Genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing N-acetylglucosamine and application of genetically engineered bacterium
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and glucosamine, which is applied in the field of genetically engineered bacteria for synthesizing N-acetylglucosamine, and can solve the problems of low production intensity and the inability of glucosamine to meet food-grade requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
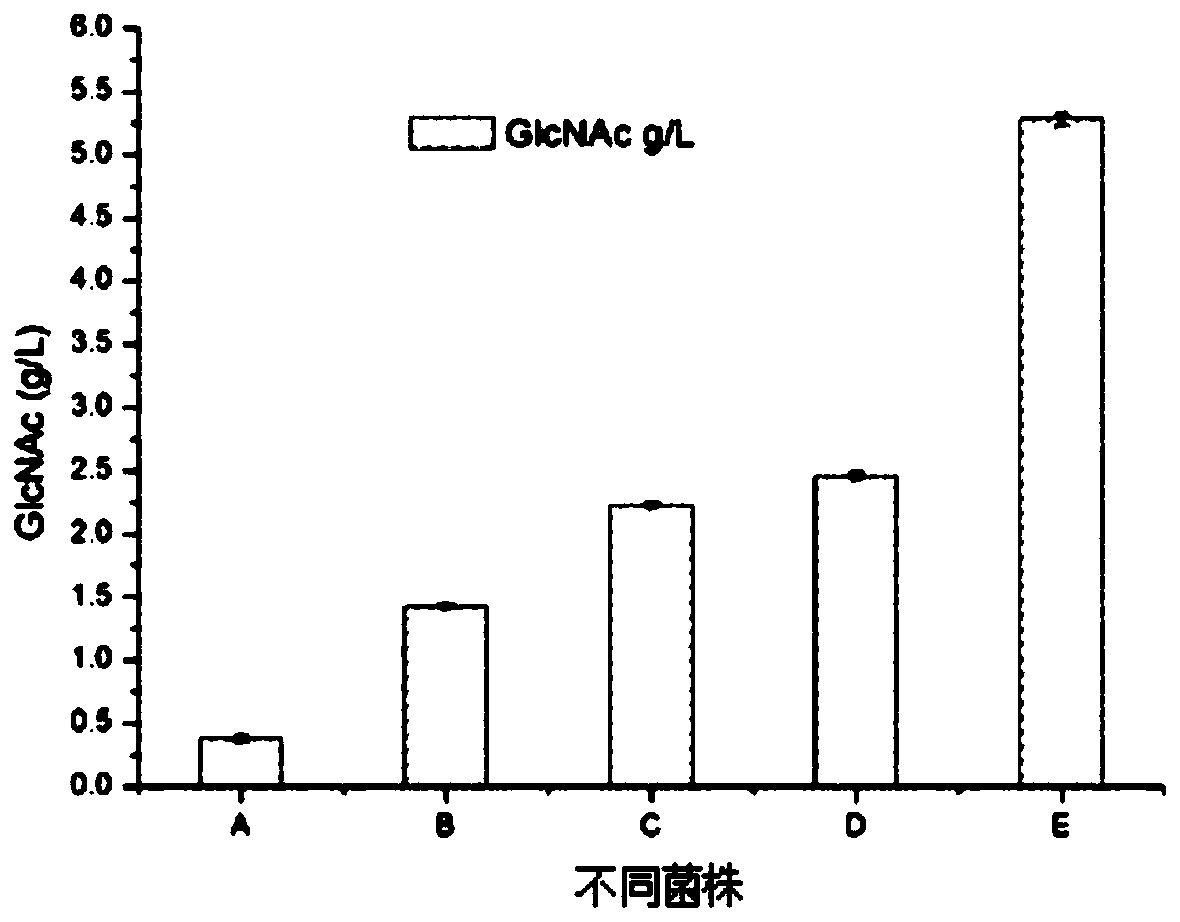
[0042] In the existing technology of using microbial fermentation to produce GlcNAc, Escherichia coli will secrete endotoxin during the fermentation process, and the glucosamine produced cannot meet the food-grade requirements; the highest yield of GlcNAc produced by yeast fermentation is only 3g / L, and The fermentation cycle is as long as 135 hours, and the production intensity is low. In view of this, the present inventor has carried out a large number of studies on the production of GlcNAc by microbial fermentation, and the specific research process is as follows:
[0043] The present invention selects food safety grade (GARS) Corynebacterium glutamicum which is not easy to infect bacteria and has mature gene manipulation technology to produce GlcNAc. The production rate of GlcNAc is directly related to the growth rate of bacteria, and it is a primary metabolite, so the fermentation type of GlcNAc belongs to the growth-coupled type. Corynebacterium glutamicum can use gluco...
Embodiment 1
[0126] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant plasmid
[0127] The primers used in this example are shown in Table 1 above.
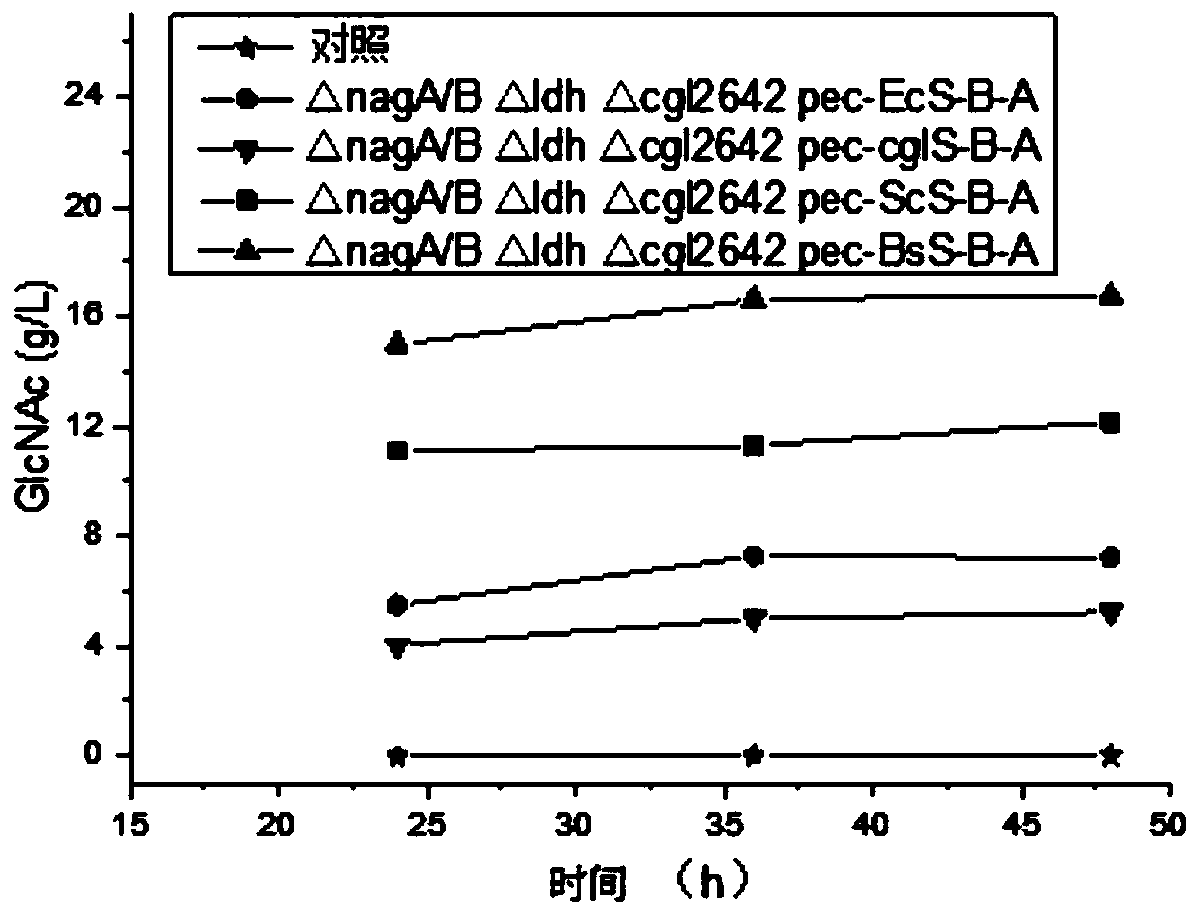
[0128] Firstly, the genomes of Corynebacterium glutamicum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Escherichia coli were extracted, and the glmS, gna1, and yqaB genes were amplified using the genomes of Corynebacterium glutamicum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Escherichia coli as templates, and these three genes were sequentially combined with the plasmid pec-xk99E was connected, and the correct plasmids pec-xk99E-cglglmS, pec-xk99E-gna1 and pec-xk99E-cglglmS-gna1, pec-xk99E-cglglmS-gna1-yqaB were obtained by sequencing.
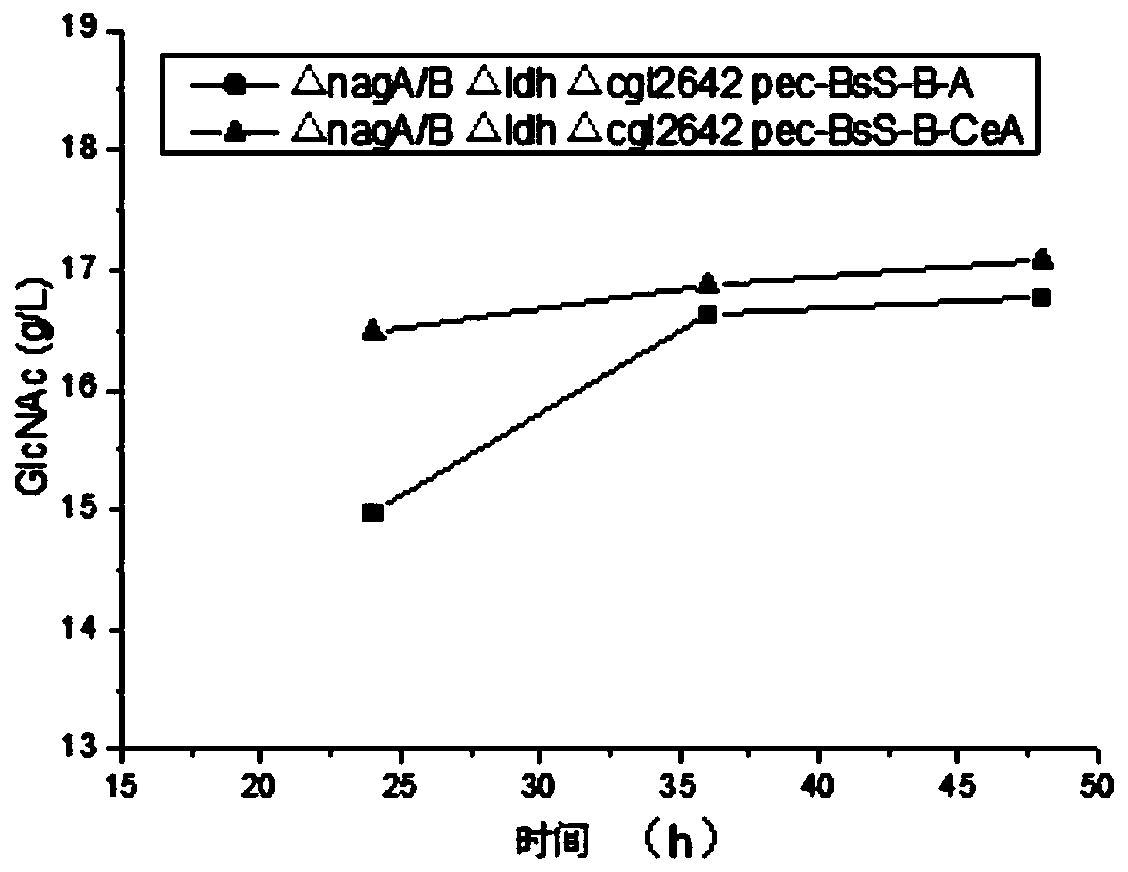
[0129] Then, the glmS genes from Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Bacillus subtilis were amplified as templates. The glmS genes from different sources were digested and ligated with the plasmid pec-xk99E-gna1, and sequenced to obtain the correct plasmids pec-xk99E-EcglmS-gna1-yqaB, pec-xk99E-ScglmS-gna1-yqaB, pec-xk99E-BsglmS...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Embodiment 2: Construction of knockout plasmid
[0131] The primers used in this example are shown in Table 2 above.
[0132] Using the genome of Corynebacterium glutamicum as a template, amplify about 1000bp of the upstream and downstream homology arms of knockout genes nagA / B, ldh, and cgl2642, and the resulting homology arms are nagA / B-L, nagA / B-R, and ldh-L, respectively , ldh-R, cgl2642-L, cgl2642-R. Then these homology arms were digested and ligated with the plasmid PK-JL according to the designed restriction sites, and sequenced to obtain the correct knockout plasmids PK-JL-nagA / B-L-R, PK-JL-ldh-L-R, PK-JL -cgl2642-L-R. Subsequently, each gene was knocked out according to the traditional knockout method of grain stick gene.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com