Lactobacillus plantarum for high-moisture oat silage and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and high moisture, which is applied in the field of silage, can solve the problems of less lactic acid bacteria preparations and high production costs, and achieve the effects of strong acid production capacity, reduced content, and low production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] This embodiment is an embodiment of strain screening, determination and preservation.
[0036] A strain of Lactobacillus plantarum used for high-moisture oat silage was isolated and screened multiple times from samples such as pickles, silage, livestock manure, gastric juice, and yogurt on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The Lactobacillus plantarum was preserved in China on May 15, 2019 The General Microbiology Center of the Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee, the Lactobacillus plantarum strain is Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum), and the preservation number is CGMCC No.17740.
Embodiment 3
[0045] This embodiment is an application example of the plant lactic acid bacteria obtained in Example 1 in the fermentation of high-moisture oat silage, and the specific method steps are as follows:
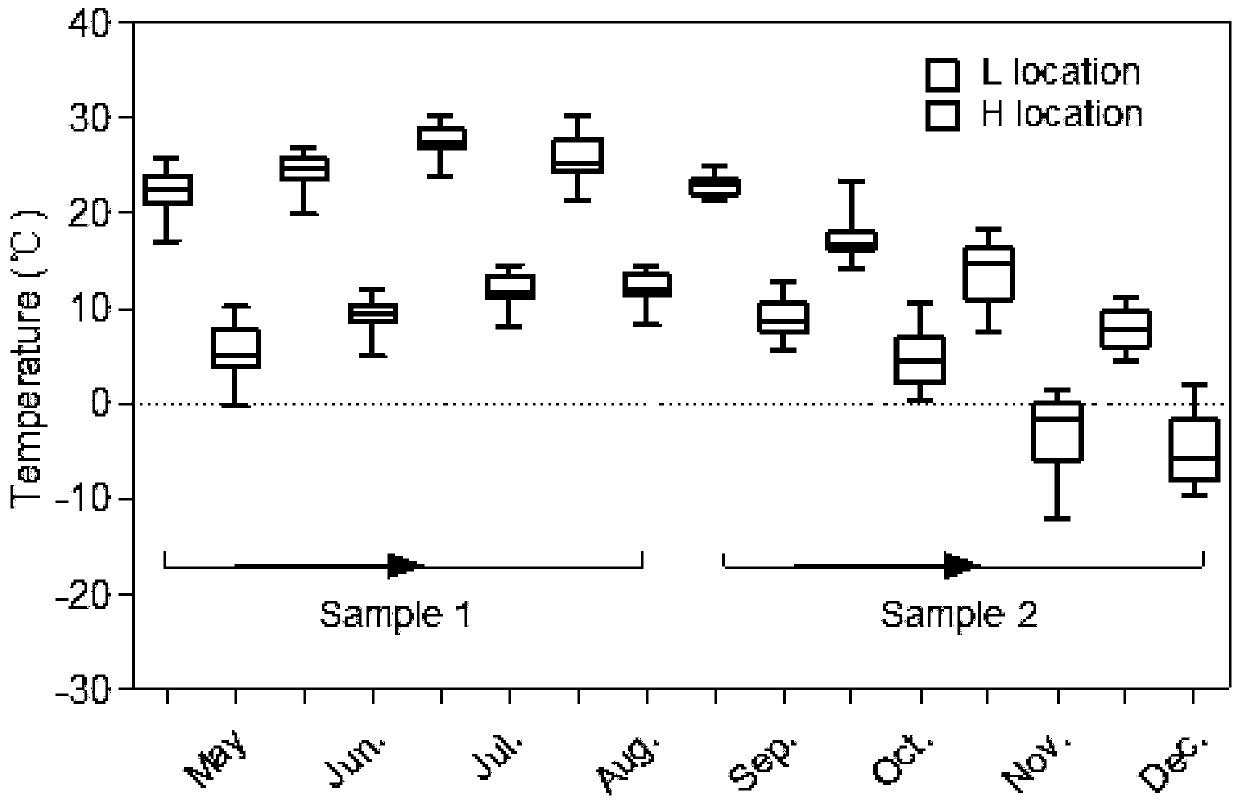
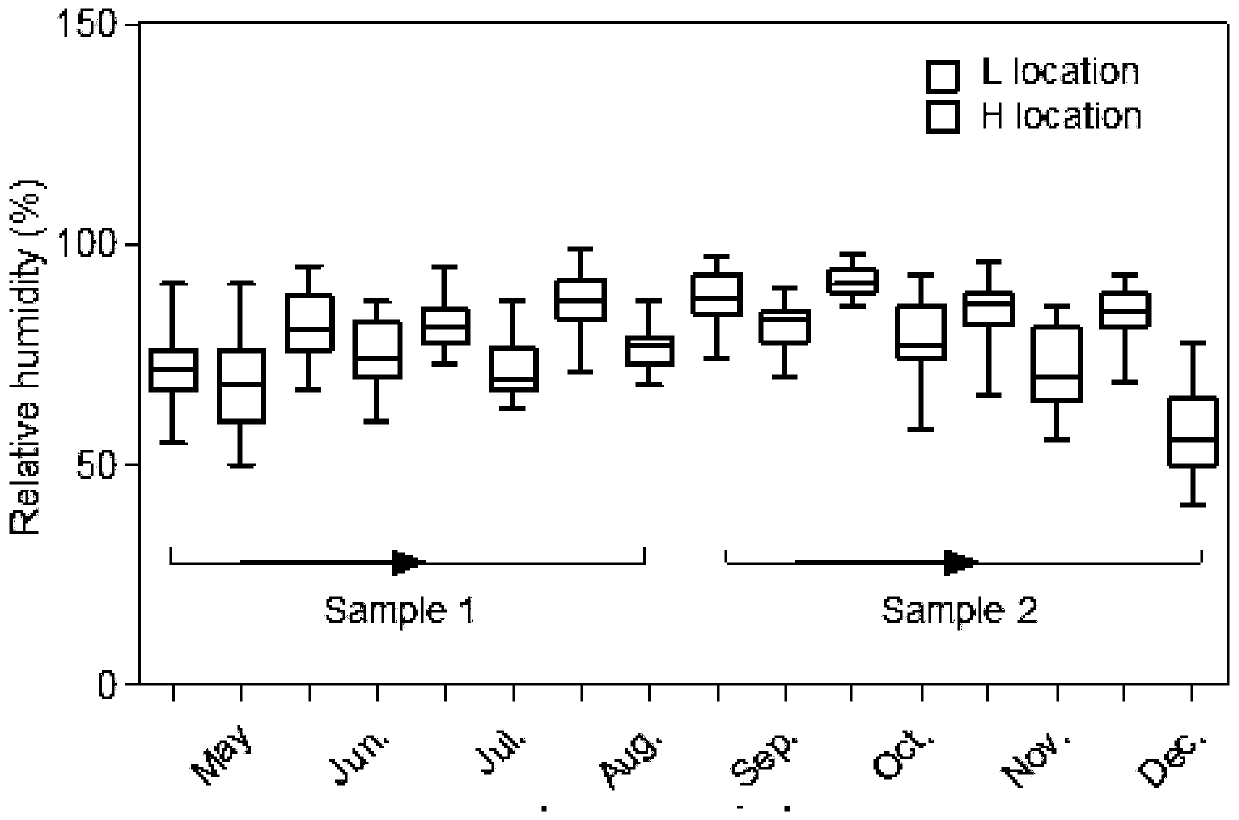
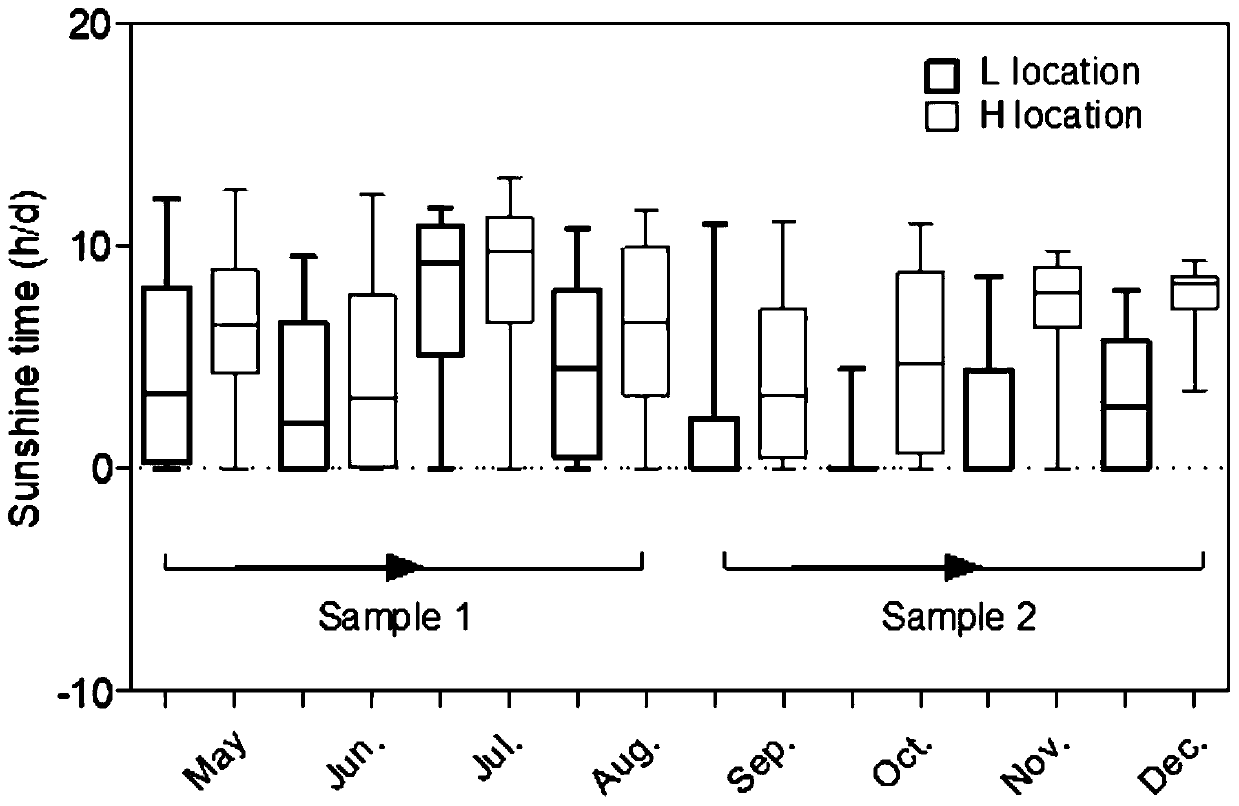
[0046] 1) Raw material preparation: Aba Hongyuan County flowering oats in September, manually harvested and chopped to 5-8cm;
[0047] 2) Strain activation: Inoculate the Lactobacillus plantarum preserved in the ampoule into the MRS liquid medium, culture at 30°C for 12-14 hours, subculture twice to obtain the activated strain, and inoculate the activated strain into the MRS liquid medium Expand the culture, use cyclodextrin to wrap the bacteria, freeze-dry, make a solid bacteria preparation, and make the number of viable bacteria >109cfu / g;
[0048] 3) Preparation and fermentation of silage raw materials: Dilute the solid bacterial preparation with distilled water, inoculate it into the fresh grass raw material according to the inoculum amount of 105 cfu / g of viable bacteria, m...
Embodiment 4
[0052] This embodiment is an application example of the plant lactic acid bacteria obtained in Example 1 in the fermentation of high-moisture oat silage, and the specific method steps are as follows:
[0053] 1) Raw material preparation: oats at flowering stage in Xinjin County, Chengdu in April, manually harvested and chopped to 5-8cm;
[0054] 2) Strain activation: Inoculate the Lactobacillus plantarum preserved in the ampoule into the MRS liquid medium, culture at 30°C for 12-14 hours, subculture twice to obtain the activated strain, and inoculate the activated strain into the MRS liquid medium Expand the culture, use cyclodextrin to wrap the bacteria, freeze-dry, make a solid bacteria preparation, and make the number of viable bacteria >109cfu / g;
[0055] 3) Preparation and fermentation of silage raw materials: Dilute the solid bacterial preparation with distilled water, inoculate it into the fresh grass raw material according to the inoculum amount of 100 cfu / g of viable ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com