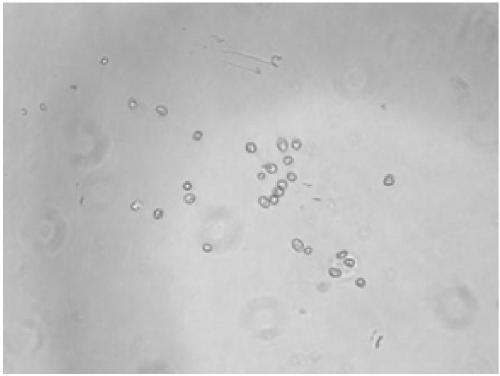
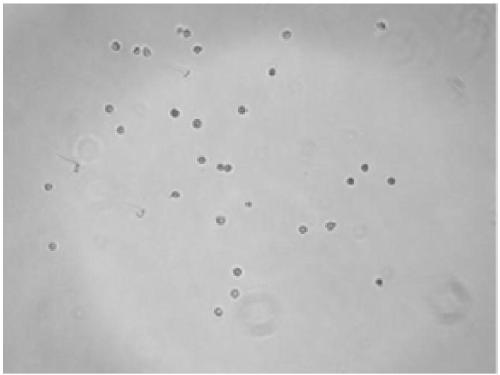
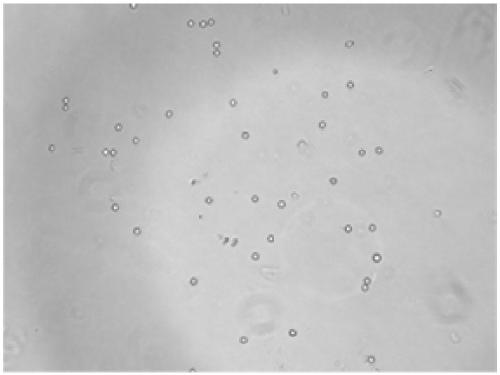
Amphibian cell dissociation kit
An amphibian and kit technology, applied in the field of amphibian cell dissociation kits, can solve problems such as unfavorable research, uncontrollable enzyme activity, cell apoptosis and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0067] Preparation method of 1000×gentamycin solution: 350 mg of gentamicin sulfate (BBI, A620217-5G, powder) was dissolved in water and the volume was adjusted to 10 ml with water.
[0068] DPBS is Duchenne's phosphate buffer solution, which differs from commonly used standard PBS in that it does not contain calcium and magnesium ions.
Embodiment 1
[0069] Embodiment 1, the preparation of kit
[0070] The kit consists of the following components: Reagent A, Reagent B, Reagent C, Reagent D, Reagent E and Reagent F.
[0071] Reagent A is a cleaning reagent. The preparation method of reagent A: take each raw material according to Table 2, fully dissolve and mix well, then filter with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and collect the filtrate, which is reagent A.
[0072] Table 2 (total volume 125ml)
[0073] raw material Dosage DPBS 100ml 1000×gentamicin 0.125ml 100× penicillin streptomycin 1.25ml Enzyme-free water 23.625ml
[0074] Reagent B is a pretreatment reagent. The preparation method of reagent B: EDTA-Na 2 -2H 2 Add O to reagent A, heat to dissolve, then adjust the pH value to 7.0 with sodium hydroxide, and then use reagent A to make up to 100ml, which is reagent B. In reagent B, the concentration of EDTA is 0.1g / 100ml.
[0075] Reagent C is enzyme lysate. Preparation method ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2, the usage method of kit
[0080] 1. Take a sample (an organ or tissue of an amphibian, such as one of the limbs), wash it in 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, and then wash it three times in reagent A (3 minutes each time) to fully remove the attachments on the tissue surface.
[0081] 2. Take the tissue that completed step 1, place it in reagent B, soak at room temperature for 10-15 minutes, and then separate the skin tissue.
[0082] 3. Take the skin tissue obtained in step 2, cut it into pieces, put it in reagent C, soak it at room temperature for 1-3 hours, then add 2 times the volume of α-MEM medium containing 10% serum to stop the digestion, and then filter it with 70 μm cells Net filter and collect the filtrate, centrifuge the filtrate at 1000rpm for 5min, collect the cell pellet, and resuspend with α-MEM medium containing 10% serum.
[0083] 4. After completing step 2, peel off the muscle tissue from the remaining tissue, cut it into pieces, put it in r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com