Nano gene drug for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and preparation method thereof
A gene drug and non-alcoholic technology, applied in the field of nano-gene drug and its preparation for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, can solve the problem of not being able to compress DNA well, and achieve high therapeutic effect, good stability, and high transformation The effect of dyeing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Preparation and characterization of embodiment 1 nano gene drug (CDPIA)
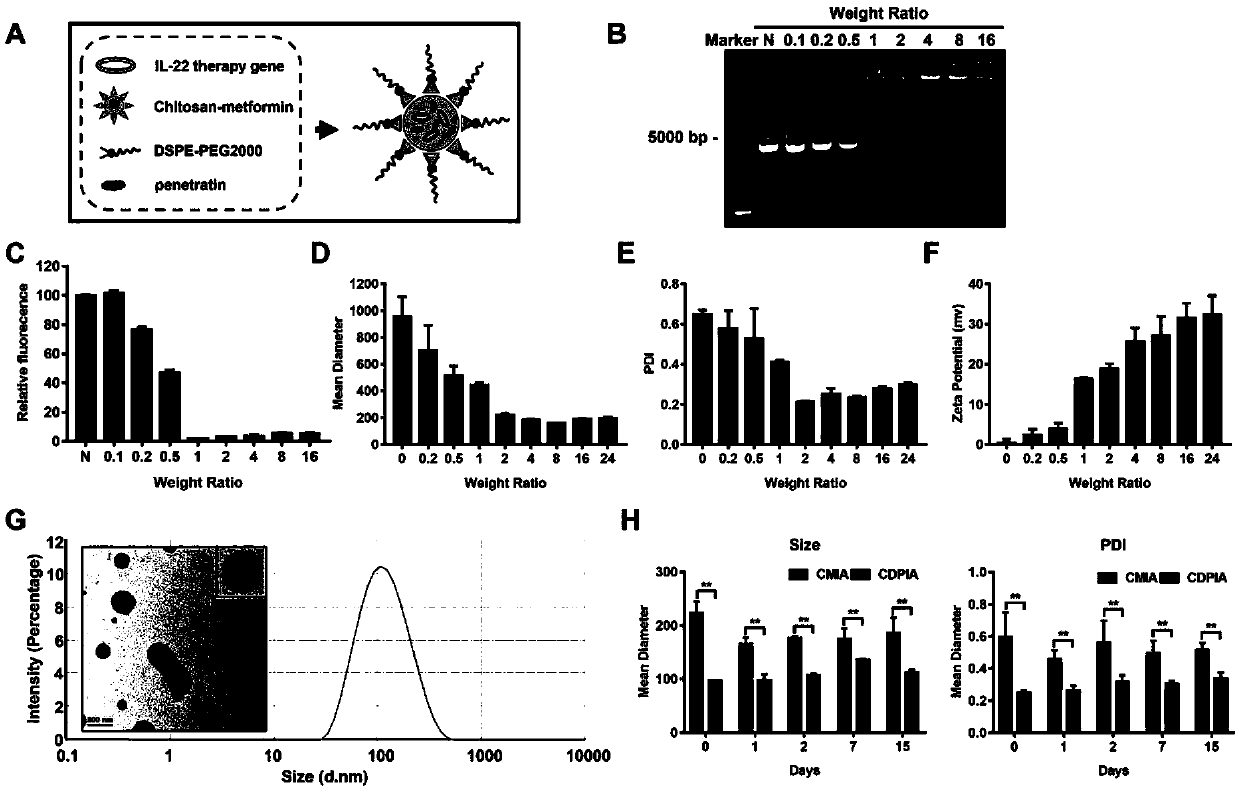
[0043] The composition and structure of the nano gene drug of the present invention are as follows: figure 1 Shown in A; First, the therapeutic gene (pIA plasmid) was dissolved in ultrapure water with a mass percentage of 5, and the Chitosan-Metformin cationic polymers of different mass ratios were added rapidly; the mixture was vortexed for 60 seconds, and the Incubate for one hour under high temperature conditions; Sephadex gel electrophoresis of cationic polymers containing different components such as figure 1 As shown in B and C, it shows that when the Chitosan-Metformin: pIA mass ratio is 1, the therapeutic gene can be fully packaged;
[0044] Then, positively charged Chitosan-Metformin, penetratingin, and DSPE-PEG2000 were dissolved in five percent by mass ultrapure water, and the negatively charged therapeutic gene was added dropwise to the mixed solution; the mixture was vortexed for 60 ...
Embodiment 2
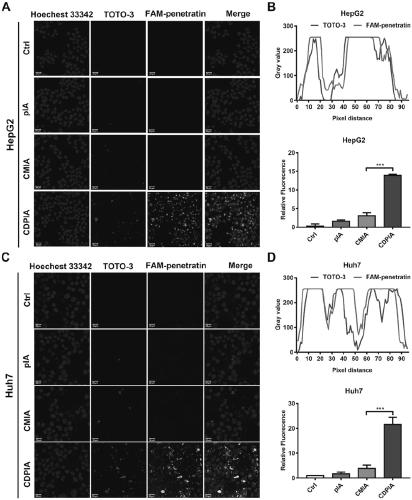
[0046] Example 2 The uptake of hepatocytes to CDPIA
[0047] Use laser confocal microscope to observe the uptake of nano-gene drug (CDPIA) by hepatocytes; first, use fluorescent dye TOTO-3 to label therapeutic gene pIA and FAM to label penetranin, and prepare fluorescent probe-labeled CDPIA by self-assembly method Nanogene drug (CDPIA); then 1×10 5 The HepG2 cells and Huh7 cells were inoculated in confocal small dishes, and when the cells grew to 70%, fluorescently labeled pIA, CMIA, and CDPIA were added to the cells for 2 hours; after washing with pre-cooled PBS for 3 times, the laser confocal Observe the uptake of hepatocytes to nano-gene drugs (CDPIA) under a focusing microscope; figure 2 As shown, the results show that the uptake rate of hepatocytes to the nanogene drug (CDPIA) modified by penetranin and self-assembled is significantly increased, while the naked plasmid (pIA) and the nanogene drug (CMIA) without penetratingin The uptake rate is low; through fluorescence...
Embodiment 3
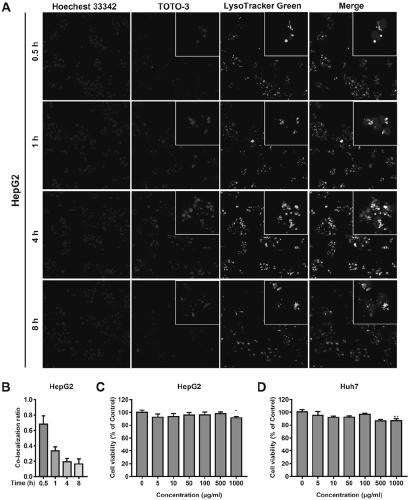
[0048] Example 3 CDPIA can escape the clearance of hepatic lysosomes and has low cytotoxicity
[0049] According to literature reports, lysosome escape is the prerequisite for the good transfection efficiency of nanogene drug after ingestion; this example further investigates the subcellular localization and lysosome escape ability of nanogene drug (CDPIA) in liver cells. CDPIA was labeled with TOTO-3 dye, lysosome was labeled with Lysotracker Green dye, and nucleus was labeled with Hoechst33342 to observe the localization of CDPIA, lysosome and nucleus; 1×10 5 HepG2 cells and Huh7 cells were inoculated in confocal small dishes; when the cells grew to a fusion rate of 70%, CDPIA was added, and then the localization of CDPIA, lysosomes and nuclei was observed at different time points; image 3 As shown in A and B, the experimental results show that CDPIA is taken up by hepatocytes within 1 hour and some nanoparticles and lysosomes co-localize (yellow); after 4 hours, the green ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com