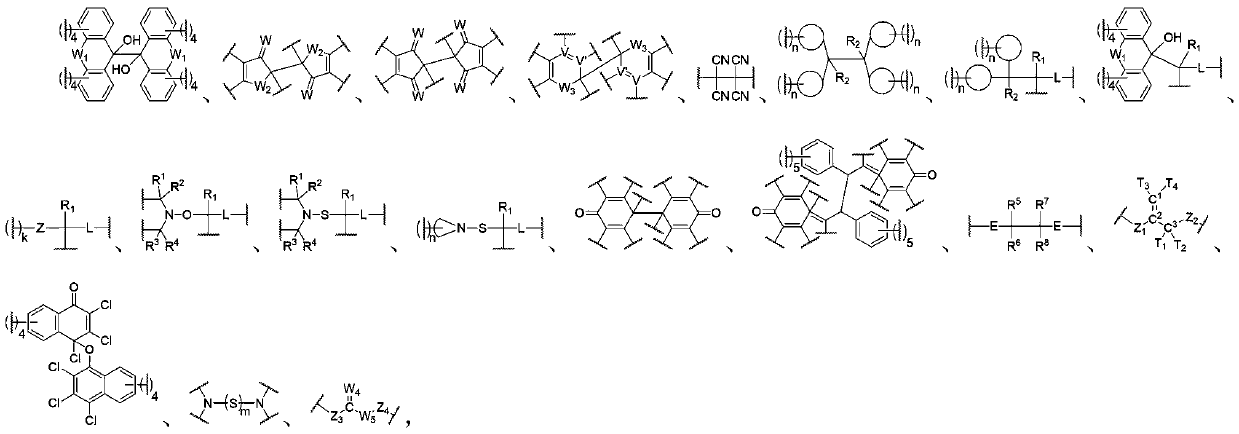
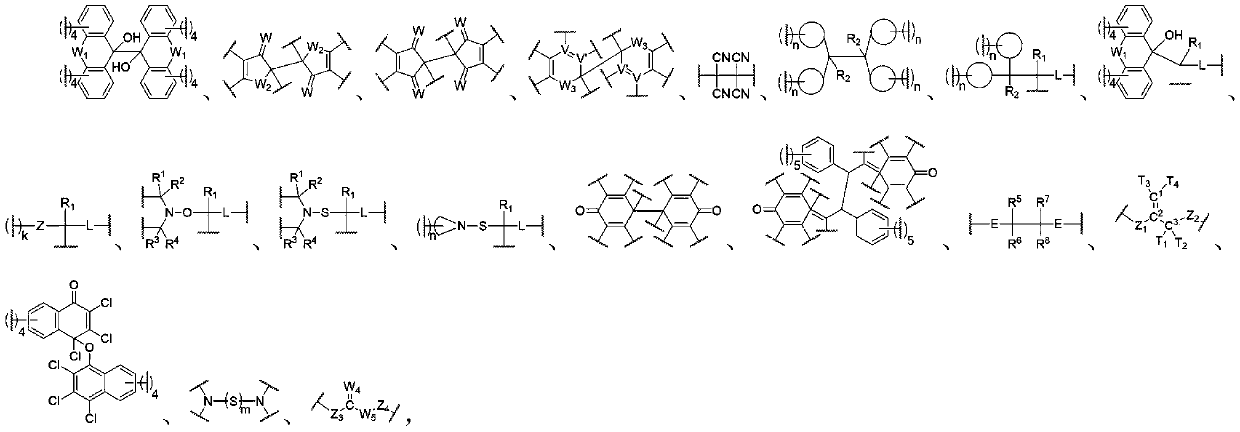
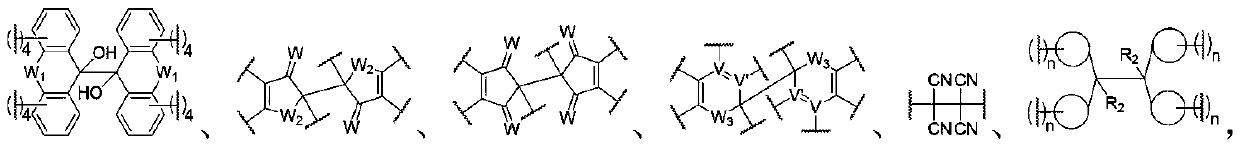
Force-induced responsive polymer based on reversible free radical type force-sensitive group
A free radical, responsive technology, applied in the field of force-responsive polymers, which can solve the problems of activating force-sensitive groups, limiting the scope of application, prone to aggregation and migration, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0350]
[0351] Take 60 molar equivalents of methyl methacrylate, 0.1 molar equivalents of methyl 2-bromopropionate, and 1 molar equivalent of pentamethyldiethylenetriamine, dissolve them in an appropriate amount of tetrahydrofuran, blow nitrogen into it to remove oxygen for 30 minutes, and then add 1 molar equivalent of cuprous bromide, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 48 hours under an argon atmosphere, after the reaction was completed, purified to obtain bromine mono-capped polymethyl methacrylate PMMA-Br; then take 10 molar equivalents of PMMA-Br, 5 moles The equivalent compound (a) and 15 molar equivalents of sodium hydroxide are placed in a reaction vessel, an appropriate amount of tetrahydrofuran solvent is added, and the reaction is stirred at room temperature for 24 hours. After the reaction is completed, a linear polymer is purified; then a certain amount of purified polymer is obtained. , dissolved in an appropriate amount of furan to obtain a polymer solution with...
Embodiment 2
[0353]
[0354] Take 65 molar equivalents of styrene, 0.8 molar equivalents of 2-cyano-2-propyl dodecyl trithiocarbonate, and 0.35 molar equivalents of azobisisobutyronitrile, place them in a reaction vessel, and use an appropriate amount of dioxane The ring was dissolved, and stirred and reacted at 65°C for 24h under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain polystyrene; then dissolved in DMF containing a small amount of water, stirred and reacted at 100°C for 20h to obtain mercapto-terminated polystyrene (a ); then take 2 molar equivalents of mercapto-terminated polystyrene (a), 1 molar equivalent of compound (b), and 2 molar equivalents of triethylamine, place them in a reaction vessel, dissolve them with an appropriate amount of tetrahydrofuran, stir and react for 3 hours, and finish the reaction , after purification and drying, a powdery solid can be obtained. Scratch or grind the resulting polymer powder vigorously, and its color will change from white to orange-red. The mecha...
Embodiment 3
[0356]
[0357] Take 0.9 molar equivalent of compound (a) and 1 molar equivalent of polytetrahydrofuran diol, place them in a reaction vessel, add an appropriate amount of dichloromethane solvent, and after the raw materials are dissolved, add 5 molar equivalents of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 1 molar equivalent 4-Dimethylaminopyridine, then stirred and reacted at room temperature for 24 hours, then added 0.25 molar equivalent of n-butyric acid, continued the reaction for 12 hours, and then removed the solvent to obtain a colloidal polymer. In this embodiment, the colloidal polymer can be stretched and stretched in a wide range, and it will turn orange during the stress deformation process, and the greater the stretch deformation, the darker the color. After the polymer sample is cut and placed in the mold, the sample can be repaired by pressing for a period of time by applying pressure; in addition, the sample can also be repaired by heating to 80°C or irradiating with ultrav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com