Application of blue light activated (S)-blebbistatin molecules to killing of drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii, and method for killing drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii through blue light activated (S)-blebbistatin molecules
An Acinetobacter baumannii, drug-resistant technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of difficult drug administration, ineffective mammalian cytotoxicity, and poor efficiency, and achieve the effect of solid and powerful technical support
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
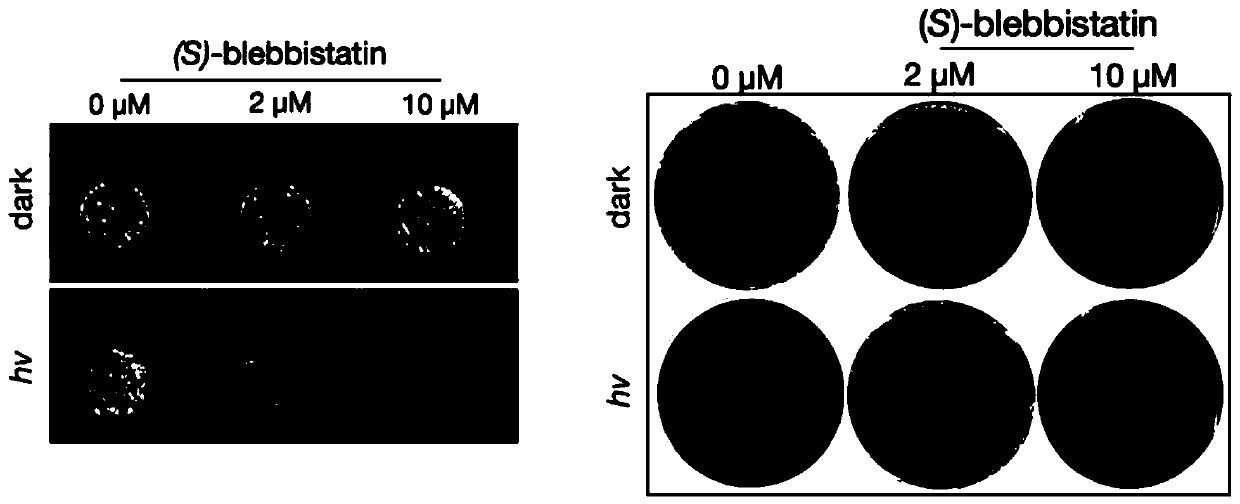
[0028] The application and method of blue light activation (S)-blebbistatin molecule killing drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (concentration gradient sterilization), including the following steps:
[0029] 1. Streak culture of clinical drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii on a culture plate to obtain monoclonal bacteria.
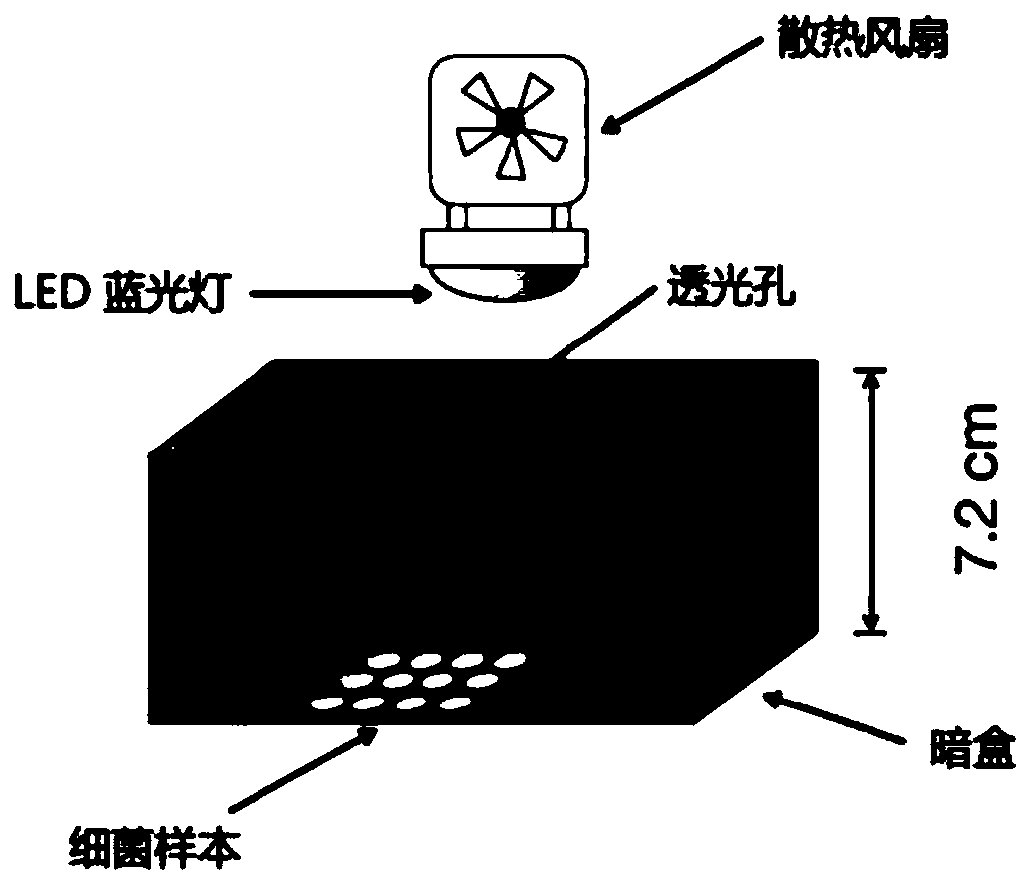
[0030] 1.1) Take out the clinical drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (number: GD0302) stored at -80°C (see figure 2 ), after dissolving on ice, use a circular inoculation stick to dip 1 μL and streak it on the LB agar plate several times.
[0031] 1.2) The upside-down plate was cultured in an incubator for 12 hours to obtain monoclonal bacteria.
[0032] 2. Inoculate into the culture medium to make the clinical drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii reach the logarithmic phase.
[0033] 2.1) Pick 1-4 monoclonal bacteria and culture them overnight on a shaker at 220 rpm in a shaker tube filled with 3 mL of LB medium.
[0034] 2.2) Take 1 / 10 of...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Application and method of killing drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii by activating (S)-blebbistatin molecules with blue light (density gradient sterilization)
[0059] The culture material, apparatus and process of this embodiment are basically the same as embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0060] (1) being different from 3.1 in embodiment 1), embodiment 2 has improved the upper limit of bacterial density and relaxed lower line density on the basis of embodiment 1, i.e. 10 8 cfu / mL-10 3 cfu / mL. Bacteria were serially diluted with 10-fold density gradient in PBS to 2×working density, that is, 2×10 7 cfu / mL, 2×10 6 cfu / mL, 2×10 5 cfu / mL, 2×10 4 cfu / mL, 2×10 3 cfu / mL.
[0061] (2) Analysis of results
[0062] This embodiment adopts drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strain (number: GD0302), and the density is 10 7 cfu / mL,10 6 cfu / mL,10 5 cfu / mL,10 4 cfu / mL,10 3 cfu / mL, after mixing with 2μM and 10μM (S)-blebbistatin, light at 420nm for 60min. It can b...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Application and method of killing drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii by activating (S)-blebbistatin molecules with blue light (different blue light wavelengths)
[0065] The culture material, apparatus and process of this embodiment are basically the same as embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0066] (1) Different from 3.1) in Example 1, the density of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii used in Example 3 is 10 8 cfu / mL, that is converted to 2 times the working density is 2×10 8 cfu / mL.
[0067] (2) Different from 3.2) in Example 1, the concentration of (S)-blebbistatin used in Example 3 is 0 μM and 2 μM, that is, the 2× working concentration is 0 μM and 2×2 μM.
[0068] (3) Different from 3.5) in Example 1, Example 3 uses two kinds of blue light sources with different wavelengths, namely 420nm and 460nm blue light sources.
[0069] (4) Different from 4.2) in Example 1, the dilution factor used in Example 3 was 20,000 times, and 100 μL was evenly spread on the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com