KASP marker primer for authenticating types of cytoplasts Cam and Pol of brassica crops and application of KASP marker primer
A technology for labeling primers and Brassica, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of high economic cost and time cost, and achieve accurate and reliable detection results and high throughput. , the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Development of KASP-tagged primers for identification of Cam and Pol cytoplasmic types in Brassica crops:
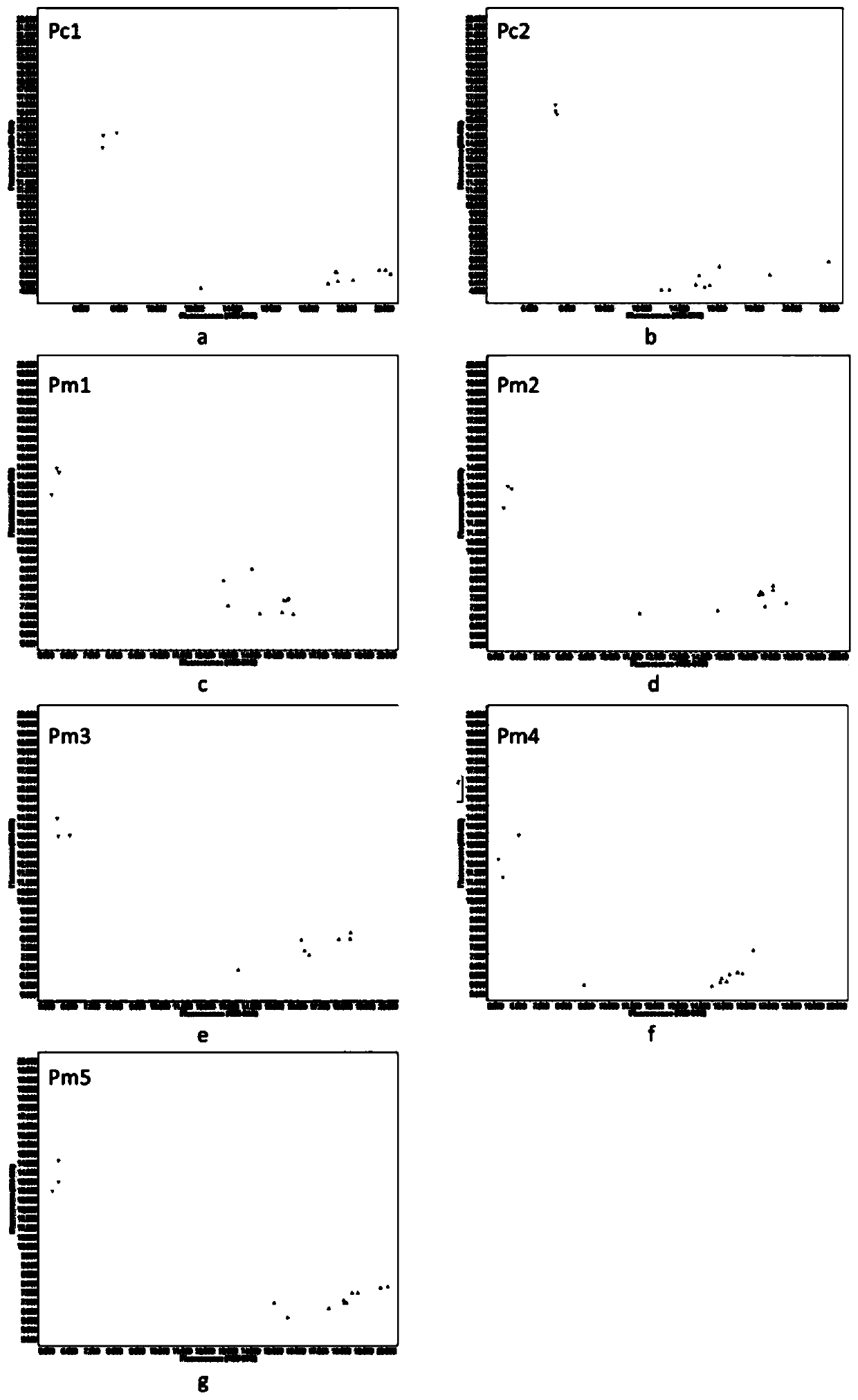
[0074] (1) Sample selection: 54 representative Brassica experimental materials were selected (see Table 1 for specific information), including Nap, Cam and Pol cytoplasmic types;
[0075] (2) Sample preparation: select 10 plants for each sample and take its fresh and young plant leaf tissue, avoid selecting diseases, insect pests and aging leaves, wash 3 times with clean water, and dry it with filter paper; fully grind it with liquid nitrogen and quickly put it into In the homogenizer, add pretreatment buffer (0.5M Sucrose+1mM EDTA+70mM KH2PO4+0.6%PVP(v / v)+0.8%BSA(v / v)+0.1%β-mercaptoethanol(v / v); PH=7.5), after mixing, homogenize in a low temperature environment; gradient centrifugation in a low temperature environment, extract cytoplasm, and then use CTAB method to extract DNA and remove RNA;
[0076] (3) High-throughput sequencing of cytoplasmic DNA: The cytopl...
Embodiment 2
[0141] Utilize the KASP primer that the present invention develops to carry out KASP experiment verification to the material of known Cam and Pol cytoplasmic type:
[0142] (1) Cam cytoplasmic material: Shengli rape, Zhongshuang 2, Shan 2B; Pol cytoplasmic material: Jianyang rape, Xiang 5A, 20A;
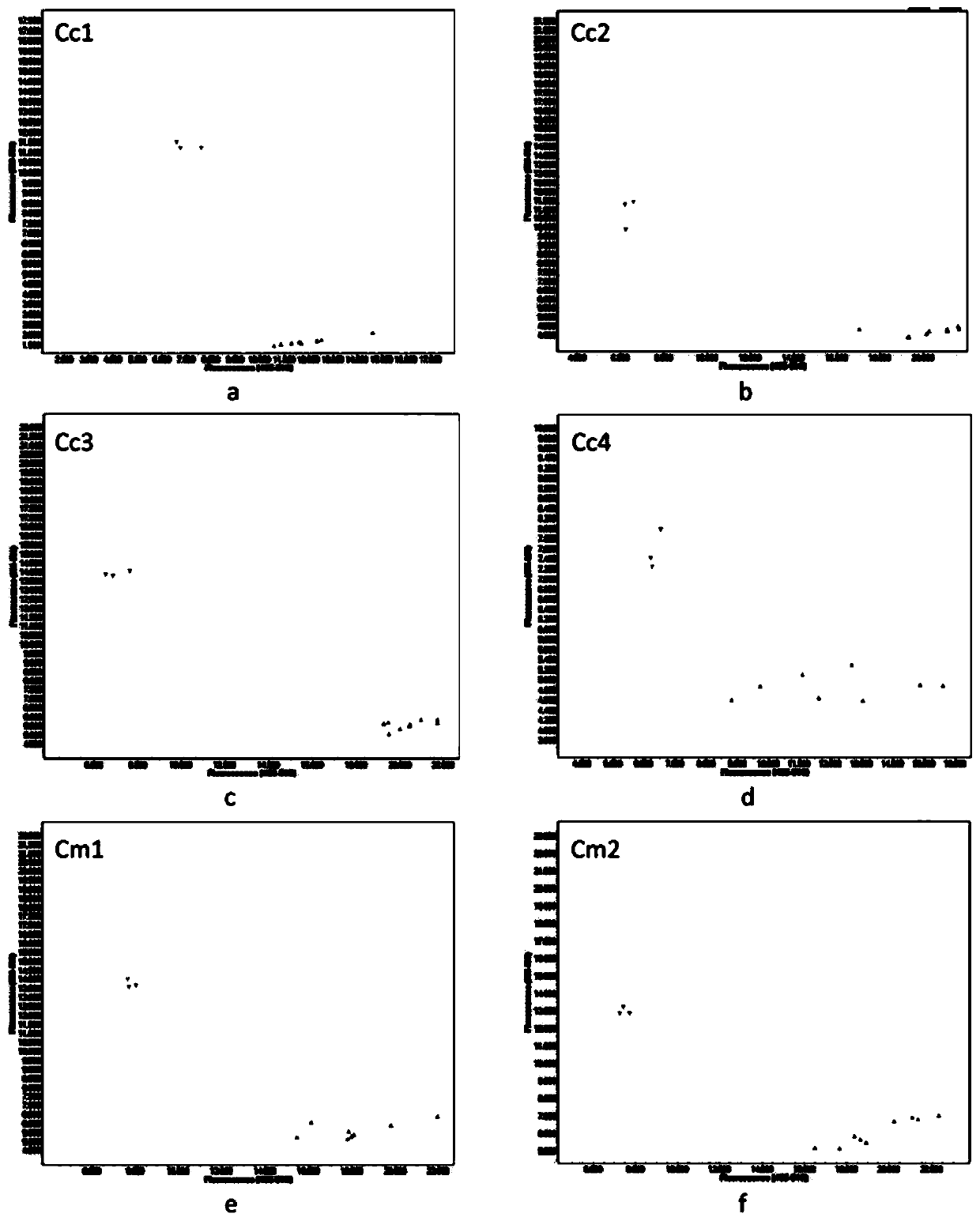
[0143] (2) PCR amplification program: 94°C for 15 minutes; use falling PCR method, 94°C for 20s, 60°C for 1min, (60°C drops to 48°C, each cycle decreases by 1.2°C) cycle 10 times; 94°C for 20s, 55°C 1min, cycle 30 times; 1min at 37°C, collect fluorescence signal in the last 1s, the results are as follows: figure 1 ;
[0144] (3) figure 1 The aggregation points close to the Y axis are the materials of Cam cytoplasm, in which figure 1 The aggregation point near the Y axis in a indicates that the detected polymorphic site is C, and the aggregation point near the X axis indicates that the detected polymorphic site is A; the aggregation point near the Y axis in b indicates that the det...
Embodiment 3
[0148] Identification of cytoplasmic types of 482 Brassica napus inbred lines:
[0149] (1) DNA sample extraction of Brassica napus to be identified: using the CTAB method to extract the total plant DNA by using the CTAB method to extract DNA from each sample of 482 Brassica napus;
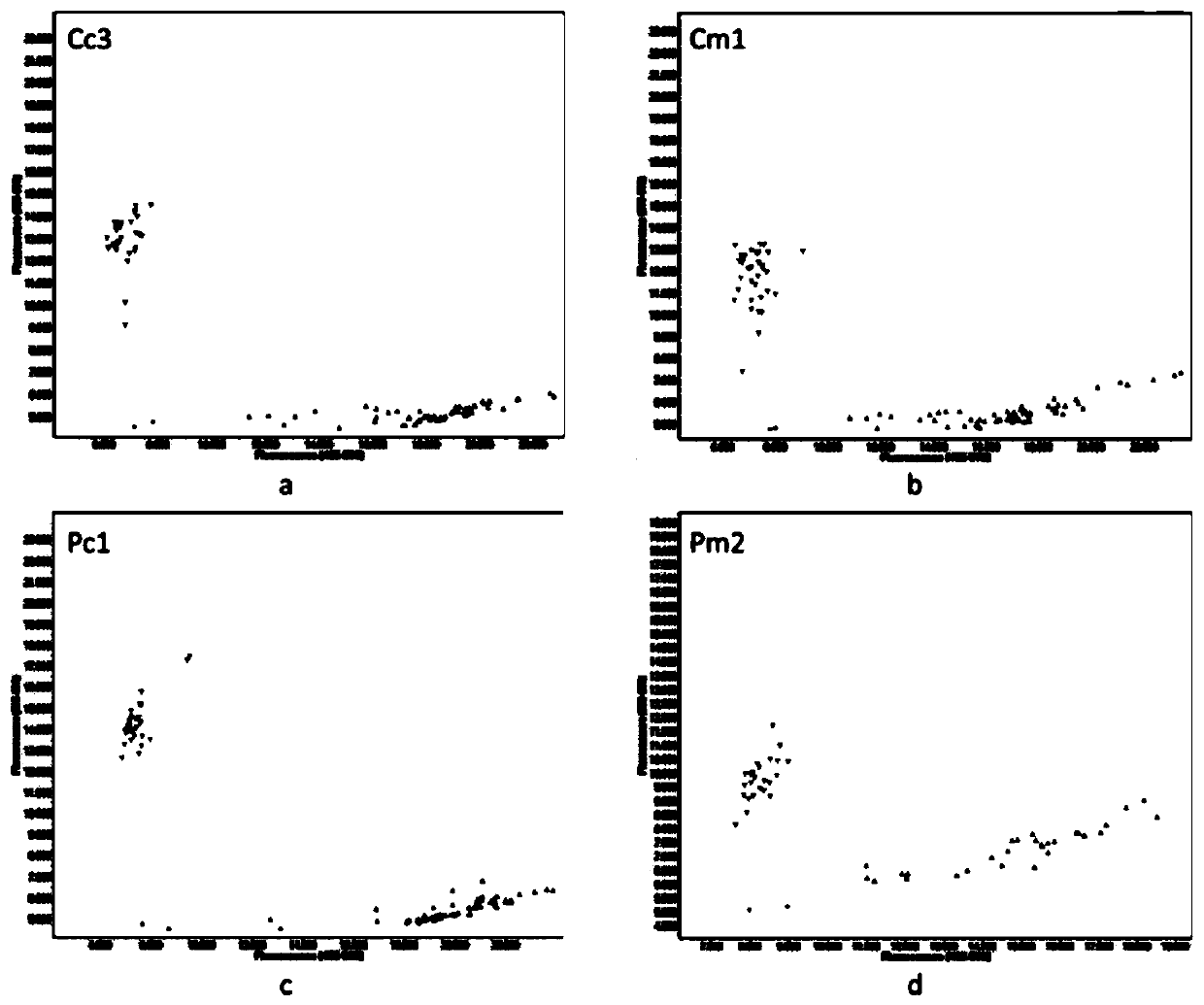
[0150] (2) Select 4 pairs of primers Cc3, Cm1, Pc1 and Pm2 from Example 1, and carry out KASP test on 482 copies of Brassica napus DNA: PCR reaction system is 5 μL, including 1 μL DNA template, 2.5 μL 2×Master Mix, 0.7 μL PrimerMix, 0.8μL ddH2O; PCR reaction program: 94°C for 15min; use falling PCR method, 94°C for 20s, 60°C for 1min, 60°C to 48°C, each cycle lowering 1.2°C, cycle 10 times; 94°C for 20s , 55°C for 1min, cycle 30 times; 37°C for 1min, collect fluorescence signal in the last 1s;
[0151] (3) Judgment method of cytoplasmic type: judge based on the alleles of each site listed in Table 2 in Brassica napus Cam and Pol cytoplasmic types, if it is the same as the alleles described in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com