Directionally-inducible and anti-apoptosis pluripotent stem cells and preparation method and application thereof
A pluripotent stem cell, directional induction technology, applied in the direction of artificially induced pluripotent cells, genetically modified cells, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem that transplanted cells are not easy to survive, the direction of differentiation is uncontrollable, and the effectiveness cannot be obtained. Guarantee and other issues, to achieve the effect of high induction efficiency, solving safety and effectiveness issues, and wide sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1 of the present invention is to obtain a directional-inducible, anti-apoptotic pluripotent stem cell, the specific operation of which is as follows:
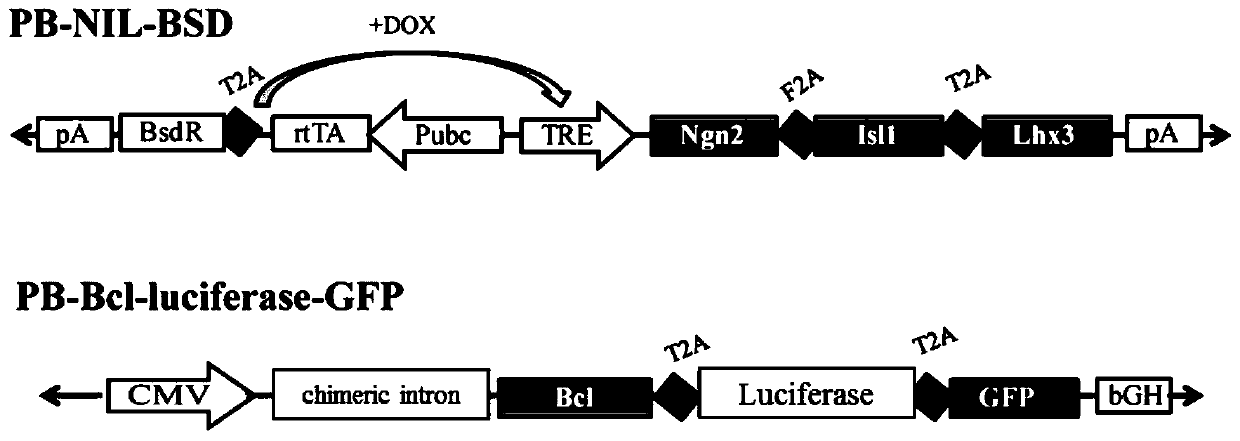
[0041] 1. Construction of Piggy-Bac (PB) vector:
[0042] (1) PB vector for inducing directed differentiation of motor neurons ①PB-Ngn2-Isl1-Lhx3(NIL)-BSD, the PB vector used in this example was donated by Italian professor Alessandro Rosa for his contribution, and the plasmid was introduced into tetracycline response factor (tetracycline response element, TRE) regulates the gene expression of Ngn2, Isl1 and Lhx3, and contains blasticidin (BSD) resistance, which can be used for cell selection.
[0043] TRE consists of seven repeated Tet operator (Tet operator, TetO) sequences.
[0044] (2) In order to improve the retention rate of hiPSCs in vivo, we constructed a PB vector ② PB-Bcl-luciferase-GFP, cloned the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl into the vector ②, and added the marker gene luciferase (luciferase) and green...
Embodiment 2
[0064]Embodiment 2 of the present invention is: an in vitro experiment of directional-induced, anti-apoptotic pluripotent stem cells, the specific operation of which is as follows:
[0065] 1. In vitro directed differentiation and identification of hiPSC-NIL-BSD+Bcl-luciferase-GFP:
[0066] (1) Induction of motor neurons: doxycycline (DOX, 1 μg / mL) was added to induce the directed differentiation of hiPSC-NIL-BSD+Bcl-luciferase+GFP.
[0067] Doxycycline DOX is a derivative of tetracycline. The inducing drug more used in the Tet-induced regulation system is DOX. Compared with tetracycline Tet, the amount of DOX required to fully activate or inhibit the expression of the target gene is less and the half-life of DOX is longer. Tetracycline drugs in this regimen can be tetracycline or its derivatives, and the DOX induction effect is better. The Tet-On system will activate transcription in the presence of tetracycline, and the transcribed Ngn2, Isl1, and Lhx3 transcription factor...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3 of the present invention is: an in vivo experiment of directional-induced, anti-apoptotic pluripotent stem cells, and its specific operation is as follows:
[0077] 1. Directed differentiation of hiPSC-NIL-BSD+Bcl-luciferase-GFP in vivo:
[0078] (1) HiPSC-NIL-BSD+Bcl-luciferase-GFP cell transplantation and in vivo induction: hiPSC-NIL-BSD+Bcl-luciferase-GFP (1×10 6 The cells were resuspended in 200 μL of DMEM / F12: Matrigle=1:1) and injected subcutaneously into immunodeficient mice (Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, SCID) (5-7 weeks old). Three mice in the same batch were intraperitoneally injected with DOX ( 50mg / kg), continuous injection for 7 days for directional induction.
[0079] 2. Identification of directed differentiation in vivo:
[0080] (1) Survival of hiPSCs in vivo: The luciferase signal was detected by in vivo imaging experiments, and then the survival of hiPSC-NIL-BSD+Bcl-luciferase-GFP in vivo was judged.
[0081] The obtained in vivo su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com