Composite bacterial agent, preparation method thereof and application in field of soil remediation
A technology of compound inoculum and bacillus, which is applied in the preparation of compound inoculants and in the field of compound microbial inoculants, can solve problems such as long-term stability of unfavorable soils
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0048] The second aspect of the present invention provides the preparation method of the composite bacterial agent described in the first aspect, the preparation method comprising the following steps: Bacillus tianshenli strain S5, Bacillus tianshenli P46, Bacillus tianshenli strain Bacillus velezensis S3 and Bacillus subtilis P30 are fermented separately to obtain fermentation liquid, and the fermentation liquid is dried to obtain bacterial powder, which is obtained by compounding the bacterial powder of the above strains with the substrate.
[0049] Preferably, the fermentation includes slant culture, primary seed culture, expanded culture and fermenter culture, and when the spore rate in the fermenter reaches more than 90%, the fermentation broth is collected.
[0050] Further preferably, the slant culture is cultured at 37°C for 24-30 hours.
[0051] Further preferably, the specific method of the primary seed cultivation is as follows: use an inoculation loop to inoculate ...
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment one, the screening of strain
[0062] 1. Materials and methods
[0063] 1.1 Samples: 11 sample materials such as soil and water samples around the electroplating plant.
[0064] 1.2 Screening medium:
[0065] Nutrient medium for bacterial strains: NB synthetic medium, 1.5% agar is added on the basis of NB medium to form a solid medium.
[0066] Screening medium (NBRIP) of phospholytic bacteria strains: glucose 1.0%, Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 0.5%, MgCl 2 0.5%, peptone 0.5%, agar powder 2.0%, pH 7.2-7.4, sterilized at 121°C for 30 minutes.
[0067] Screening medium for sulfate-reducing bacteria strains: dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.05%, anhydrous calcium chloride 0.01%, ammonium chloride 0.1%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2%, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.05%, sodium chloride 0.1 %, 0.05% ascorbic acid, 0.05% L-Cys cysteine, 0.5% anhydrous sodium sulfate, 0.65% sodium lactate solution, 2.0% agar powder, pH 6.8-7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 30min.
[006...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Embodiment two, identification and safety test of bacterial classification
[0085] 1. Materials and methods
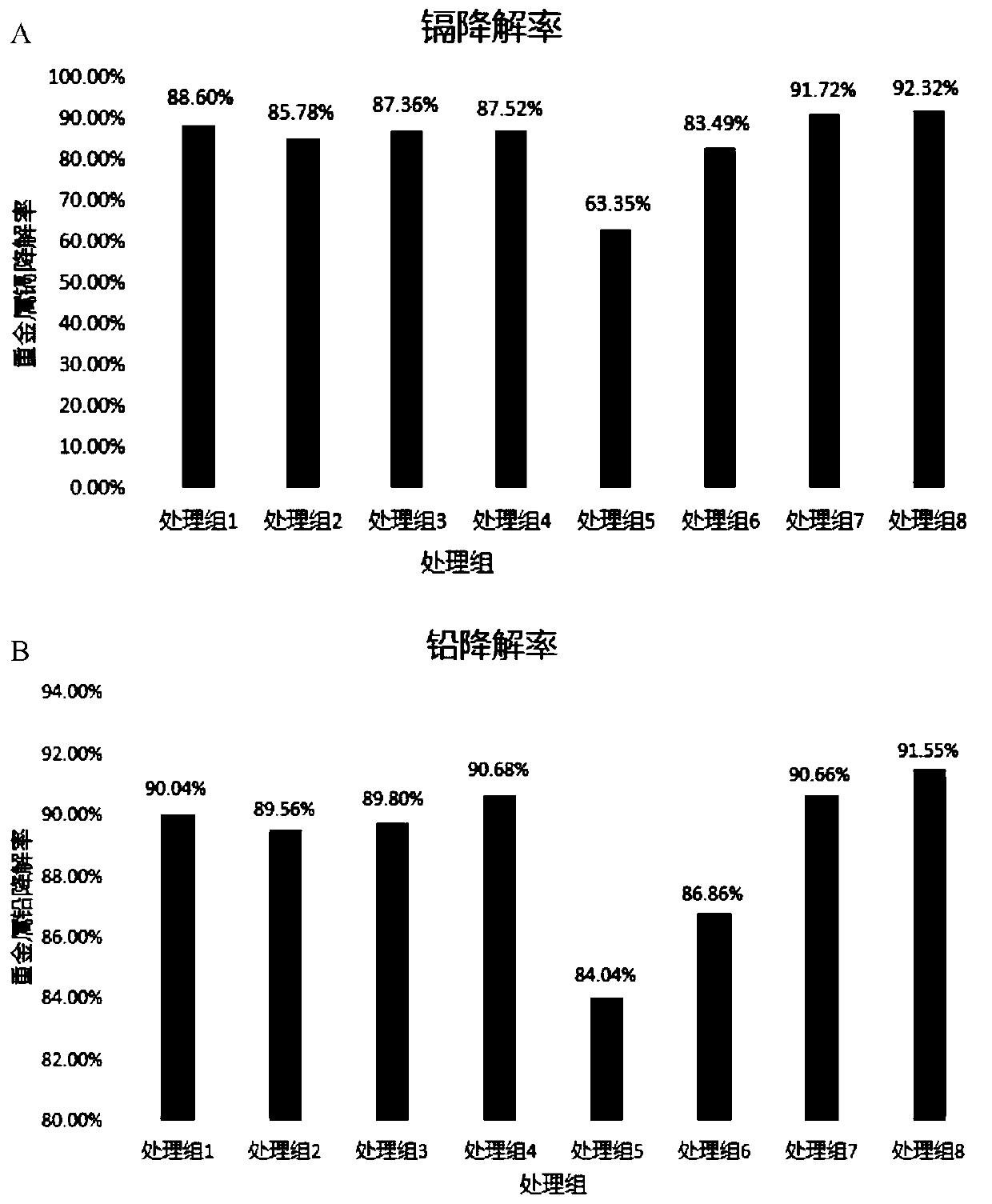
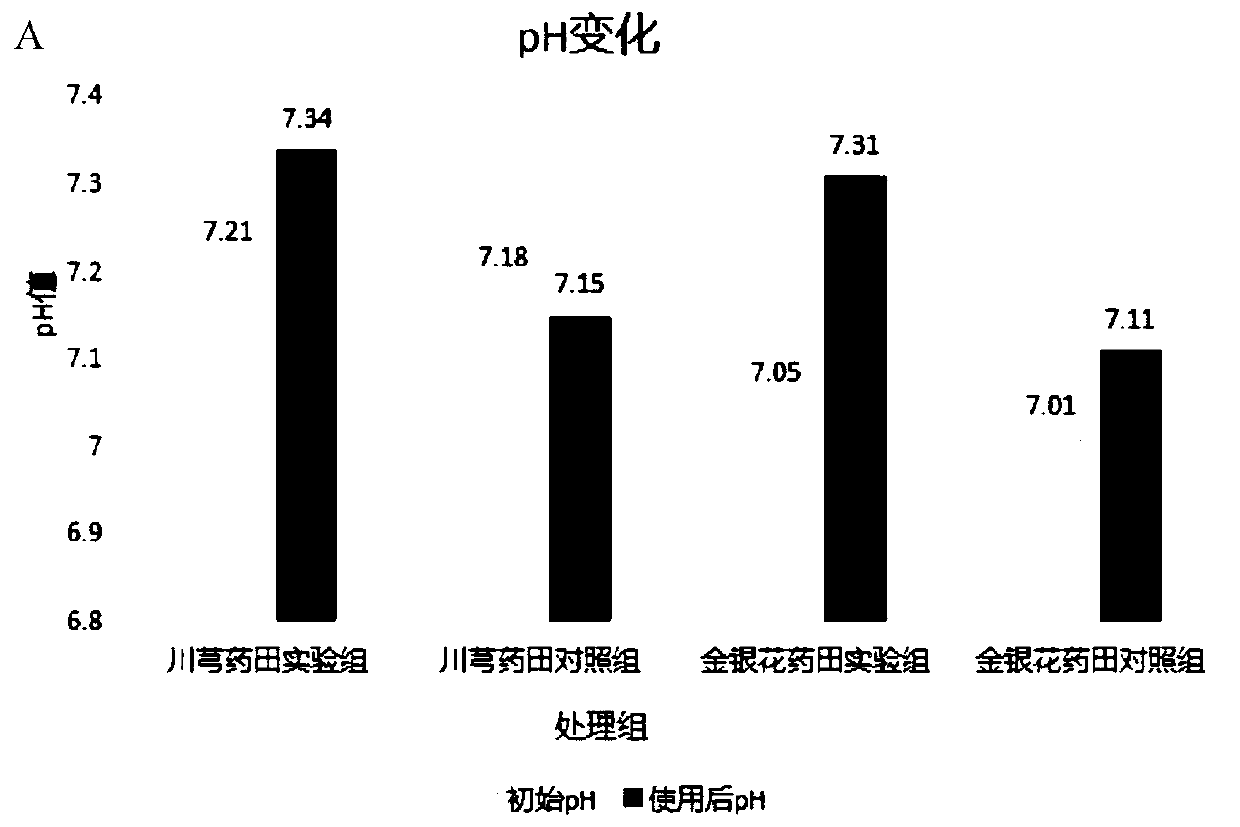
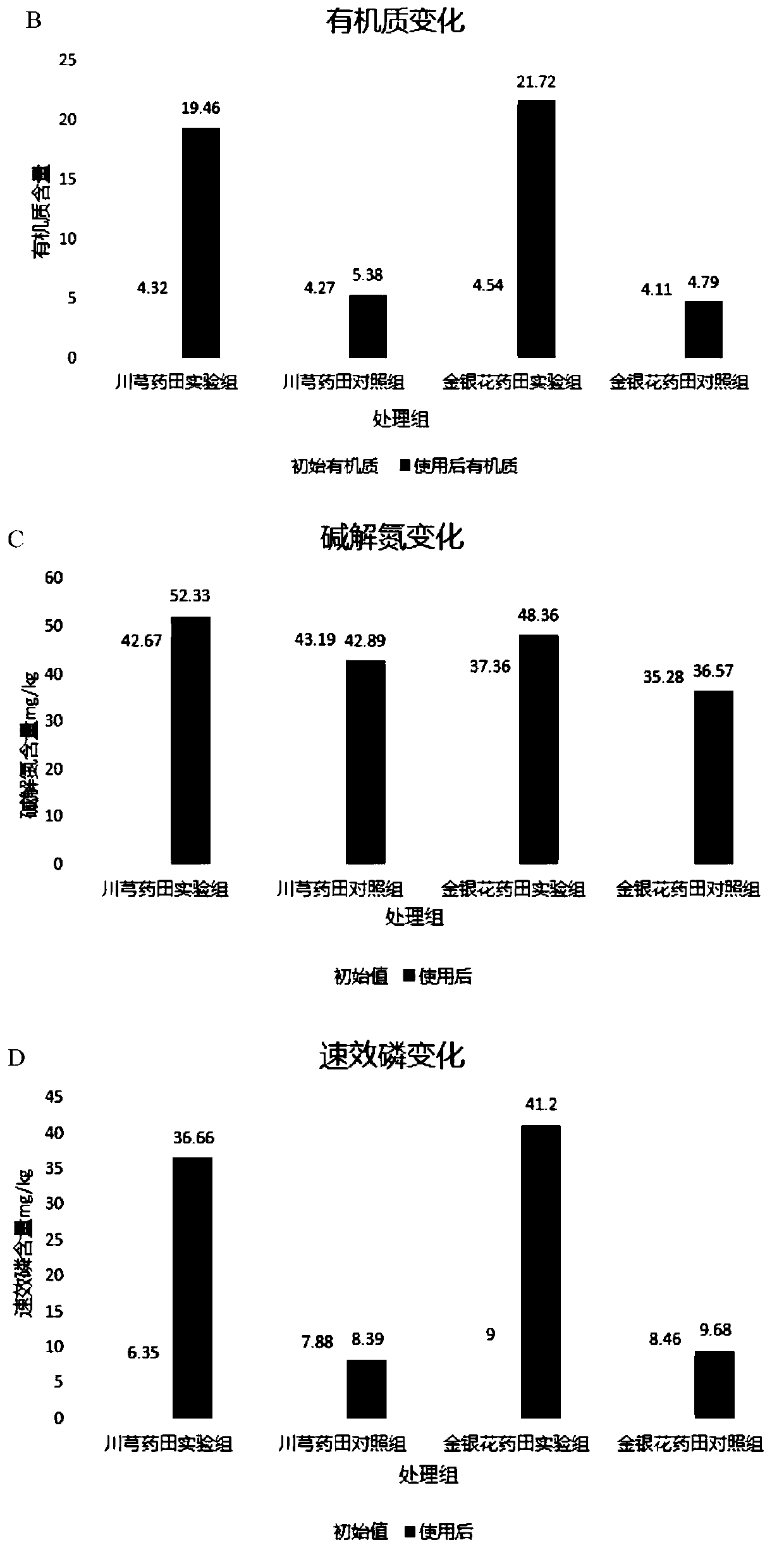
[0086] 1.1 Bacterial strains: The microorganisms isolated from the soil and water samples of the electroplating plant were screened through primary screening and secondary screening, and a total of 4 strains with high heavy metal degradation performance were screened out, and the numbers were P30, P46, S3 and S5.
[0087] 1.2 Morphological identification and molecular identification of bacteria: Unless otherwise specified, general morphological and molecular tests were carried out with reference to "Bergey's Bacterial Identification Manual" (9th edition) and "Microbiology Experimental Manual".
[0088] 1.3 Safety test: The phytotoxicity test of the bacteria is carried out by using "pearl" tomato seeds and "crystal" lettuce seeds. Seeds were soaked in 2% concentration of single bacterial solution, mixed bacterial solution (1:1:1) and distilled water (control gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com