Preparation method of fish skin mucous gland bioreactor and application of preparation method
A bioreactor and mucous gland technology, applied in the field of animal bioreactor preparation, can solve the problems of high cost, harsh culture conditions of isolated animal cells, low success rate and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: Identification of skin-specific expression genes by genomics technology, and acquisition of fish skin and mucus gland cell-specific promoters
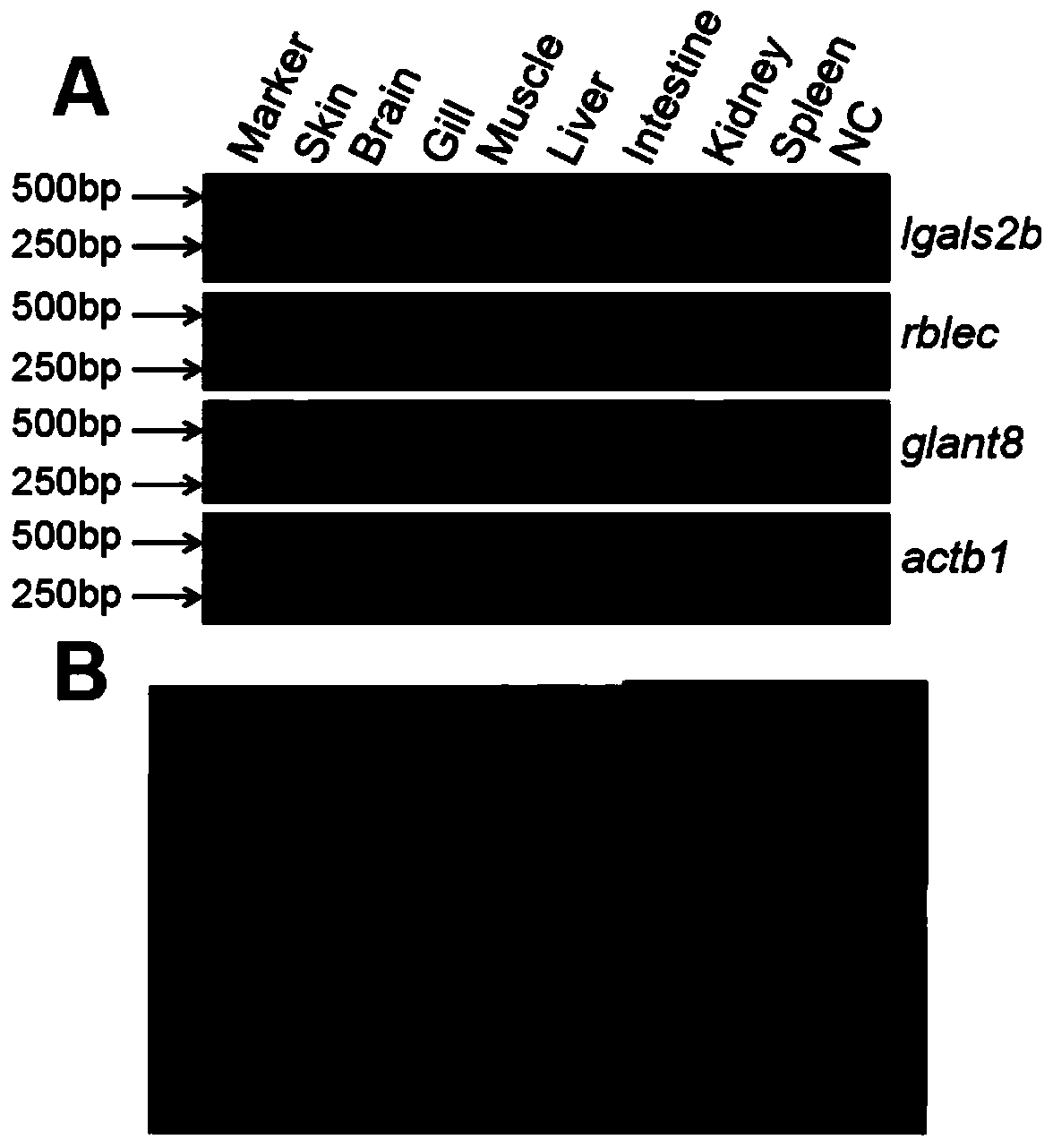
[0050] Total RNA was extracted from loach skin, a sequencing library was constructed, and transcriptome sequencing was performed on a high-throughput sequencing platform. The sequencing results were de novo assembled using Velvet software, and a total of 40,364 cDNA sequences were obtained. Through comparison and analysis of the Blast genome database, the genes and cDNA sequences highly expressed in the skin were obtained, and then PCR primers and RNA probes were designed according to the protein cDNA sequences, and RT-PCR and overall in situ hybridization analysis were performed. Among the highly expressed genes, lgals2b, rblec3 and glant8 were screened out, three genes that can be specifically expressed in loach skin and intestine, the results are shown in figure 2 , wherein (A) RT-PCR detects tissue distribution o...
Embodiment 2
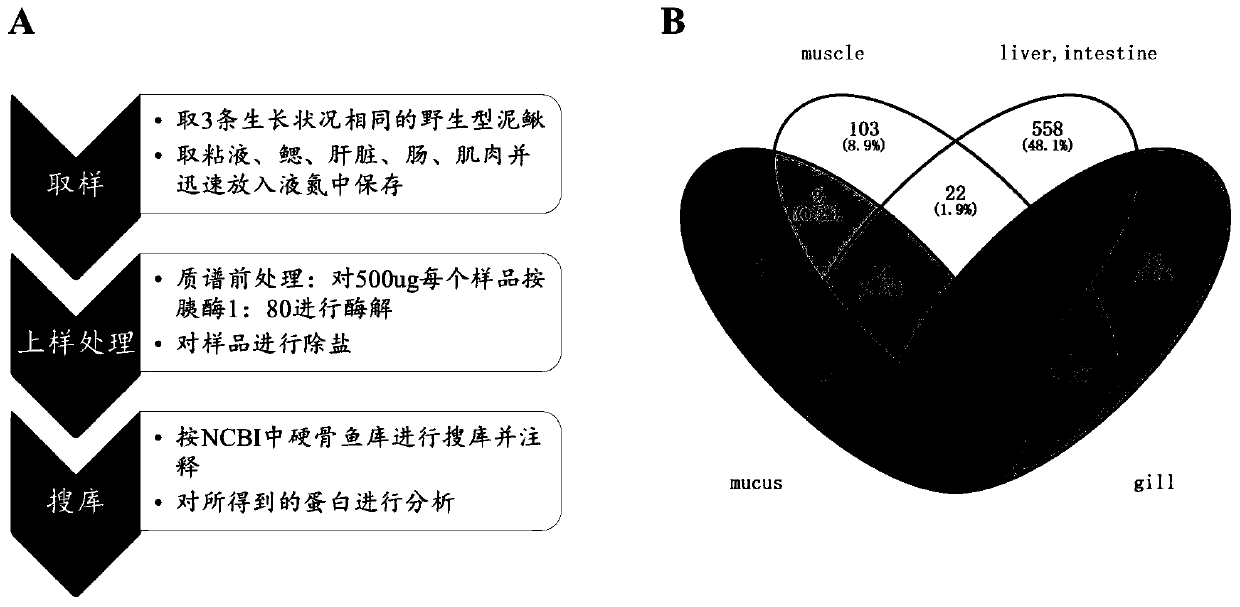
[0051] Example 2: Proteomics technology to identify mucus-specific proteins, and obtain fish skin and mucus gland cell-specific promoters
[0052] Extract different tissue samples and mucus from loach gills, muscles, intestines, liver, etc., and perform sample pretreatment on proteins according to the requirements of proteomics mass spectrometry. Due to the lack of genomics data in loach, the present invention compares the mass spectrometry data with the NCBI bony fish database, analyzes samples between different tissues, and finds 160 specific proteins in loach mucus samples, the results are shown in image 3 , wherein (A) pre-processing steps for mass spectrometry loading of different histone samples. (B) Venn diagram of protein species identified in each tissue; muscle (Muscle), liver (Liver), intestine (Intestine), gill (Gill), mucus (Mucus). The GI number of the loach mucus-specific protein was converted into the UniProt KB format through the UniProt database, and the da...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Search published literature and find genes or promoters specifically expressed in fish skin and mucous gland cells
[0054] To detect whether the existing krt8 promoter can drive the specific expression of the target gene in loach skin.
[0055] Construction of pT2-krt8-EGFP:
[0056] 1. Total RNA was extracted from 24-48hpf zebrafish embryos, and after grinding, follow the Total RNA was extracted according to the operating instructions of Reagent. Take 1 μL of RNA electrophoresis to check the quality of RNA and determine the concentration of RNA. Take 4 μg of newly prepared RNA for reverse transcription, and store the remaining RNA at -80°C after aliquoting.
[0057] 2. Synthesis of first-strand cDNA by reverse transcription
[0058] (1) Add the following reagents to a nuclease-free PCR tube in sequence: Total RNA, 5 μL (4 μg); Oligo-dTprimer, 1 μL Nuclease-free, 6 μL; total volume, 12 μL. (2) After mixing and centrifuging, put it into a PCR instrument...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com