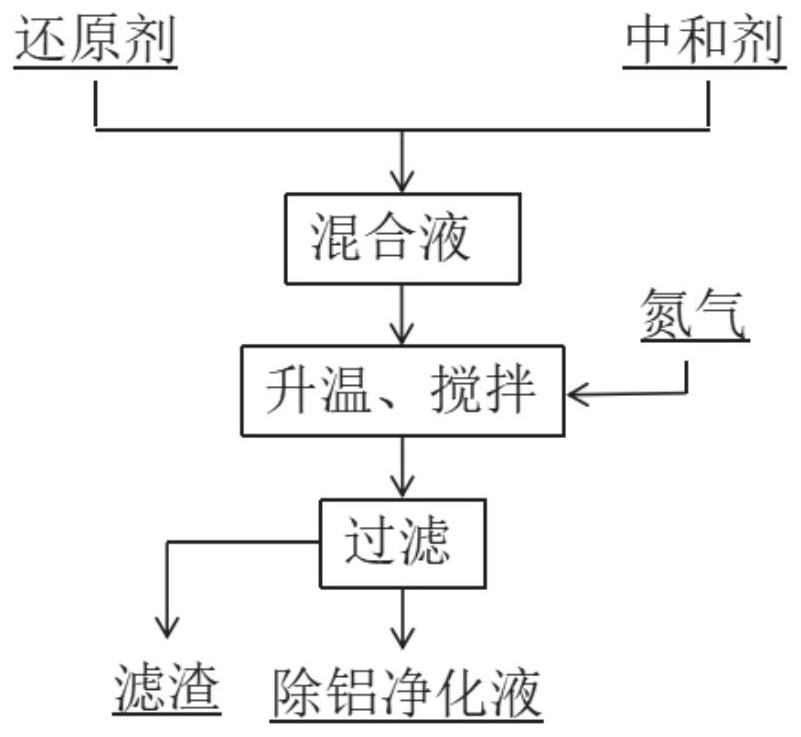
A method for removing aluminum and recycling waste lithium iron phosphate batteries
A ferrous phosphate and waste technology, which is applied in the field of removing aluminum impurities, can solve the problems that affect the electrochemical performance of lithium iron phosphate positive electrode active materials, do not consider defluorination, purification and removal of copper, aluminum impurities, etc., to facilitate automatic production , Improve the effect of fluoride removal, good effect of impurity removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Measure 300 mL of the solution leached by sulfuric acid, add 8 g of reducing iron powder and 4 g of urea in sequence, and stir in a 60°C constant temperature water bath with a nitrogen atmosphere. When the pH rises to 3.0, filter the off-white filter residue and the filtrate after cleaning. The content of aluminum ion in the solution was 18mg / L through ICP detection, and the composition of the filter residue was tested by XRF as shown in Table 2.
[0094] Table 2
[0095]
Embodiment 2
[0102] Measure 600mL of the solution leached in sulfuric acid, add 10g of reducing iron powder and 8g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in sequence, and stir in a constant temperature water bath at 80°C under a nitrogen atmosphere. When the pH rises to 3.0, filter to obtain the off-white filter residue and the cleaned filtrate. The content of aluminum ion in the solution was 5mg / L through ICP detection, and the composition of the filter residue was tested by XRF as shown in Table 4.
[0103] Table 4
[0104]
[0105]
Embodiment 3
[0107] Compared with Example 2, the difference is that it is not carried out in a protective atmosphere, and the specific operations are as follows:
[0108] Measure 600 mL of the solution leached by sulfuric acid, add 10 g of reducing iron powder and 8 g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in sequence, stir in a constant temperature water bath at 80°C, when the pH rises to 3.0, filter to obtain a gray filter residue and a filtrate after cleaning. The content of aluminum ion in the solution was 134 mg / L through ICP detection, and the composition of the filter residue was tested by XRF as shown in Table 5.
[0109] table 5
[0110]
[0111] Compared with Example 2, it is not carried out in a preferred protective atmosphere, and the aluminum removal effect is reduced.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| survival rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| survival rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com