Method for preparing N40M type sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnetic material by adding 38M waste
A neodymium-iron-boron, magnetic material technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic material magnetism, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost, economic loss, preparation of permanent magnet materials, etc., to reduce production cost and process cost. The effect of reducing, good magnetic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
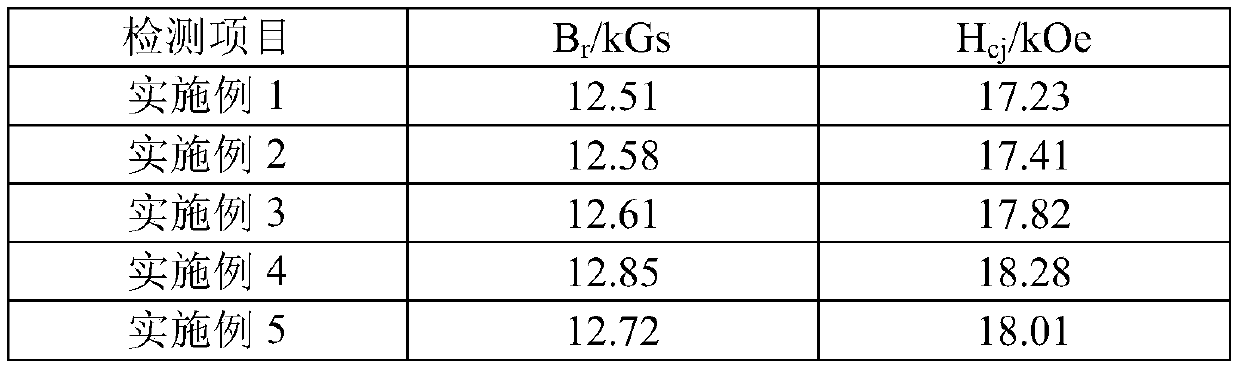
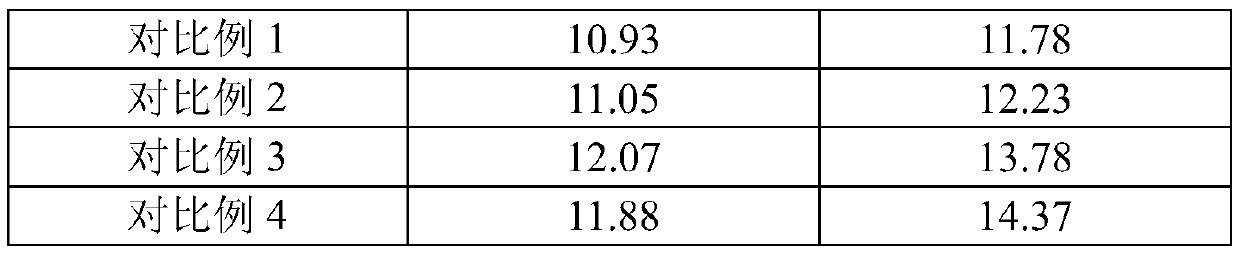
Embodiment 1
[0040] A method for preparing N40M type sintered NdFeB magnetic material by adding 38M waste material, comprising the following steps:
[0041] S1: prepare raw materials, the raw materials include 77% of 38M waste, 0.08% of antioxidants, 0.08% of gasoline and 22.84% of new mixed metal materials; wherein the mixed metal new materials are made of the following mass fractions of raw materials: praseodymium neodymium alloy 28.6%, praseodymium neodymium dysprosium alloy 3.57%, boron 4.94%, copper 0.16%, aluminum 0.51%, zirconium 0.16%, cobalt 0.45%, alloy iron 0.092%, iron is the balance; 38M scrap contains the following mass percentage of raw materials: Praseodymium neodymium alloy 28.5%, gadolinium iron 2%, boron 4.9%, copper 0.18%, aluminum 0.5%, zirconium 0.15%, cobalt 0.4%, cerium 2.5%, iron is the balance;
[0042] S2: smelting the above-mentioned raw materials under vacuum conditions, adjusting the speed of the copper roll to 45m / s, and the smelting temperature to 1350°C to ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference between this example and Example 1 is: Step S1: prepare raw materials, the raw materials include 82% of 38M waste, 0.12% of antioxidants, 0.12% of gasoline and 17.76% of new mixed metal materials, wherein the mixed metal new materials It is made of raw materials with the following mass fractions: praseodymium neodymium alloy 32.6%, praseodymium neodymium-dysprosium alloy 4.17%, boron 5.54%, copper 0.22%, aluminum 1.11%, zirconium 0.22%, cobalt 0.51%, alloy iron 0.102%, iron is the remainder Quantity; 38M scrap is made of raw materials with the following mass fractions: praseodymium neodymium alloy 29.5%, gadolinium iron 2.5%, boron 5.6%, copper 0.23%, aluminum 0.8%, zirconium 0.2%, cobalt 0.5%, cerium 3.5%, iron 0.5% The remainder; the others are the same as in Example 1.
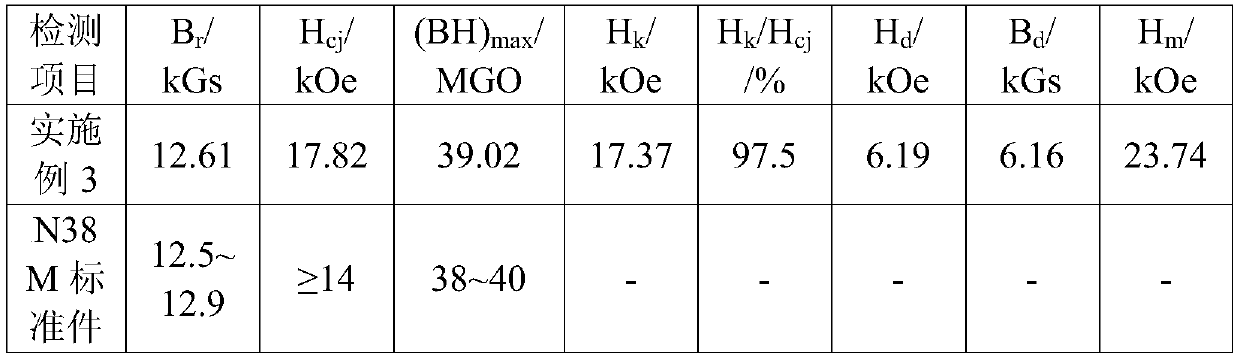
Embodiment 3
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is:
[0051] Step S1: prepare raw materials, the raw materials include 80% of 38M waste, 0.1% of antioxidants, 0.1% of gasoline and 19.8% of new mixed metal materials, wherein the new mixed metal materials are made from the following mass fractions of raw materials:
[0052] Praseodymium neodymium alloy 30.6%, praseodymium neodymium-dysprosium alloy 3.87%, boron 5.24%, copper 0.19%, aluminum 0.81%, zirconium 0.19%, cobalt 0.48%, alloy iron 0.097%, iron is the balance;
[0053] 38M scrap is made of raw materials with the following mass fractions: praseodymium neodymium alloy 29%, gadolinium iron 2.3%, boron 5.3%, copper 0.21%, aluminum 0.65%, zirconium 0.18%, cobalt 0.45%, cerium 3%, iron is the balance ; Others are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Intrinsic coercive force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Remanence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com