Prussian blue positive electrode material, sodium ion battery and preparation method and application thereof
A sodium-ion battery and cathode material technology, applied in the direction of positive electrodes, battery electrodes, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as poor cycle performance, imperfect crystal structure, and low capacity of sodium-ion batteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
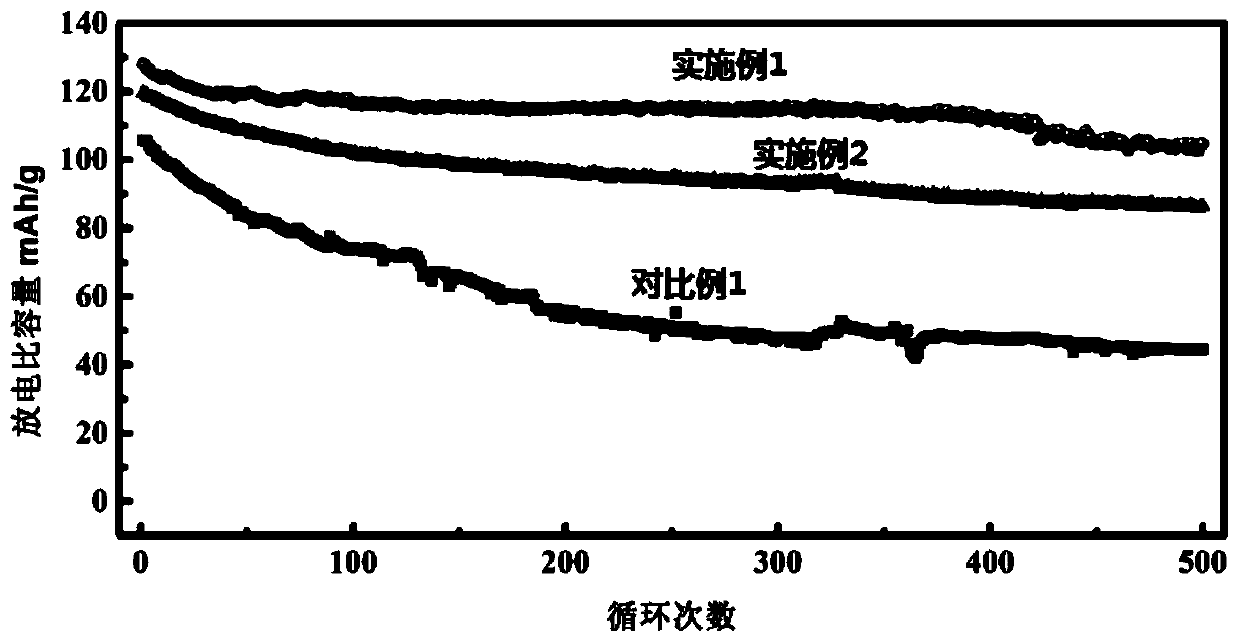
Embodiment 1
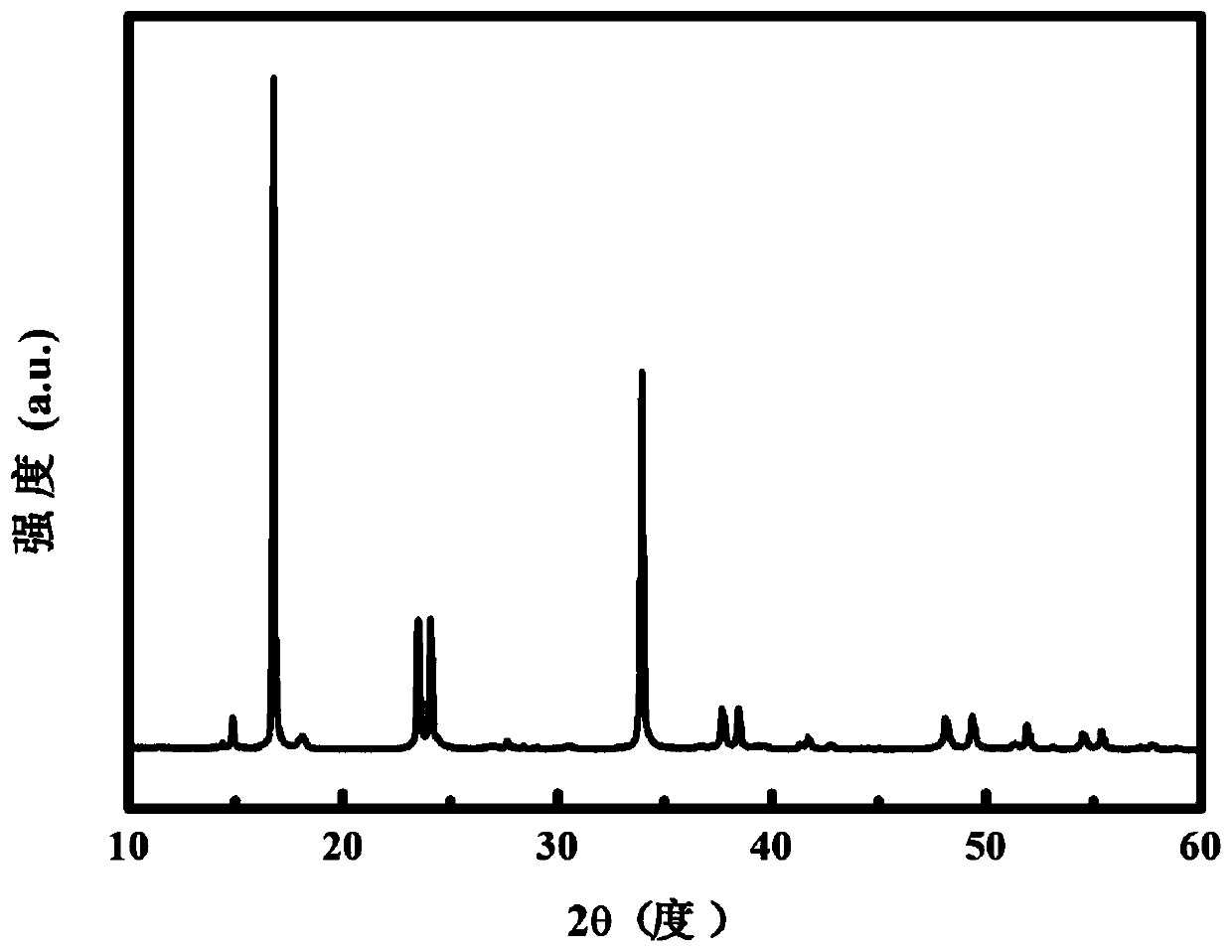
[0046] Preparation of Prussian blue positive electrode material sodium ferrocyanide manganese:
[0047] (1) Weigh 0.01 mol of disodium manganese edetate and sodium ferrocyanide and dissolve them in 200mL of deionized water to prepare solution A, wherein disodium manganese edetate and ferrocyanide The concentration of sodium is 0.05mol / L;
[0048] (2) Weigh 0.02mol ascorbic acid, dissolve it in 100mL deionized water, and prepare solution B, wherein the concentration of ascorbic acid is 0.2mol / L;
[0049] (3) Place solution A on a magnetic stirrer and stir, and use a peristaltic pump to add solution B dropwise to solution A stirred at high speed. During the dropping process, white precipitates are formed, and the dropping time is about 3.5 hours. mixture;
[0050] (4) Continue to stir the mixed solution at room temperature for 0.5h and then let it stand for 6h;
[0051] (5) Centrifuge the mixed solution after standing to obtain a white precipitate, and dry the white precipita...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Preparation of Prussian blue positive electrode material sodium ferrocyanide manganese:
[0054] Step (2) Weigh 0.05 mol of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, dissolve it in 100 mL of deionized water, and prepare solution B, wherein the concentration of sodium dihydrogen phosphate is 0.5 mol / L. The rest of the steps were the same as in Example 1 to obtain sodium manganese ferrocyanide, a positive electrode material of Prussian blue type. The content of each element was measured by inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer (ICP-AES), and its molecular formula was calculated as Na 1.88 Mn[Fe(CN) 6 ] 0.97 1.3H 2 O.
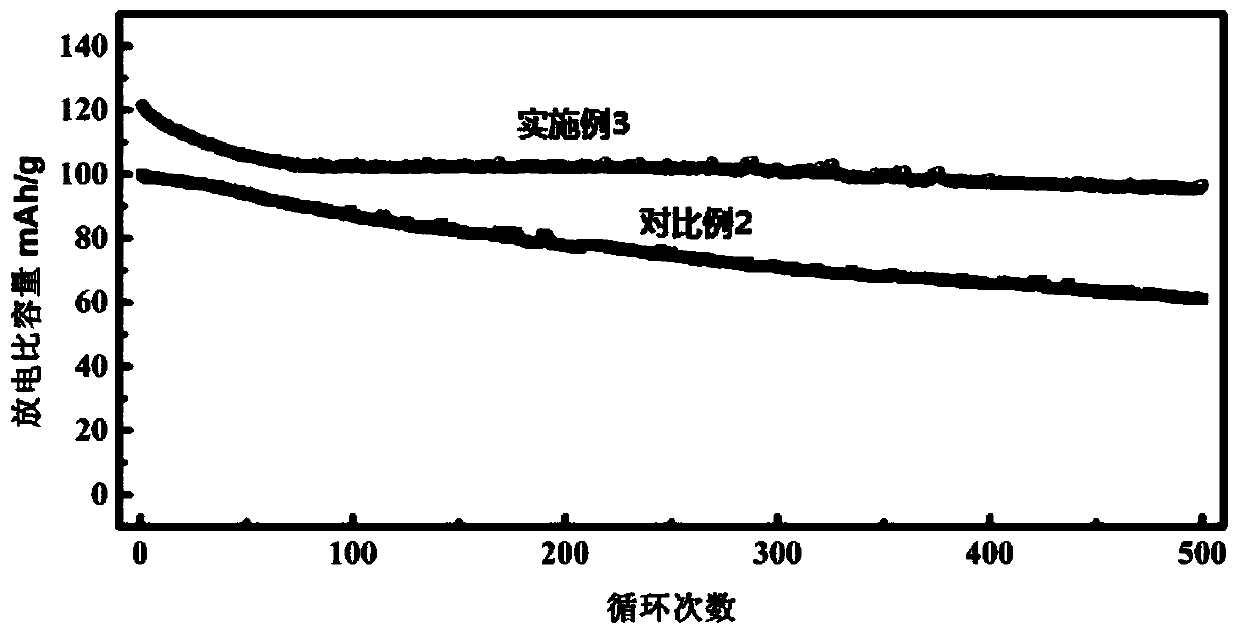
Embodiment 3
[0056] Preparation of Prussian blue positive electrode material cobalt ferrocyanide sodium:
[0057] The disodium manganese EDTA in Example 1 was replaced with disodium cobalt EDTA, and the rest of the steps were the same as in Example 1 to obtain the Prussian blue positive electrode material sodium manganese ferrocyanide. The content of each element was measured by inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer (ICP-AES), and its molecular formula was calculated as Na 1.88 Co[Fe(CN) 6 ] 0.97 1.1H 2 O.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Discharge specific capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com