Surface modification pretreatment method of flexible organic polymer substrate
A surface modification and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of surface modification pretreatment of flexible substrates, can solve the problems of poor surface roughness and uniformity of substrates, large damage to flexible substrates, and difficulty in controlling the surface treatment characteristics of substrates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] In a closed system filled with oxygen circulation (oxygen concentration 40% by volume), commercially available polyethylene terephthalate substrates (PET, thickness 100 µm) were placed under a low-pressure ultraviolet lamp for stepwise irradiation treatment . The treatment temperature is 65° C., first irradiating with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 280 nm for 10 minutes, and then irradiating with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 190 nm for 1 minute.
Embodiment 2
[0016] In a closed system filled with oxygen circulation (oxygen concentration 65% by volume), commercially available polyethylene terephthalate substrates (PET, thickness 100 µm) were placed under a low-pressure ultraviolet lamp for stepwise irradiation treatment . The treatment temperature is 45° C., first irradiating with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 254 nm for 6 minutes, and then irradiating with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 185 nm for 4 minutes.
Embodiment 3
[0018] In a closed system filled with oxygen circulation (oxygen concentration 80% by volume), the commercially available polyethylene terephthalate substrate (PET, thickness 100 µm) was placed under a low-pressure ultraviolet lamp for stepwise irradiation treatment . The treatment temperature is 80° C., first irradiating with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 190 nm for 1 minute, and then irradiating with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 100 nm for 6 minutes.
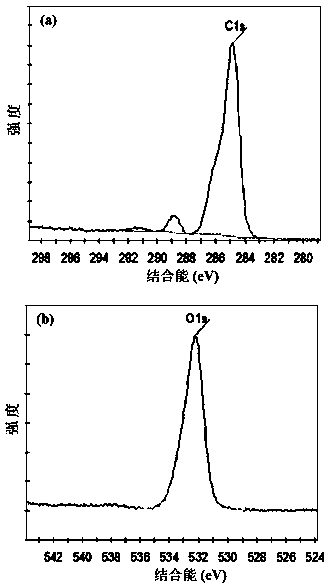
[0019] For the PET base material pretreated in the above-mentioned examples 1-3 and the untreated PET control sample, the surface roughness of the flexible PET base material was evaluated by atomic force microscopy (AFM), and the X-ray photoelectron energy spectrum analyzer was used to evaluate the surface roughness of the flexible PET base material. (XPS) analysis of the surface chemical composition of PET substrates.
[0020] The results showed that the surface roughness of the untreated PET substrate was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com