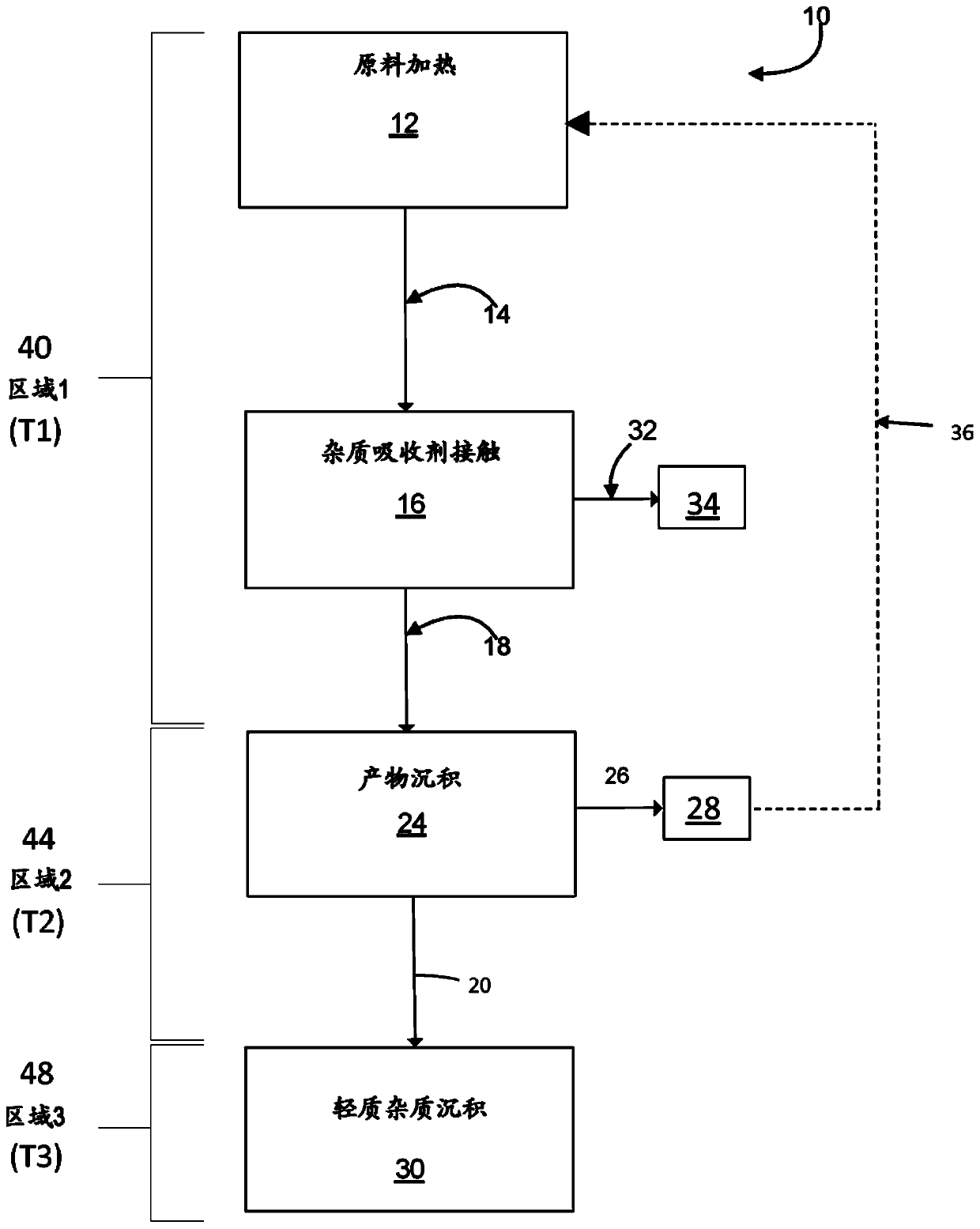
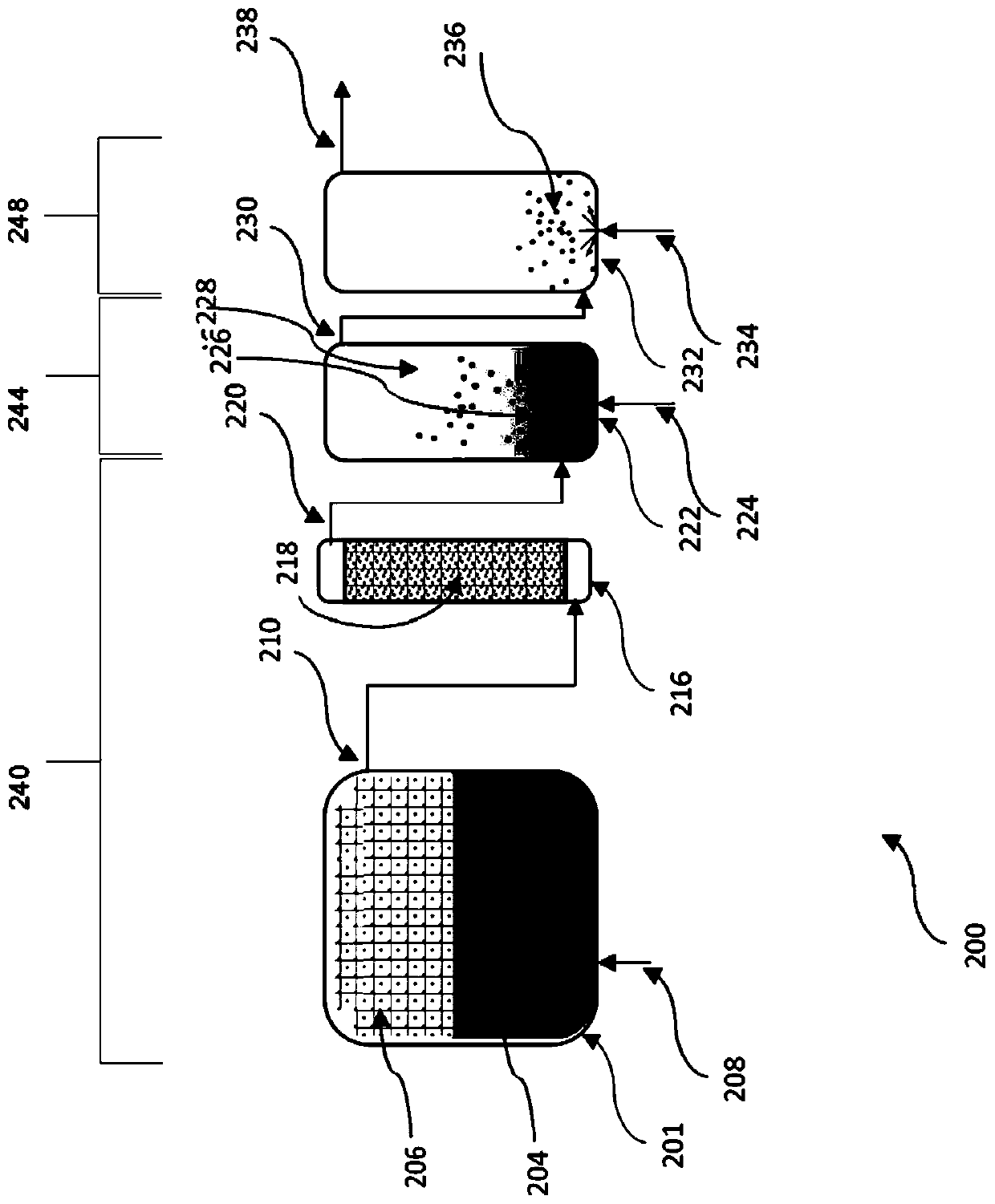
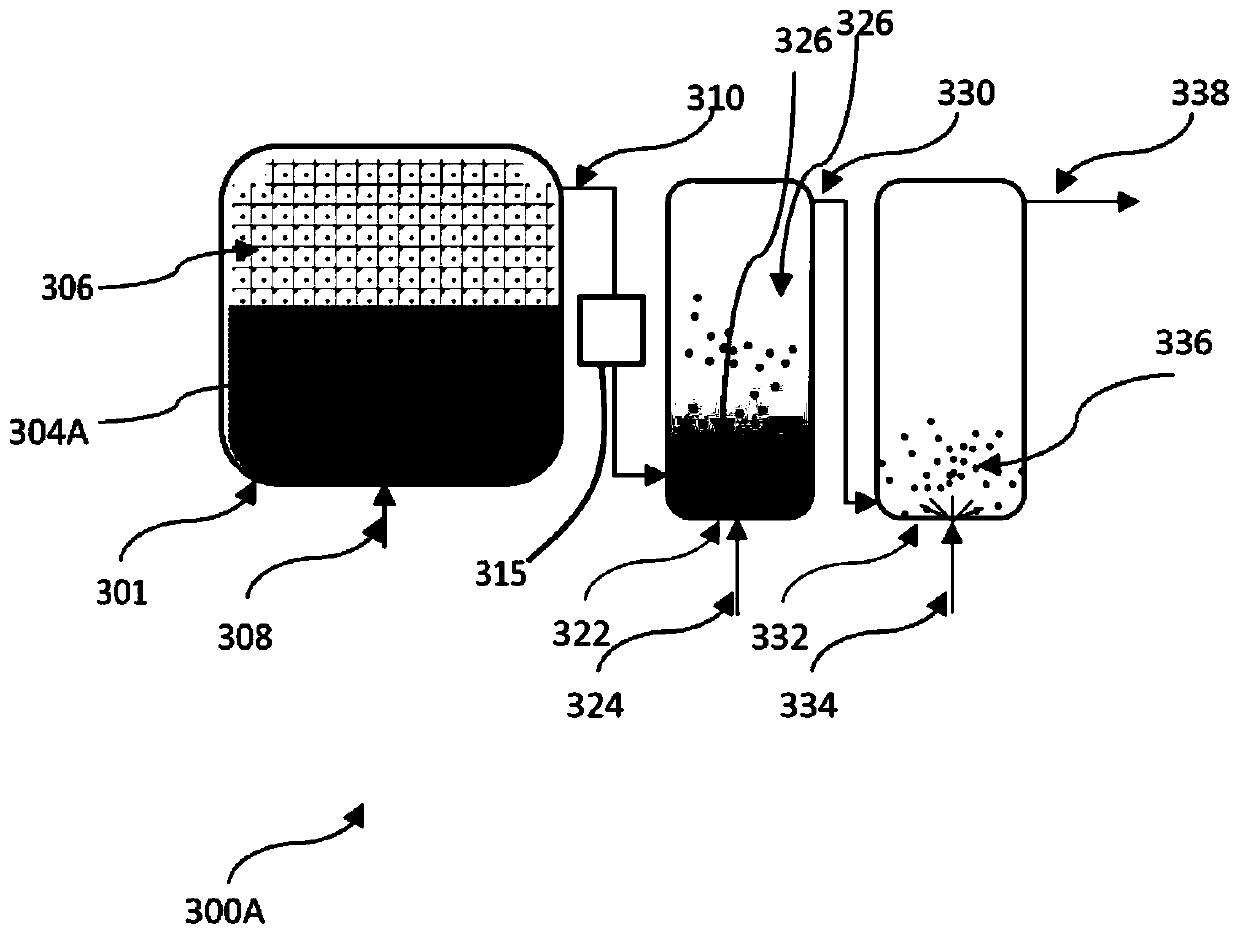
Ultra-high purity tungsten chlorides
A technology of tungsten chloride and potassium chloride, which is applied in the direction of tungsten halide, gaseous chemical plating, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of high content of tungsten and iron in the application of electronics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] Example 1: Purification of tungsten hexachloride in the presence of sodium chloride
[0127] 63.6 g of crude tungsten hexachloride was mixed with 6.3 g of pre-dried sodium chloride and charged into a glass sublimator. The sublimator was preheated to 250 degrees Celsius for two hours under nitrogen atmosphere and ambient pressure. After this step, the sublimator was cooled to 180 degrees Celsius and placed under a vacuum of 80 mTorr to collect the purified tungsten hexachloride on a cold finger cooled with a stream of room temperature nitrogen. After 2 hours of sublimation, 60 g of purified tungsten hexachloride was collected on the cold finger.
[0128] Trace metal analysis by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) showed significant reductions in iron, chromium, nickel, and copper, as shown in Table 1.
[0129] Table 1
[0130]
[0131] 55 g of purified tungsten hexachloride from the first sublimation were mixed with 5.5 g of pre-dried sodium chl...
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2: Purification of Tungsten Hexachloride in the Presence of Potassium Chloride
[0133] Crude tungsten hexachloride was mixed with various amounts of pre-dried potassium chloride to study the effect of potassium chloride loading on the purification of trace impurities of tungsten hexachloride. Both mixtures were pre-ground using a mortar and pestle to achieve better contact between tungsten hexachloride and potassium chloride. The mixture was preheated at 250 °C for 2 hours. Tungsten hexachloride was sublimed from the mixture at 180 °C for 2 hours under a vacuum of 50-80 mTorr.
[0134] Purified tungsten hexachloride was collected on a cold finger and analyzed for trace metals using ICP-MS. The dependence of trace metal removal on KCl loading is shown in Table 2.
[0135] Table 2
[0136]
[0137] Results showed that the method demonstrated high-purity tungsten hexachloride with less than 0.5 ppm iron and less than 0.1 ppm molybdenum. Higher potassium ...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of high-purity tungsten pentachloride
[0139] High-purity tungsten hexachloride containing less than 0.5 ppm of iron and molybdenum impurities is loaded into a glass boiler vessel and heated to 290 degrees Celsius. 1 standard liter per minute (SLPM) of purge gas containing 5 vol% hydrogen was supplied to the vessel to bring vapor into the tubular reactor heated to 400 degrees Celsius. The flow rate and vapor retention time were maintained to complete the conversion of tungsten hexachloride to tungsten pentachloride. High-purity tungsten pentachloride is collected from the cooled condenser. The amount of iron and molybdenum impurities in the purified tungsten pentachloride was measured to be less than 0.5 ppm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com