Catalyst for preparing higher olefins through carbon dioxide hydrogenation and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for producing high-carbon olefins and carbon dioxide, which is applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of low hydrogenation activity, low catalyst activity, and low carbon atom utilization, and achieve high space-time yield and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: Preparation and performance evaluation of catalyst FeK3 / SWNTs with single-walled carbon nanotube bundles as carrier, iron as active component and potassium as promoter.
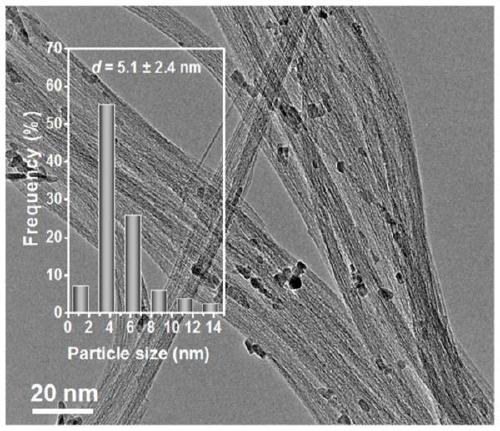
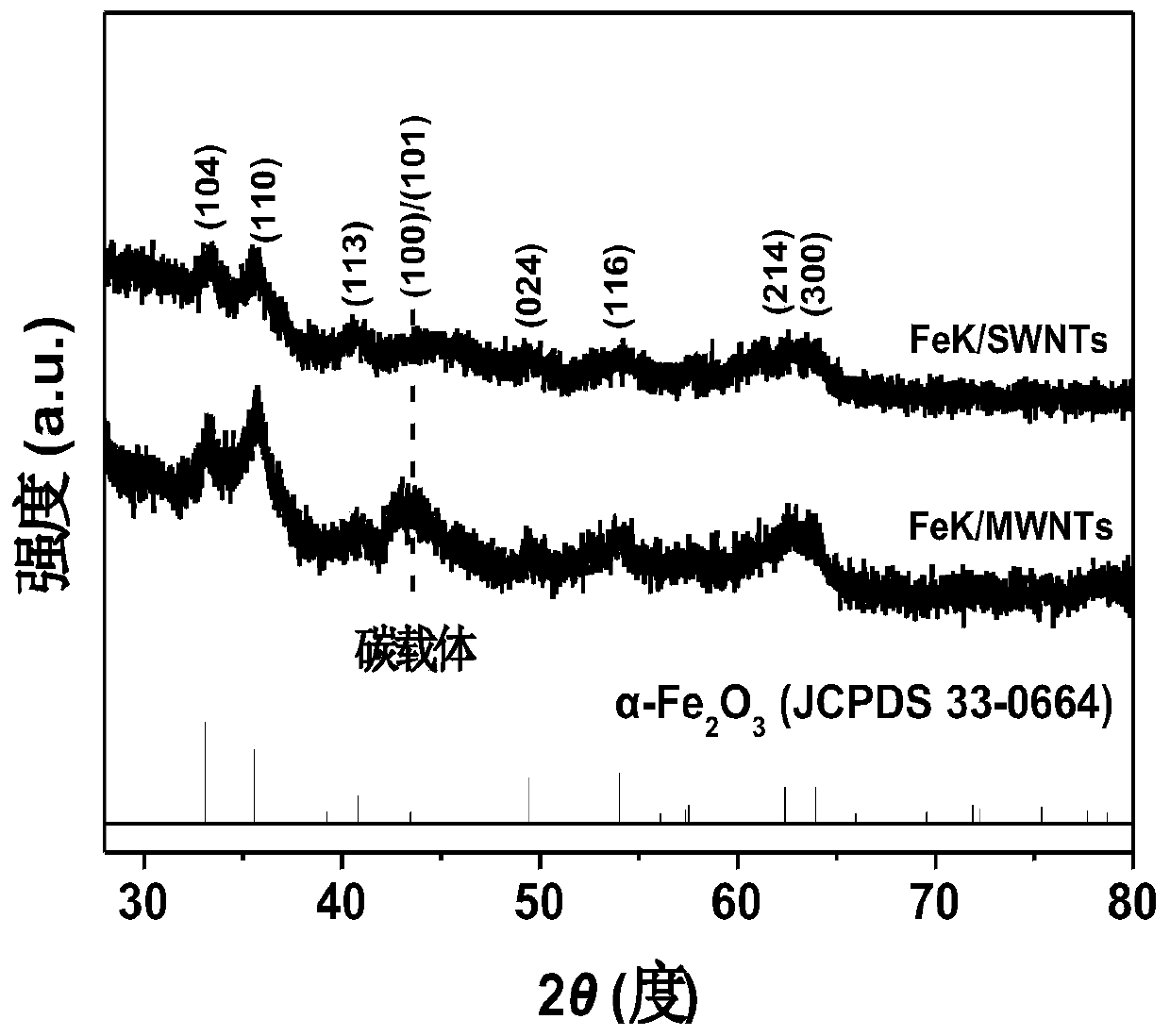
[0025] (1) Take a certain amount of single-walled carbon nanotube bundles (composed of metal-type zigzag-shaped single-walled carbon nanotubes with a diameter of 0.47 nm) and disperse them in 100 ml of deionized water, sonicate for 2.0 h, and then magnetically stir for 1.0 h; Add a certain concentration of iron salt solution dropwise to the above suspension while stirring. Continue to stir for 6.0 h after the dropwise addition, then evaporate to dryness in a 60°C water bath, then place in an oven at 110°C to dry overnight, and finally place in a tube furnace and roast at 350°C for 4 h under the protection of argon, and after cooling down to room temperature Take out the sample and grind it for later use;
[0026]The Fe / SWNTs catalyst prepared above was dispersed in 100 ml of deionized water...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Effect of Reaction Pressure on Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation to Higher Olefins
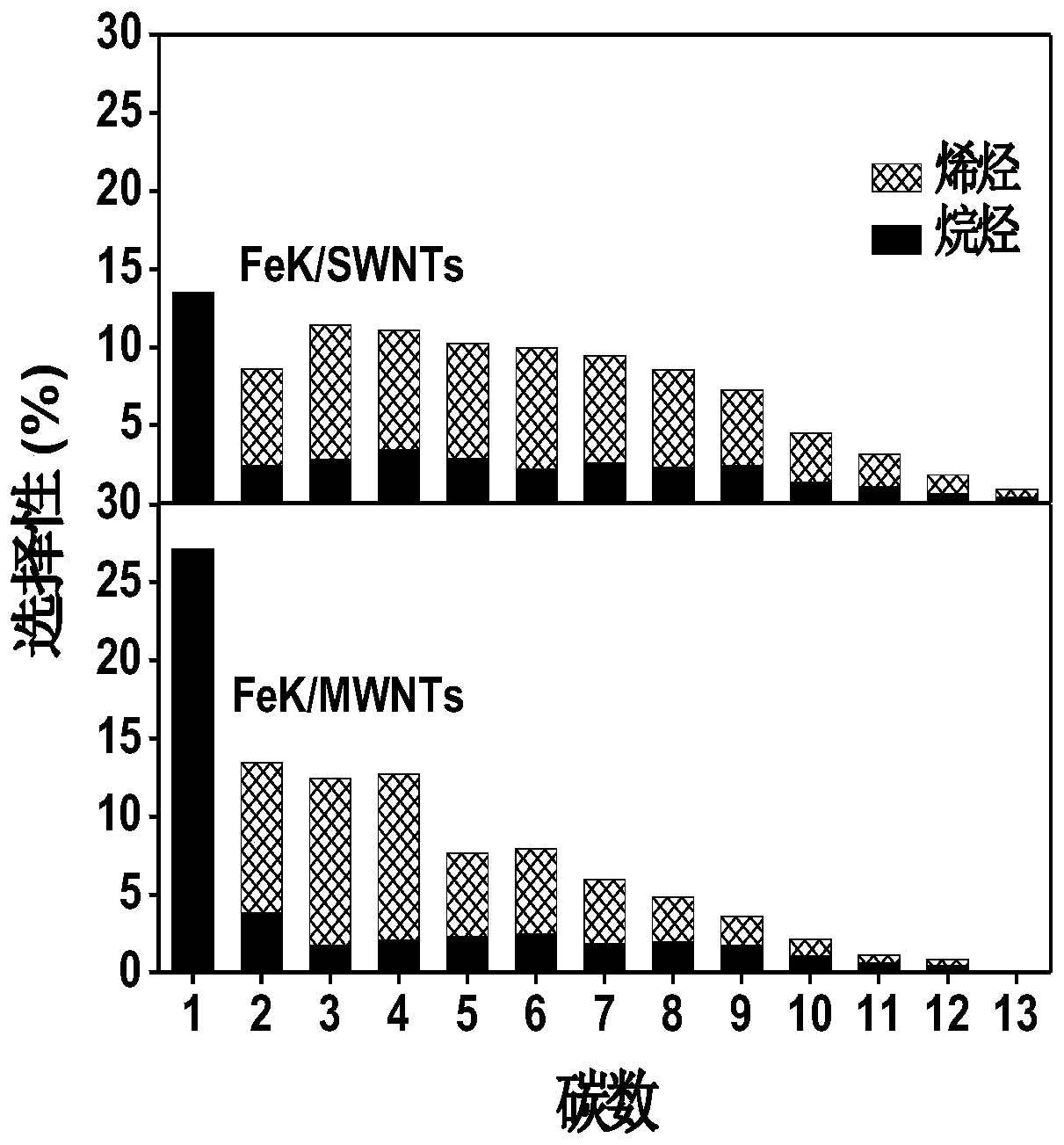
[0031] Take 0.2 g FeK3 / SWNTs catalyst and confine it in the middle of the fixed-bed reactor with quartz sand; before the activity evaluation, the catalyst was activated with carbon monoxide at 350 °C for 8 h, and then passed through H 2 / CO 2 The mixed gas of = 3 was reacted at 340°C, and the reaction pressure range was 1.0-3.0 MPa. During the reaction process, high temperature and high pressure sampling valves were used to sample at regular intervals, and the product composition was analyzed online by gas chromatography. The reaction results of this example are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that increasing the reaction pressure can effectively increase the conversion rate of raw materials and the selectivity of high-carbon olefins, and the optimal reaction pressure is 2.0 MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Effect of Reaction Temperature on Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation to Higher Olefins
[0033] Take 0.2 g FeK3 / SWNTs catalyst, and use quartz sand to confine it in the middle of the fixed-bed reactor; before activity evaluation, the catalyst was activated with carbon monoxide at 350 °C for 8 h, and then passed through H 2 / CO 2 The mixed gas of = 3 is reacted at 2.0 MPa, and the reaction temperature range is 270-380°C. During the reaction process, high temperature and high pressure sampling valves were used to sample at regular intervals, and the product composition was analyzed online by gas chromatography. The reaction results of this example are shown in Table 3. It can be seen that moderate reaction temperature can effectively improve the selectivity of higher olefins, and the optimal reaction temperature is 340°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com