Method for treating eutrophic seawater by compounding bacteria and chitosan
A technology of eutrophication and composite treatment, applied in chemical instruments and methods, seawater treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of polyelectrolyte charge density increase, water quality eutrophication treatment, eutrophication seawater treatment efficiency is low, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of suitable promotion and reduction of water pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
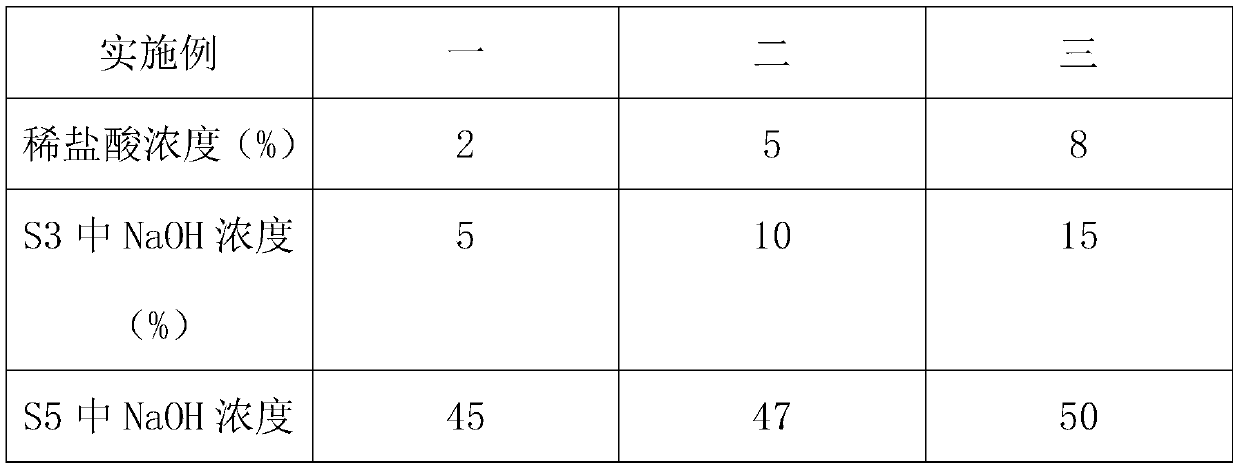
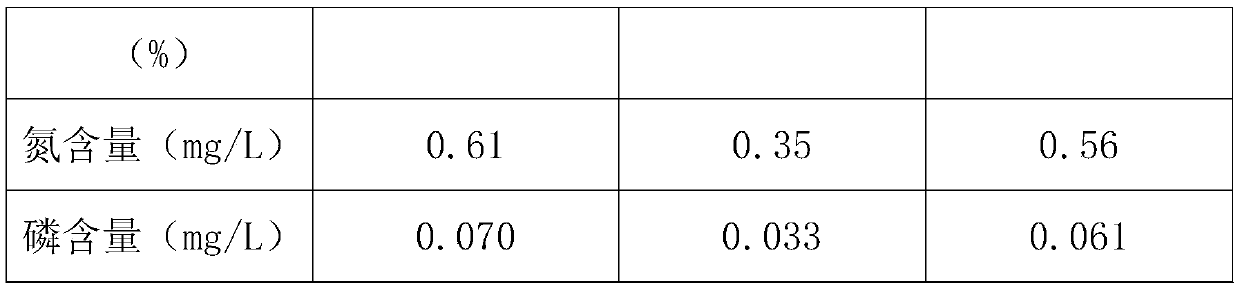
[0021] A method for compounding eutrophic seawater with fungus chitosan, comprising the following steps:
[0022] S1. Inoculate Bacillus subtilis, Streptomyces jingyang, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Rhodopseudomonas palustris into the culture medium according to a certain ratio to carry out compound bacteria culture, and regularly detect the activity of the compound bacteria, Select compound colonies with strong activity;
[0023] S2. Wash the shrimp shells used for preparing chitosan with clear water, and dry them, then soak the raw materials in dilute hydrochloric acid solution for 1 hour, then filter and wash with water until neutral;
[0024] S3. Boil the shrimp shells treated in S2 in sodium hydroxide solution for 1 hour, continue to filter, wash until neutral, and dry them;
[0025] S4, using potassium permanganate and sodium bisulfite to carry out chlorination and decolorization treatment on the dried shrimp shells;
[0026] S5. The decoloriz...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for compounding eutrophic seawater with fungus chitosan, comprising the following steps:
[0031] S1. Inoculate Bacillus subtilis, Streptomyces jingyang, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Rhodopseudomonas palustris into the culture medium according to a certain ratio to carry out compound bacteria culture, and regularly detect the activity of the compound bacteria, Select compound colonies with strong activity;
[0032] S2. Wash the shrimp shells used for preparing chitosan with clear water, and dry them, then soak the raw materials in dilute hydrochloric acid solution for 2 hours, then filter and wash with water until neutral;
[0033] S3. Boil the shrimp shells treated in S2 in sodium hydroxide solution for 2 hours, continue to filter and wash until neutral, and dry them;
[0034] S4, using potassium permanganate and sodium bisulfite to carry out chlorination and decolorization treatment on the dried shrimp shells;
[0035] S5. The deco...
Embodiment 3
[0039] A method for compounding eutrophic seawater with fungus chitosan, comprising the following steps:
[0040] S1. Inoculate Bacillus subtilis, Streptomyces jingyang, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Rhodopseudomonas palustris into the culture medium according to a certain ratio to carry out compound bacteria culture, and regularly detect the activity of the compound bacteria, Select compound colonies with strong activity;
[0041] S2. Wash the shrimp shells used for preparing chitosan with clear water, and dry them, then soak the raw materials in dilute hydrochloric acid solution for 3 hours, then filter and wash with water until neutral;
[0042] S3. Boil the shrimp shells treated in S2 in sodium hydroxide solution for 3 hours, continue to filter and wash until neutral, and dry them;
[0043] S4, using potassium permanganate and sodium bisulfite to carry out chlorination and decolorization treatment on the dried shrimp shells;
[0044] S5. The deco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com