Method for improving resistance of formic acid and acetic acid in cellulose hydrolysate by utilizing formic acid dehydrogenase
A cellulose hydrolyzate and formate dehydrogenase technology, which is applied in the field of bioengineering to achieve the effects of cost saving, improving resistance and improving formate dehydrogenase activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: Construction of bacterial strain S.cerevisiae-FDH
[0024] 1) Using the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae model strain S288C as a template for PCR amplification to obtain the Fdh gene fragment, the nucleotide sequences of the upstream and downstream primers are shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 respectively:
[0025] Upstream primer: attg cggccgct atgtcgaagggaaaggttttg (SEQ ID NO. 1)
[0026] Downstream primer: acgcgc gtcgac ttatttcttctgtccataag (SEQ ID NO.2)
[0027] The kit used for PCR amplification is HS DNA Polymerase (Code No.: R010A) was purchased from Treasure Bioengineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd., and the PCR reaction was carried out according to the instructions of the kit.
[0028] The PCR amplification conditions are: 98°C pre-denaturation for 5 minutes; 98°C for 15s, 55°C for 15s, 72°C for 60s, 30 cycles; 72°C for 7min;
[0029] 2) The obtained Fdh gene fragment was double-digested with restriction endonucleases Not I and Sal I, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: adopt two-step method to ferment cellulose raw material to produce xylitol and ethanol, the investigation of the growth situation on the plate containing formic acid and acetic acid
[0035] 1) Preparation of activation medium: activation medium: YNB 6.7g / L, glucose 10g / L, amino acid supplement solution without Trp.
[0036] 2) Activation of the strains: the strain S. cerevisiae-FDH prepared in Example 1 and the original strain S. cerevisiae S288C stored in the refrigerator were inoculated into the activation medium, placed in a shaker at 30° C., and cultured at 150 rpm for 24 hours.
[0037] 3) Preparation of seed medium: seed medium: YNB 6.7g / L, glucose 20g / L, amino acid supplement solution without Trp.
[0038] 4) The activated bacteria in step 2) were transferred to the seed medium prepared in step 3), and placed in a shaker at 30° C., 150 rpm for 24 hours.
[0039] 5) Preparation of differential medium: differential medium: YNB 6.7g / L, glucose 20g / L,...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Fermentation in liquid medium containing acetic acid
[0043] 1) Activation medium: YNB 6.7g / L, glucose 10g / L, amino acid supplement solution without Trp.
[0044] 2) The strain S.cerevisiae-FDH prepared in Example 1 and the original strain stored in the refrigerator were inoculated into the activation medium, placed in a shaker at 30° C., and cultured at 150 rpm for 24 hours.
[0045] 3) Preparation of seed medium: seed medium: YNB 6.7g / L, glucose 20g / L, amino acid supplement solution without Trp.
[0046] 4) Take the activated bacteria and transfer them to the seed medium prepared in step 3), place them in a shaker at 30° C., and cultivate them at 150 rpm for 24h-48h.
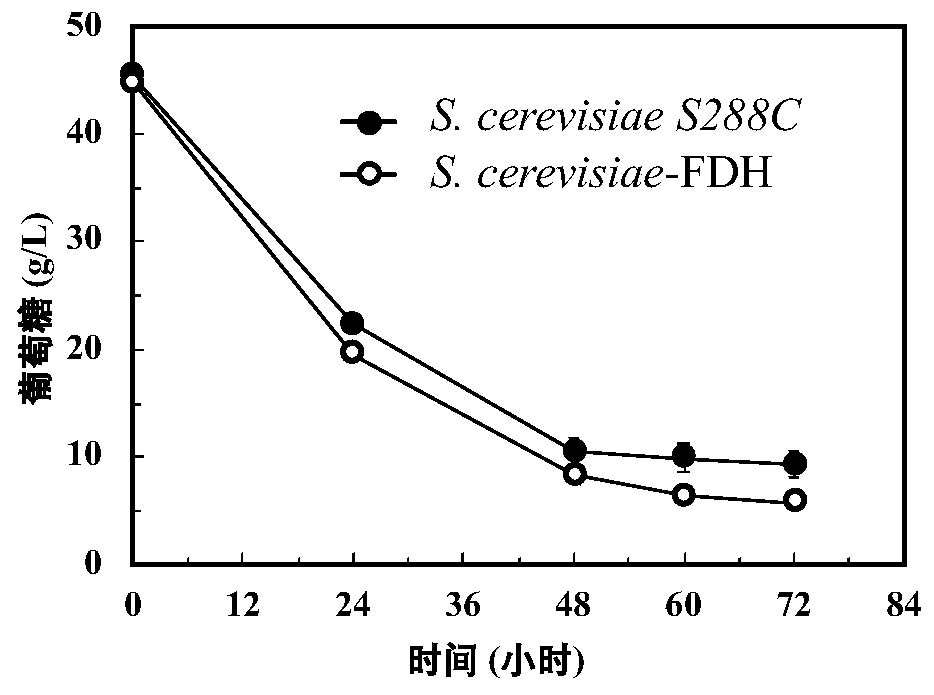
[0047] 5) Preparation of fermentation medium: fermentation medium: YNB 6.7g / L, glucose 40g / L, Trp-free amino acid supplement solution, acetic acid 4g / L.
[0048] 6) After the strains are activated and the seeds are expanded and cultivated, the cells are collected by centrifugation, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com