Preparation method and imaging method of quantum dots for clinical skeletal in vivo imaging
A technology of in vivo imaging and quantum dots, applied in preparations for in vivo experiments, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, chemical instruments and methods, etc. supply and metabolism status, bone tissue sensitivity and resolution are not as good as CT and X-ray, and cannot dynamically observe bone tissue metabolism, etc., to achieve deep tissue penetration ability, good biocompatibility, fidelity and resolution increase Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
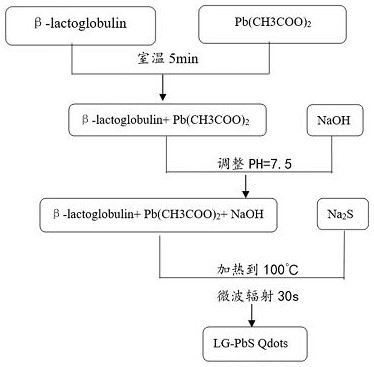
[0026] Preparation of quantum dots for clinical bone imaging in vivo, the specific process is as follows:
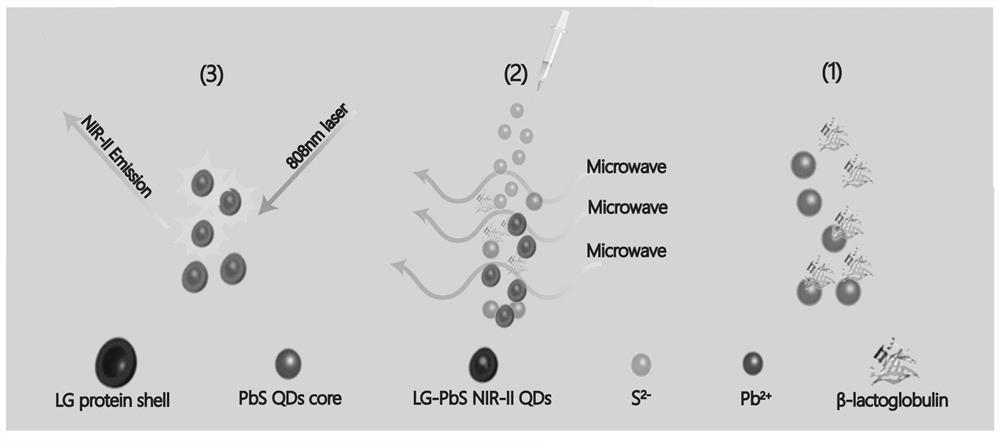
[0027] Take 500 μL of β-lactoglobulin (β-LG) at a concentration of 50 mg / mL and 500 μL of Pb(CH 3 COO) 2 Mix and stir for 5 min at room temperature; then titrate the pH value of the mixed solution to 7.5 with 1M NaOH; 2 S was quickly injected into the mixed solution with a pH value of 7.5, heated to 100 °C, and maintained under microwave irradiation for 30 s to obtain the final product PbS QDs, and the final product was stored at 4 °C. The preparation method flow is as follows figure 1 As shown, the synthesis schematic is shown as figure 2 shown.
[0028] The method for using the quantum dots prepared above for clinical bone imaging in vivo is as follows:
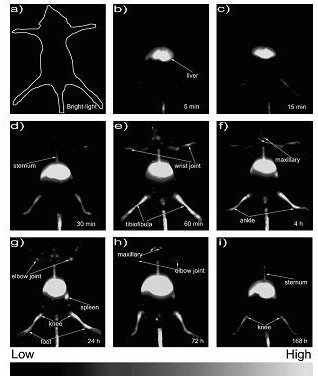
[0029] In this example, mice were selected as the experimental research object. After the mice were anesthetized, 300 μL of LG-PbS QDs were injected through the tail vein of the mice. The original solution of LG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com