Double-drug-loading carrier-free nanoparticle and preparation method thereof
A carrier-free, dual-drug-loading technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as the inability to get rid of the dependence on synthetic carrier materials, the inability to efficiently load drugs, and safety issues, and achieve synergistic anti-tumor, good biocompatibility and biological Safety, the effect of avoiding toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
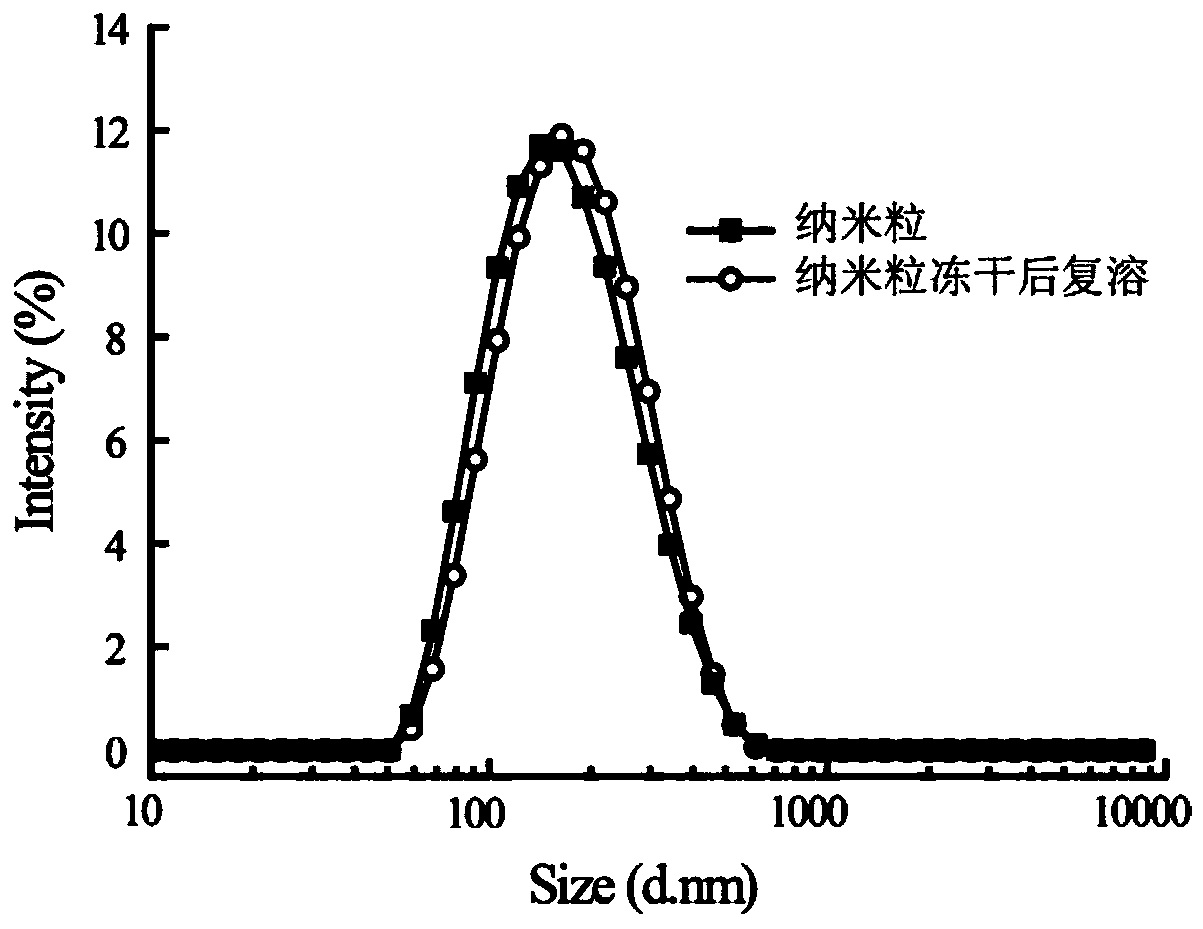
[0030] Example 1 Preparation of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN38) / chlorin e6 (Ce6) dual drug-loaded carrier-free nanoparticles (SN38 / Ce6 NPs): accurately weigh 7.6 mg of SN38 powder and 3.8 mg Ce6, dissolve in 1 mL DMF, ultrasonically dissolve to form an organic phase; the above organic phase is added dropwise to 15 mL of deionized water under 250 W ultrasonic conditions, the temperature is controlled below 20 °C, and the ultrasonic is continued for 10 minutes , Dialysis to remove the organic solvent (ie, the mixed liquid after the organic phase and the water phase are mixed); high pressure homogenization under 150 MPa pressure 3 times, 1.5 min each time, SN38 / Ce6 NPs are obtained. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measures its particle size. Add 1% (w / v%) of the lyophilized protective agent lactose to the SN38 / Ce6 NPs solution and freeze-dry for 12 h to obtain SN38 / Ce6NPs lyophilized powder. SN38 / Ce6 NPs freeze-dried powder is reconstituted with water or 5% glucose. DLS mea...
Embodiment 2
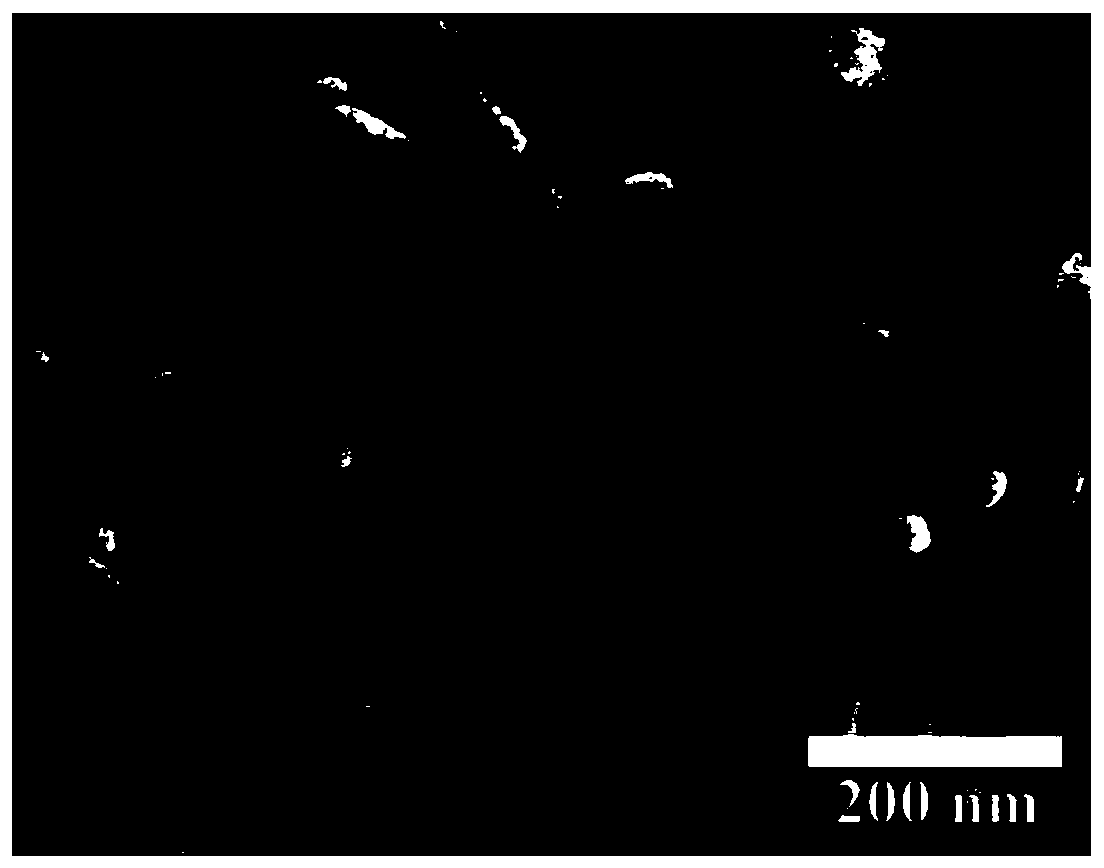
[0032] Example 2 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe the morphology of dual drug-loaded carrier-free nanoparticles: SN38 / Ce6 NPs prepared according to Example 1 were freeze-dried without lyophilization protection agent, and the lyophilized powder was electrically conductive The glue is fixed on the copper column and sprayed with gold for 240 s under vacuum and 30 mA current. Observe under scanning electron microscope.
[0033] The SN38 / Ce6 NPs observed in Example 2 showed a regular rod-like structure ( figure 2 ), the length and diameter of the nanorods are relatively consistent, with an average length of 250 nm and a diameter of about 20 nm. Since the particles in the solution are assumed to be spherical during DLS measurement, the measured particle size is the equivalent volume particle size. Therefore, the results of SEM and DLS will slightly deviate.
Embodiment 3
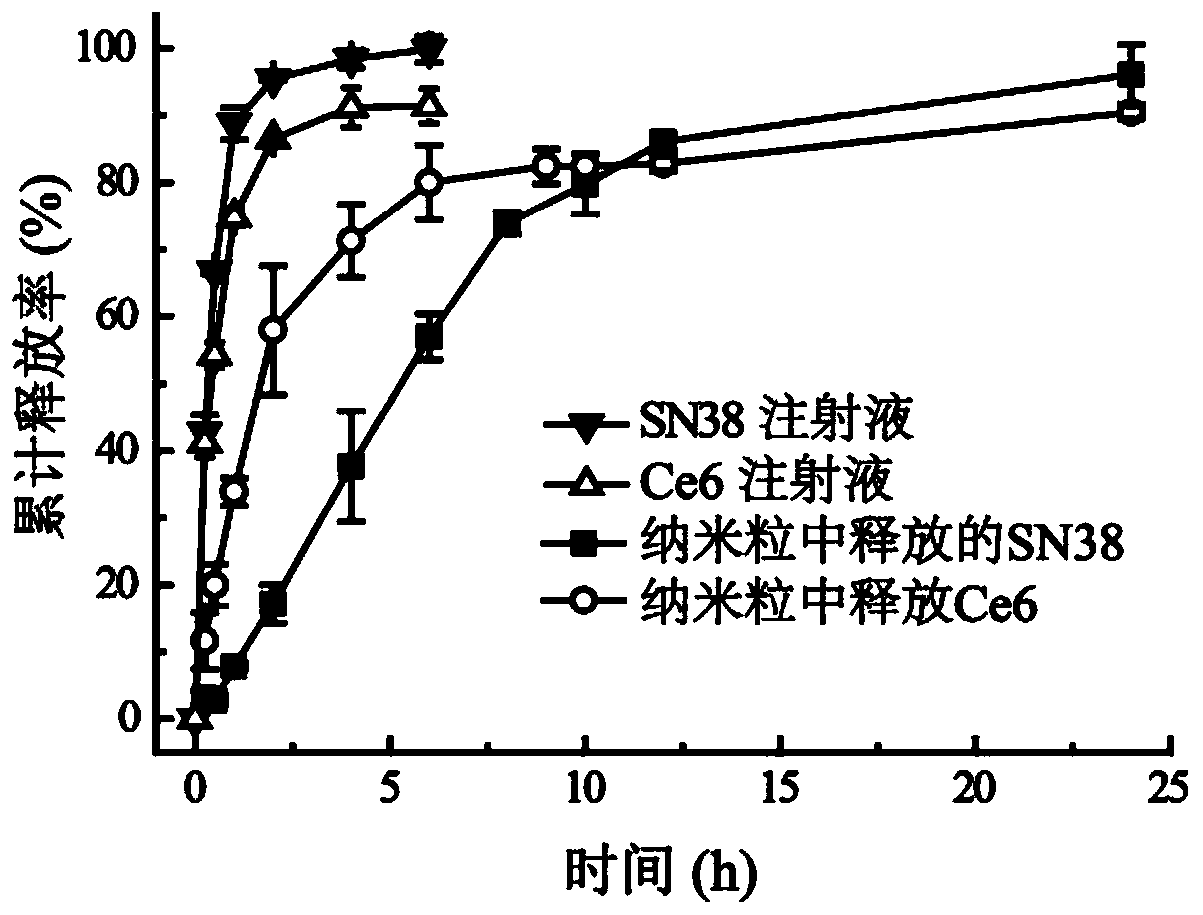
[0034] Example 3 The dynamic membrane dialysis method was used to determine the in vitro release curve of dual drug-loaded carrier-free nanoparticles: Three batches of SN38 / Ce6 NPs were prepared according to Example 1, and SN38 injection and Ce6 injection (self-made with alkalized water) were used as controls. Dilute with deionized water to a SN38 concentration of 25 µg / mL and a Ce6 concentration of 12.5 µg / mL to conduct an in vitro release test. Precisely draw 2 mL of medicated solution, put it into a dialysis bag (MWCO=8000~14000) soaked in distilled water, tie the bag tightly, add 100mL 0.01 M PBS (including 1% SDS), and place it in a 37 °C water bath Release in a constant temperature oscillator (100 rpm). At preset time points (0.0833, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 h), 5 mL was sampled, and an isothermal and equal volume of release medium was added at the same time. Calculate the cumulative drug release percentage based on the measured drug concentration and dra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com