Method for preparing plutella xylostella RDL subunit knockout strain and application of method
A Plutella xylostella, gene knockout technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as inability to inherit offspring, inability to completely suppress genes, and no research on resistance of Plutella xylostella, so as to monitor drug resistance, improve accuracy, and guide rational use of drugs in the field Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Selection of target sites
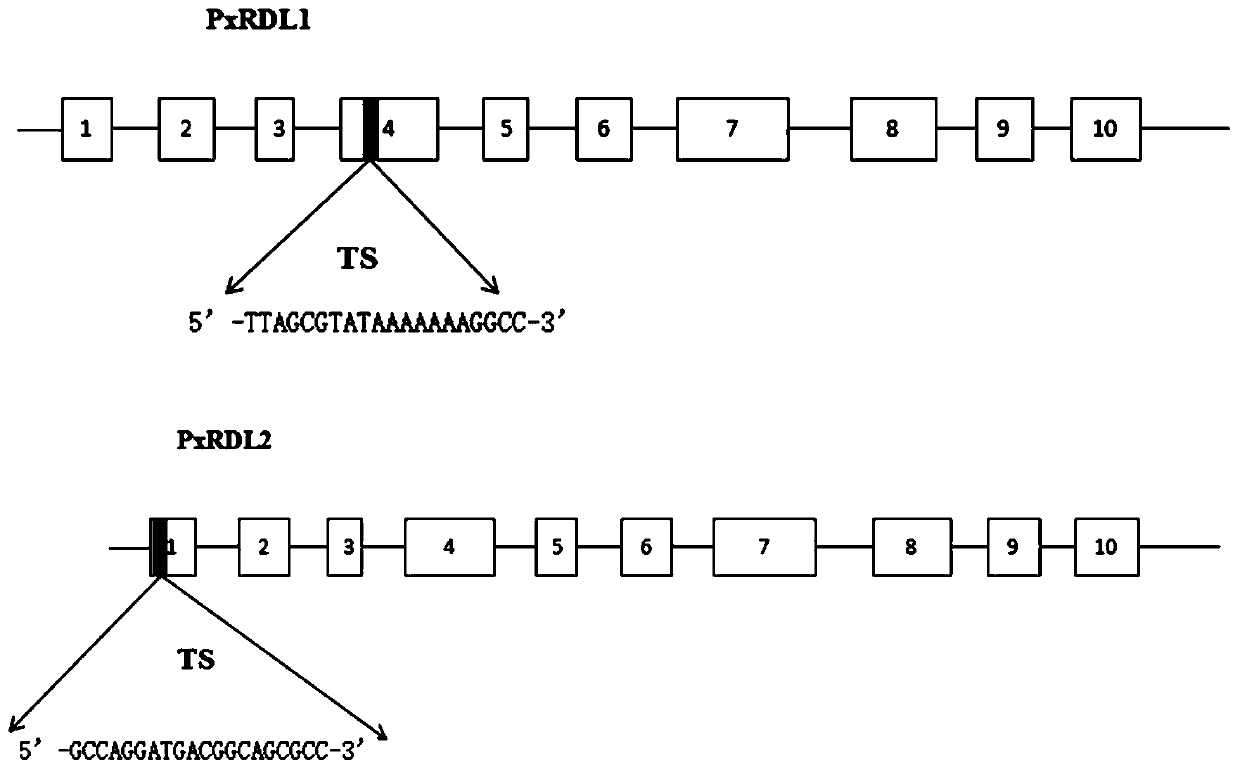
[0037] The cDNA and gDNA sequences of Plutella xylostella RDL1 were downloaded from NCBI to determine the distribution of exons. Search for possible target sites through the online website http: / / www.rgenome.net / , and design the target site sequence PxRDL1-sg of the RDL1 gene: 5'-TTAGCGTATAAAAAAAAGGCC-3'(N20; Seq ID NO: 1), located at The fourth exon of the RDL1 gene; the target sequence of the RDL2 gene, PxRDL2-sg: 5'-GCCAGGATGACGGCAGCGCC-3' (N20; Seq ID NO: 2), is located at the first exon of the RDL2 gene. Plutella xylostella RDL subunit gene structure and knockout target see figure 1 .
[0038] (2) Synthesis of sgRNA
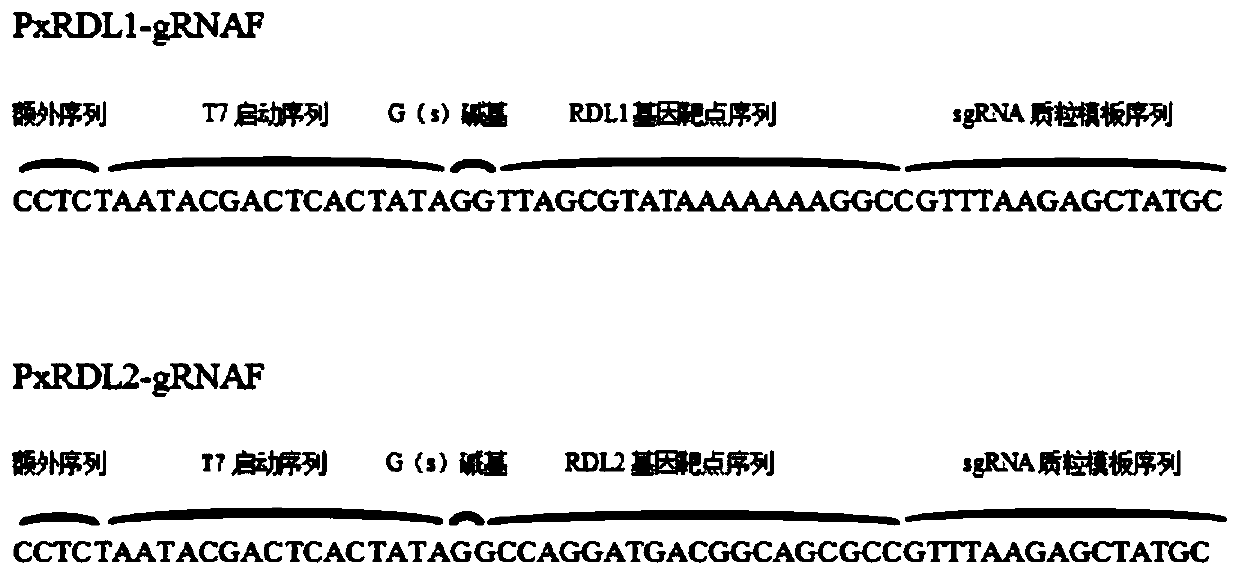
[0039] 1) Refer to Guide-it TM sgRNA In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual kit (Takara Bio USA, Inc.) Instructions designed sgRNA template amplification primers PxRDL1-gRNAF (SEQ ID NO: 3), PxRDL2-gRNAF (SEQ ID NO: 4). For the structure of operable elements of sgRNA template amplification primer...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2 Plutella xylostella RDL knockout strain construction
[0065] (1) Collect normally eclosion wild-type diamondback moth, put the egg card stained with vegetable juice into the mating box to attract diamondback moth to lay eggs, collect once within 15 minutes, transfer the collected egg card to a clean glass slide for later use .
[0066] (2) The sgRNAs of RDL1 and RDL2 prepared in Example 1 were mixed with Cas9 protein (Cas9-N-NLSNuclease, GenCrispr, Z03388, China), and the mixed system was: 5uL sgRNA (300ng / uL), 3uL Cas9 protein (1ug / uL) uL), 2uL RNase free water, sgRNA and Cas9 protein are mixed in a mass ratio of 1:2. Incubate at 37°C for 15 minutes. 3uL of the incubated mixture was poured into the drawn capillary needle with the tip of a long gun, and injected after opening under the microscope using the parts of the injection instrument. Place the injected egg cards in a box with suitable feed and wait for hatching. The hatch rate was 11% after RDL1 in...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3 Indoor Toxicity Test of Plutella xylostella RDL Subunit Knockout Strain
[0074] Indoor virulence determination of the two mutants and wild-type diamondback moth obtained in Example 2 using fipronil by leaf dipping method (https: / / www.irac-online.org / methods / plutella-xylostella-larvae / ) In the test, the drug concentration was designed between 0.01 mg / L-6 mg / L according to the LC50 of the two drugs against the wild-type diamondback moth. The result is as Figure 6 It was shown that the LC50 of the RDL1 (RDL1KO) knockout strain was 2.29, the RDL2 (RDL2KO) knockout strain LC50 was 0.05, and the wild-type (WT) LC50 was 0.22. Compared with the wild type, after RDL1 knockout, the resistance of diamondback moth to fipronil was increased by 10 times; after RDL2 knockout, the sensitivity of diamondback moth to fipronil was increased by 4 times. It is concluded that in the normal wild-type Plutella xylostella, the RDL1 subunit performs the main function of GABA recept...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com