Plant medicine for treating diabetes and hyperlipidemia and preparation method thereof
A technology for plant medicines and hyperlipidemia, which is applied in the directions of pharmaceutical formulations, plant raw materials, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, and can solve problems such as drug damage, limited therapeutic value, and use restrictions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
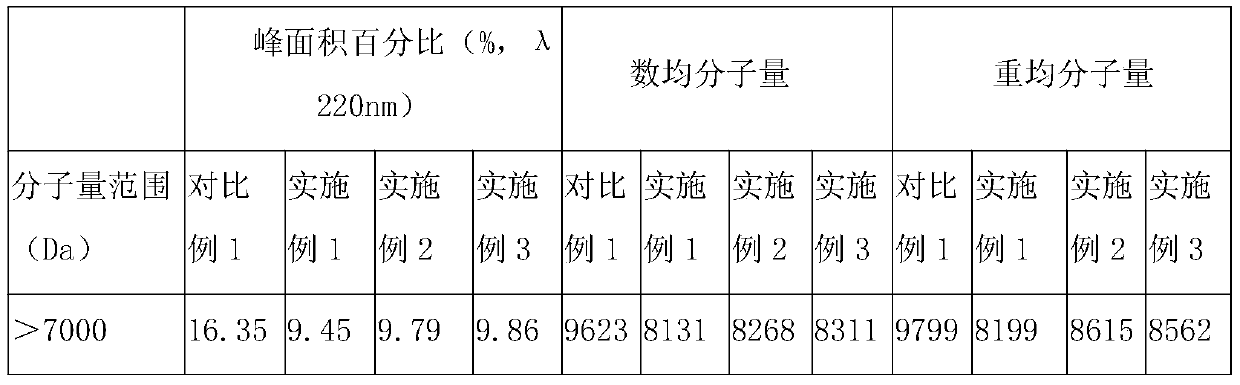
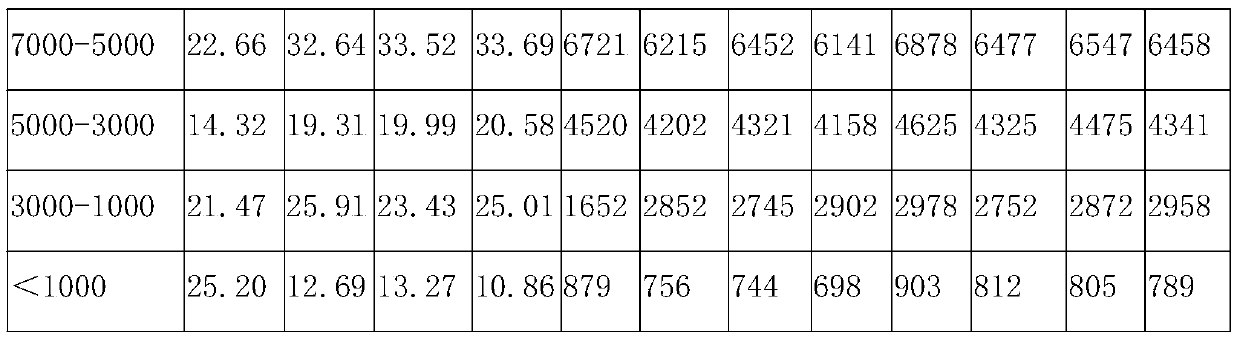
[0065] In parts by weight, the plant medicine for treating diabetes and hyperlipidemia in this embodiment includes: 25 parts of oat glucan, 15 parts of konjac glucomannan, 15 parts of wheat flour, 5 parts of oat bran, 10 parts of kelp powder, 8 parts of cocoa powder, 25 parts of bitter melon peptide powder, 15 parts of Coptis chinensis, 5 parts of sealwort extract, 8 parts of gardenia fruit oil, 5 parts of wolfberry, 12 parts of mulberry leaf extract, 10 parts of Ophiopogon japonicus, 2 parts of ginseng extract, 5 parts of mannose oligosaccharides, 3 parts of black fungus, 5 parts of astragalus, and 5 parts of hawthorn. Wherein, the nutritional yeast includes selenium-enriched yeast and / or chromium-enriched yeast; the pancreatic enzymes include trypsin, pancreatic amylase and pancreatic lipase, and by weight, trypsin: trypsin: trypsin Lipase = 1:2:2.
[0066] Further, the preparation method of the bitter melon peptide powder comprises the following steps:
[0067] S11. Take ...
Embodiment 2
[0106] The only difference between this example and Example 1 is that, in parts by weight, the plant medicine for treating diabetes and hyperlipidemia in this example consists of the following components: 35 parts of oat glucan, konjac glucomannan 25 parts of sugar, 20 parts of wheat flour, 8 parts of oat bran, 15 parts of kelp powder, 10 parts of cocoa powder, 30 parts of bitter gourd peptide powder, 20 parts of Coptis chinensis, 10 parts of sealwort extract, 10 parts of gardenia fruit oil, 10 parts of wolfberry, 15 parts of mulberry leaf extract, 12 parts of Ophiopogon japonicus, 3 parts of ginseng extract, 8 parts of mannose oligosaccharides, 5 parts of black fungus, 8 parts of astragalus, and 10 parts of hawthorn.
Embodiment 3
[0108] The only difference between this example and Example 1 is that, in parts by weight, the plant medicine for treating diabetes and hyperlipidemia in this example consists of the following components: 30 parts of oat glucan, konjac glucomannan 22 parts of sugar, 18 parts of wheat flour, 7 parts of oat bran, 12 parts of kelp powder, 9 parts of cocoa powder, 28 parts of bitter melon peptide powder, 17 parts of berberine, 8 parts of sealwort extract, 9 parts of gardenia fruit oil, 6 parts of wolfberry, 14 parts of mulberry leaf extract, 11 parts of Ophiopogon japonicus, 2.5 parts of ginseng extract, 7 parts of mannose oligosaccharides, 4 parts of black fungus, 6 parts of astragalus, and 7 parts of hawthorn.
[0109]
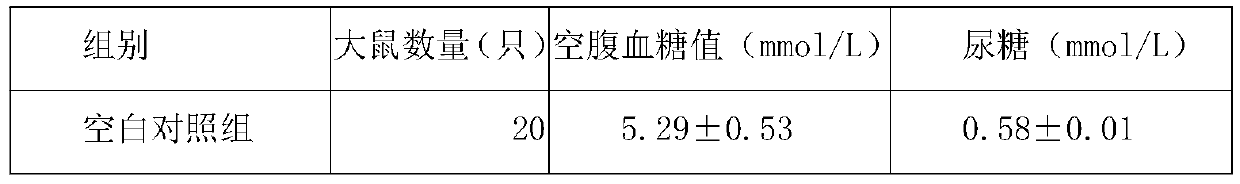
[0110] Using the method described in Example 1 of the patent application with application number 201710832199.8 ("A new method for the whole process of low-temperature production of bitter melon polypeptide protein extract, bitter melon polypeptide protein extr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com