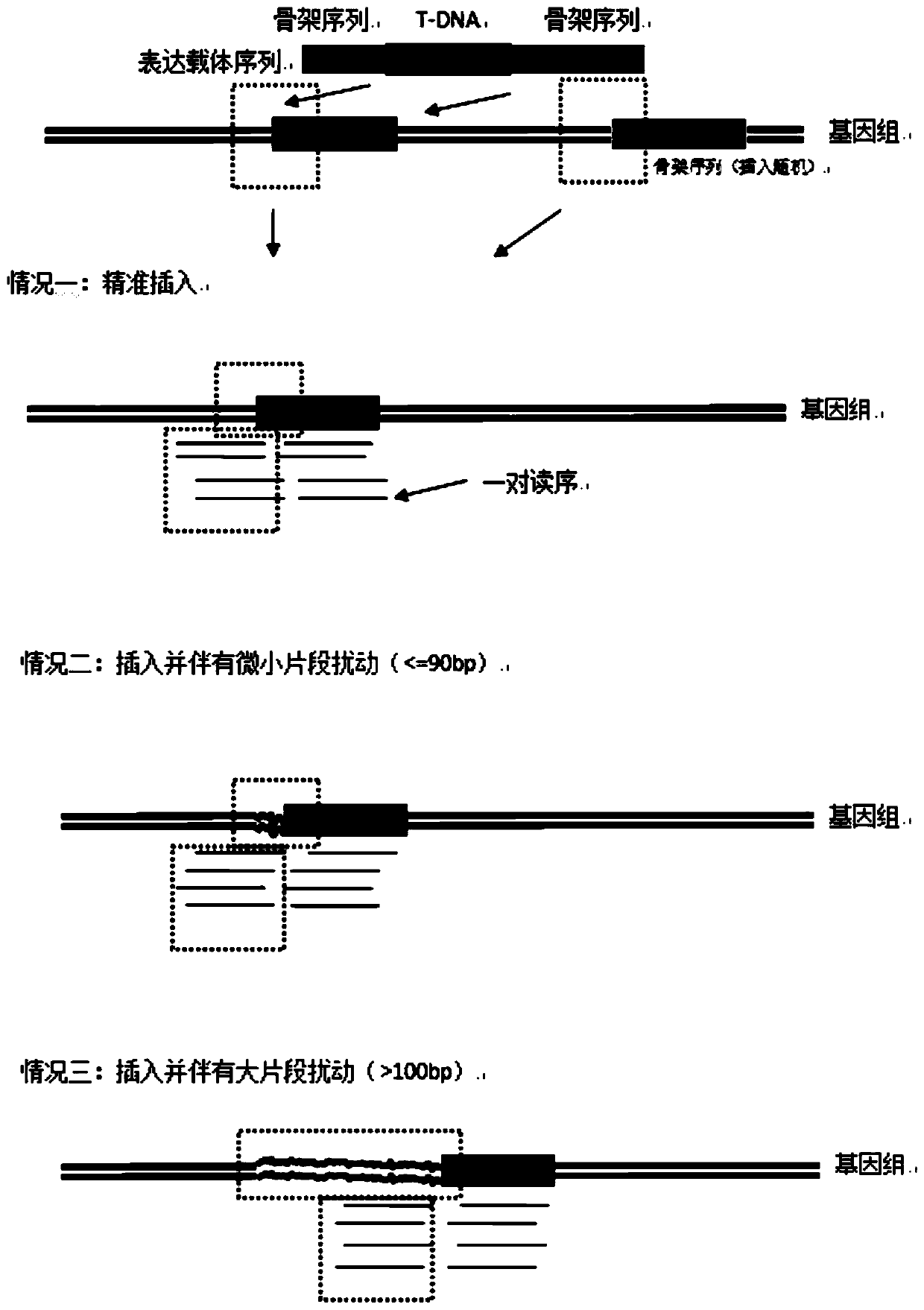
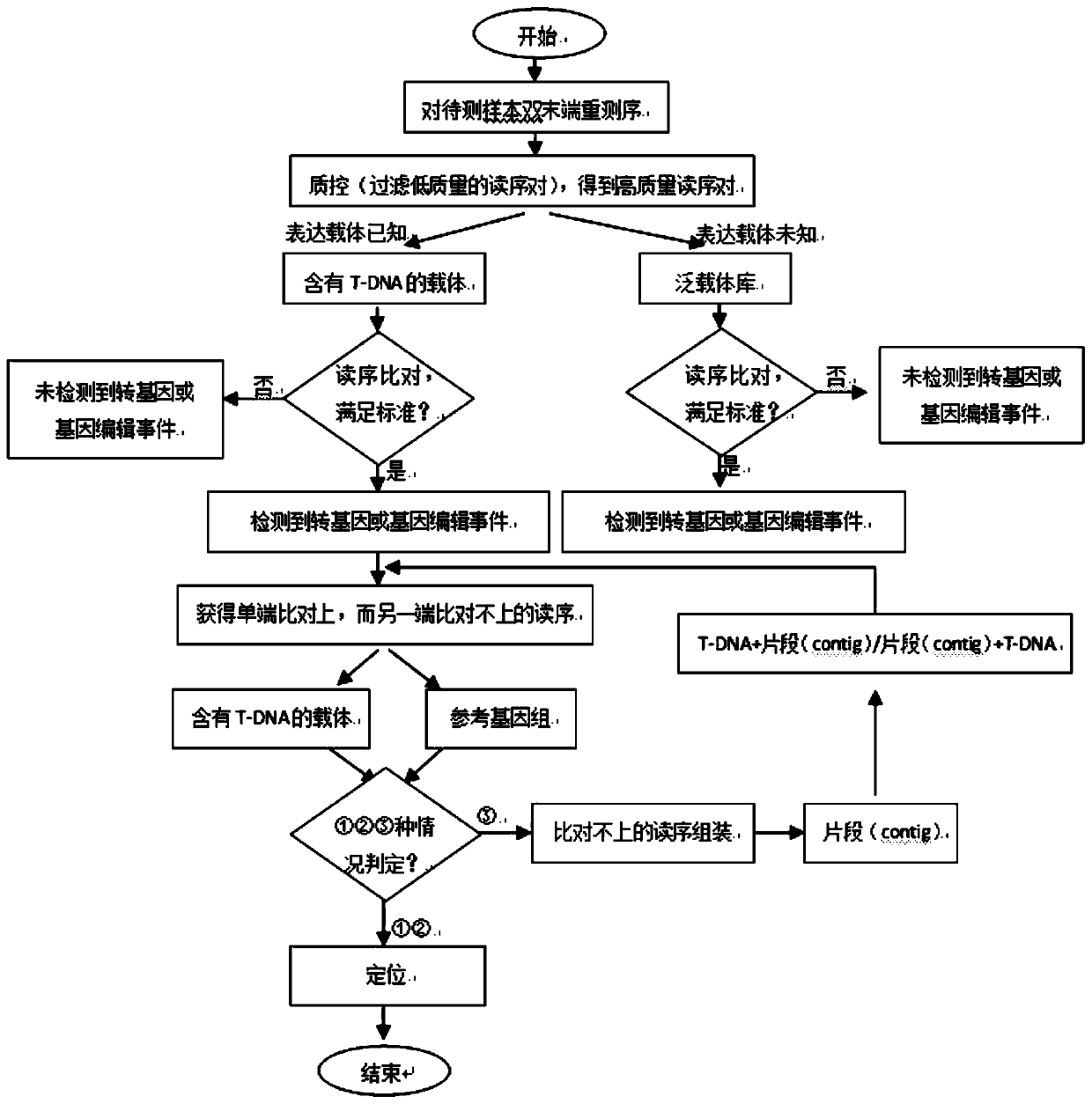
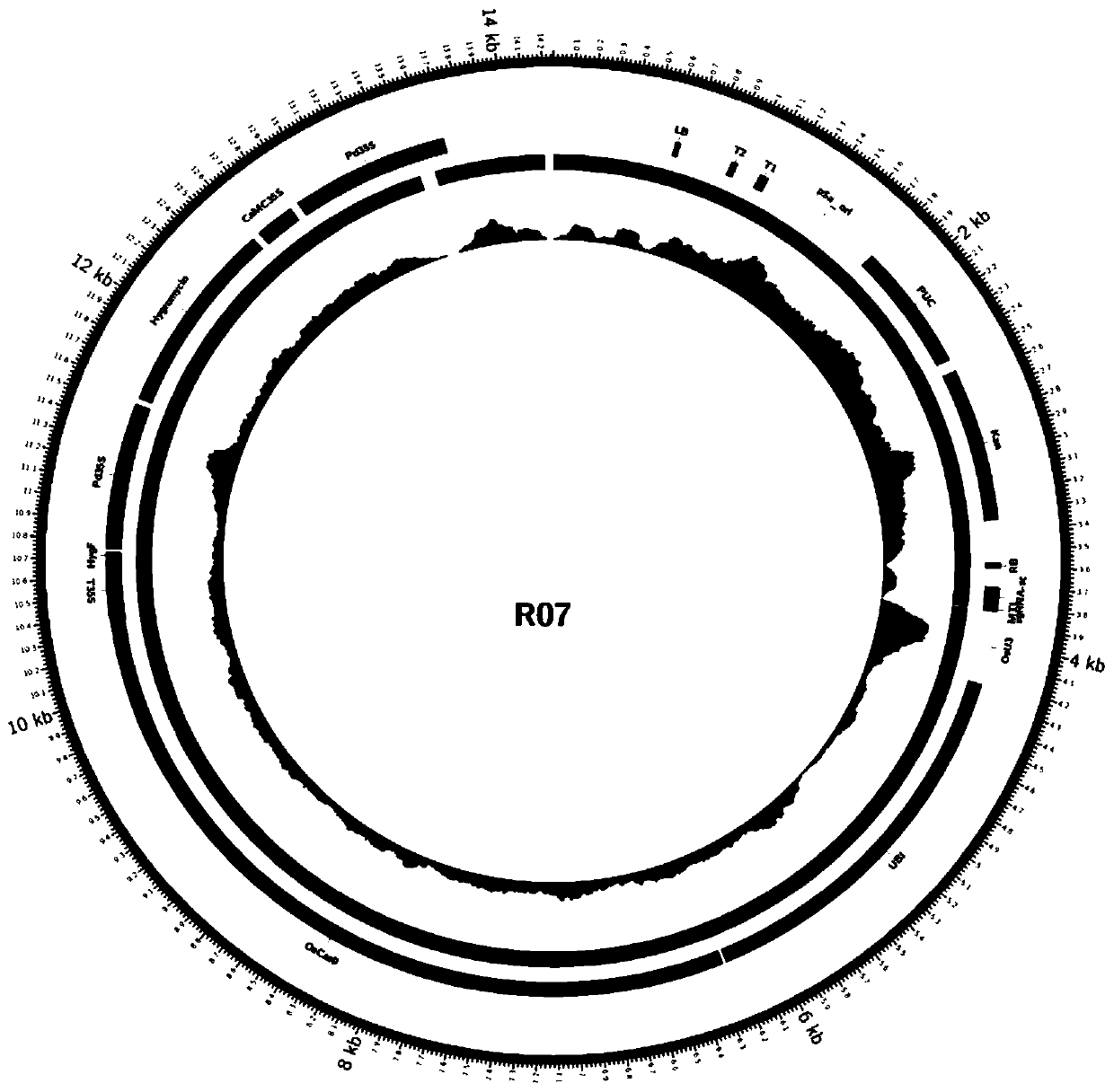
Method for rapidly identifying transgenic or gene editing material and insertion site thereof by using whole genome resequencing data
A genome-wide, insertion site technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problems of reducing method sensitivity, false negative and missed detection probability, not considering recombination or disorder, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and is conducive to safety risk assessment , reduce sensitivity, time-consuming effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] A method for rapidly identifying gene editing materials and their insertion sites using whole genome resequencing data, the specific steps are as follows:
[0066] (1) Extraction of experimental materials and genomic DNA of plants to be tested: rice gene editing sample R07 uses pHUN4c12S as the carrier, with a full length of 12314bp, and the gene editing target gene is MTL (LOC_Os03g27610), which encodes a phospholipase.
[0067] First, according to the MTL gene sequence, design the target sequence (20nt) in the third exon of the gene, connect the target sequence into the vector pHUN4c12S, and obtain the pHUN4c12S-MTL plasmid; then, transfer the plasmid into the Agrobacterium competent; finally pass Agrobacterium-mediated transgenic method, pHUN4c12S-MTL was transferred into japonica rice variety Xidao 1. After screening, differentiation and rooting, T 0 Transgenic regenerated seedlings were planted to obtain T1 plant R07, and then the tested plant was transplanted to ...
Embodiment 2
[0102] (1) Extraction of experimental materials and genomic DNA of plants to be tested: soybean transgenic sample L22 uses pSOY19 as a vector, with a total length of 9557 bp, and the target gene g10-epsps contained in the vector functions as a glyphosate tolerance gene.
[0103] According to the g10-epsps gene sequence, the target sequence was ligated into the vector pSOY19 to obtain the pSOY19-g10-epsps expression plasmid vector; then, the plasmid was transformed into Agrobacterium competent; finally, the pSOY19 -g10-epsps was transferred into the acceptor Huachun 3. The transgenic soybean L22 was obtained after screening, differentiation and rooting.
[0104] After the strains were normally cultured to 100 days of seedling age, the leaves were taken, and the genomic DNA of the plant to be tested was extracted with a conventional DNA extraction kit, and the whole genome was resequenced. . The soybean reference genome is the cultivar Williams 82 sequence Gmax_275_v2.fa, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0137] (1) Extraction of experimental materials and genomic DNA of plants to be tested: Take rice gene editing sample R14 as an example, pHUN4c12S is used as the carrier, the full length is 12314bp, and the gene editing target gene is OsLCT1 (LOC_Os06g38120), which encodes a low-affinity ion transporter protein.
[0138] First, according to the OsLCT1 gene sequence, a target sequence (CCCGGCAGCGCACCGATGTTGCT) was designed in the third exon of the gene, and the target sequence was connected into the vector pHUN4c12S to obtain the pHUN4c12S-LCT1 plasmid; then, the plasmid was transferred into the competent Agrobacterium; Agrobacterium-mediated transgenic method, pHUN4c12S-LCT1 was transferred into japonica rice variety Tianjing 1. After screening, differentiation and rooting, T0 transgenic regenerated shoots were obtained. Continue planting to obtain T1 plant R14. After the plant to be tested is planted in the field for about 30 days, the leaves are taken, and the genomic DNA o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com