Near-infrared fluorescent microsphere with emission peak value of greater than or equal to 1300 nm, preparation method and applications thereof
A fluorescent microsphere and near-infrared technology, applied in the field of nanomedical biotechnology detection, can solve the problems of inability to realize whole blood sample detection and unstable existence, and achieve the effect of simple biomarking process, good stability, and increased fluorescence intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1: Synthesis of near-infrared carboxypolystyrene fluorescent microspheres with an emission peak of 1300nm
[0077] The emission peak is 1300nm near-infrared carboxypolystyrene fluorescent microspheres, including carboxypolystyrene balls and near-infrared fluorescent dyes embedded in the carboxypolystyrene balls.
[0078] The particle size of the carboxylated polystyrene spheres is 300 nm.
[0079] The maximum emission wavelength of the near-infrared fluorescent dye is 1300nm, and the structure is as follows:
[0080]
[0081] The specific preparation steps of near-infrared carboxypolystyrene fluorescent microspheres are as follows:
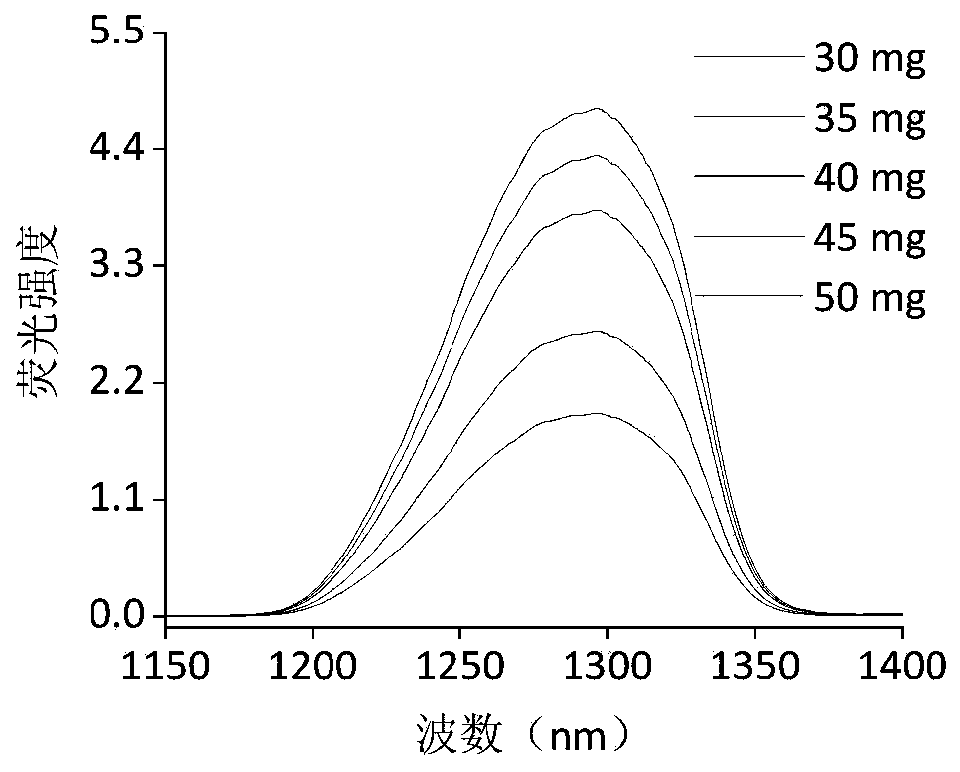
[0082] 1. Disperse 30, 35, 40, 45 and 50 mg of near-infrared fluorescent dyes in 10 mL of tetrahydrofuran solution to form an organic phase;
[0083] 2. Take 1g of 300nm carboxypolystyrene spheres (5 in parallel) and centrifuge to remove the surfactant in the synthesis process, redissolve in 50mL ultrapure water, and fully ultr...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2: Synthesis of near-infrared aminopolystyrene fluorescent microspheres with an emission peak of 1350nm
[0089] The emission peak is 1350nm near-infrared amino polystyrene fluorescent microspheres, including amino polystyrene balls and near-infrared fluorescent dyes embedded in the amino polystyrene balls.
[0090] The particle size of the aminopolystyrene spheres is 300 nm.
[0091] The maximum emission wavelength of the near-infrared fluorescent dye is 1350nm, and the structure is as follows:
[0092]
[0093] The specific preparation steps of near-infrared aminopolystyrene fluorescent microspheres are as follows:
[0094] 1. Disperse 30, 35, 40, 45 and 50 mg of near-infrared fluorescent dyes in 10 mL of chloroform solution to form an organic phase;
[0095] 2. Take 1g of 300nm aminopolystyrene spheres (5 in parallel) and centrifuge to remove the surfactant in the synthesis process, redissolve in 50mL ultrapure water, and fully ultrasonicate to form an a...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Embodiment 3: the preparation of AFP immunochromatography test strip
[0101] 1. Emission peak at 1300nm near-infrared carboxypolystyrene fluorescent microspheres coupled with AFP-Ab 1 (Jingda Bio) to prepare fluorescent probes:
[0102] 1) Take 100 mg of near-infrared carboxypolystyrene fluorescent microspheres prepared in Example 1, centrifuge, redissolve in 18 mL of BBS buffer solution with pH 7.4, and sufficiently ultrasonicate to disperse evenly to obtain a dispersion system.
[0103] 2) Add 10 mg EDC and 5 mg NHSS respectively to the dispersion system, and react at room temperature for 2 hours.
[0104] 3) After the reaction, wash by centrifugation, redissolve in 10 mL of BBS buffer solution with pH 7.4, and add 5 mg of AFP-Ab to it 1 Type monoclonal antibody, reacted at room temperature for 4 hours.
[0105] 4) After the reaction, wash by centrifugation, redissolve in 10 mL of BBS buffer solution with pH 7.4, add 100 mg of BSA to it, and react at room temperatur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Emission peak | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The peak | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com