Application of F01 polysaccharide for resisting viruses
An anti-virus effect and anti-virus technology, applied in the field of anti-plant virus pesticides and pesticides, can solve the problems of difficult prevention and control of plant virus diseases, no anti-plant virus agents, and no cell structure of plant viruses. The effect of residual drug resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
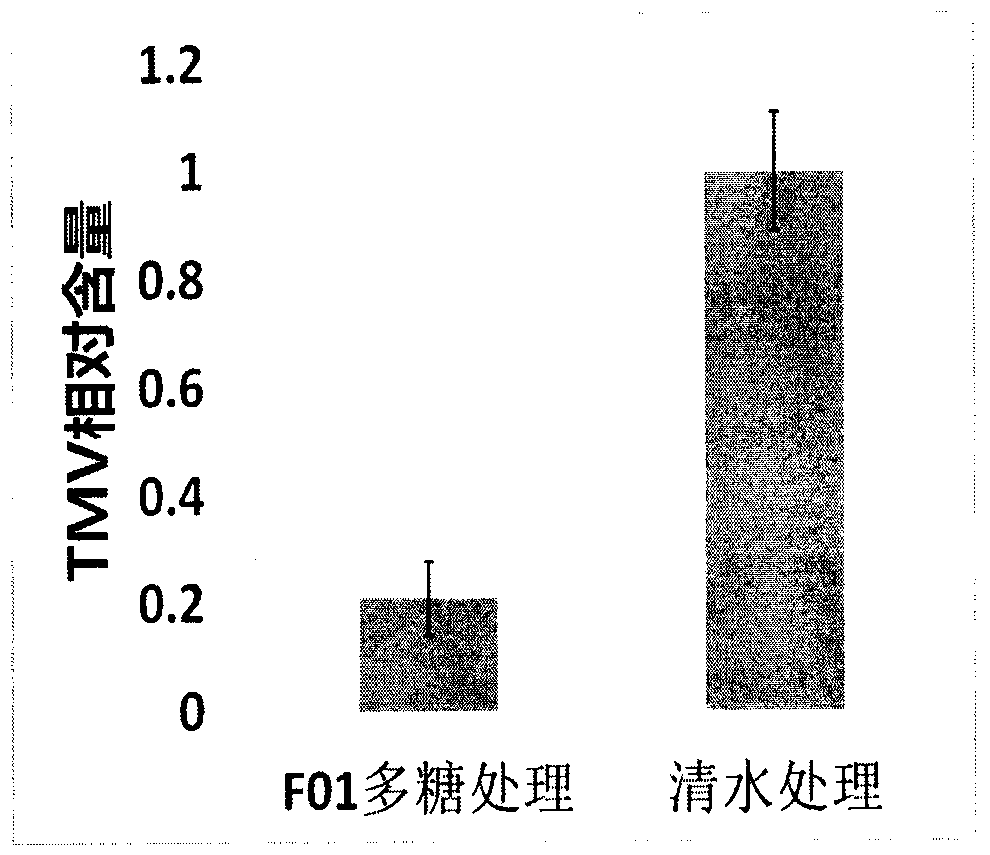
[0011] Example 1: Indoor therapeutic effect of F01 polysaccharide on TMV virus.
[0012] (1) Experimental conditions: indoor potted tobacco was selected as the crop, and the variety was Nicotiana cordata; the target was TMV.
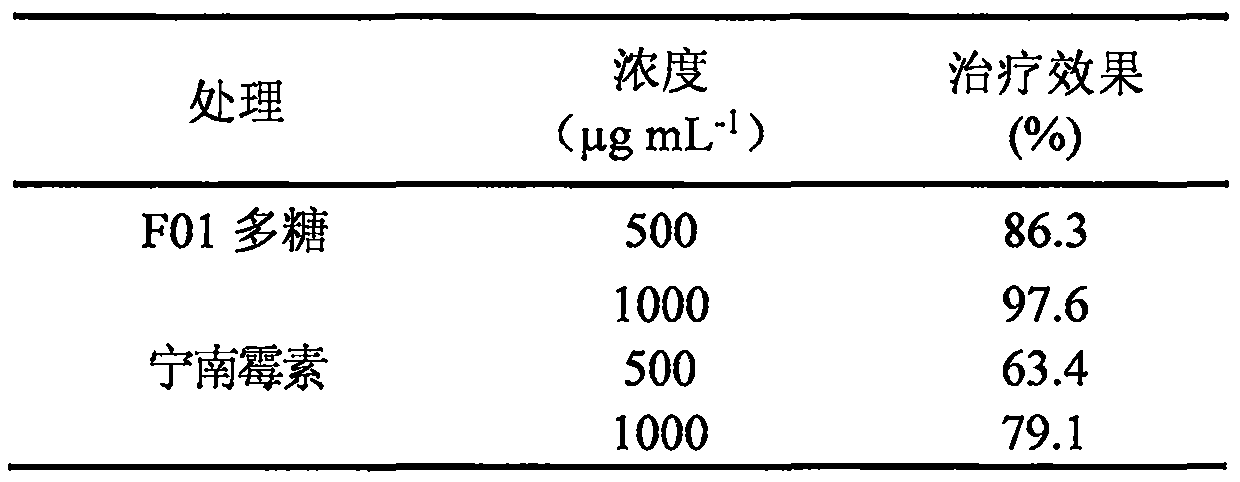
[0013] (2) Experimental design and arrangement: the test agent is F01 polysaccharide, and 8% Ningnanmycin water preparation control agent and clear water control are set up. 3 treatments, repeated 3 times.
[0014] (3) Application method: Tobacco heart leaf grows to the 5-6 leaf stage and is used for the test. Using the half-leaf dead spot method, the entire leaf was first inoculated with TMV virus, and 2 hours after inoculation, the left half of the leaf was smeared with F01 polysaccharide or the control agent, and the right half of the leaf was smeared with water as a control.
[0015] (4) Investigation method: 5 days after applying the agent, count the number of dead spots on the left and right half leaves, and calculate the control effect according...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2: Field control effect of F01 polysaccharide on tobacco mosaic virus disease.
[0021] (1) Experimental conditions: field tobacco was selected as the crop, and the variety was K326; the target was TMV.
[0022] (2) Experimental design and arrangement: the test agent is F01 polysaccharide, and 8% Ningnanmycin water preparation control agent and clear water control are set up. 3 treatments, repeated 3 times, a total of 9 plots. The experimental plots were arranged in random blocks.
[0023] (3) Application method: Spray the pesticide 20 days after transplanting the tobacco, and spray the pesticide for the second time after every 7 days.
[0024] (4) Investigation method: Conduct drug efficacy investigation 14 days after the second application of the drug, and record the incidence according to the following standards:
[0025] Grade 0: The whole plant is disease-free; Grade 1: The new leaves show slight mosaic; Grade 2: One-third to one-half of the leaves show ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Field control effect of F01 polysaccharide on wheat yellow dwarf virus disease.
[0032] (1) Experimental conditions: the crop is field wheat, the variety is Xiaoyan 6; the target is BYDV.
[0033] (2) Experimental design and arrangement: the test agent is F01 polysaccharide, and 8% Ningnanmycin water preparation control agent and clear water control are set up. 3 treatments, repeated 3 times, a total of 9 plots. The experimental plots were arranged in random blocks.
[0034] (3) Application method: Spray the pesticide 20 days after the wheat turns green, and spray the pesticide for the second time after every 7 days.
[0035] (4) Investigation method: 14 days after the second spraying, the drug efficacy investigation was carried out. 10 connected wheat plants were investigated at each point, and 250 wheat plants were investigated in each plot. The incidence was recorded according to the following standards:
[0036] Grade 0: No disease in the whole plant;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com