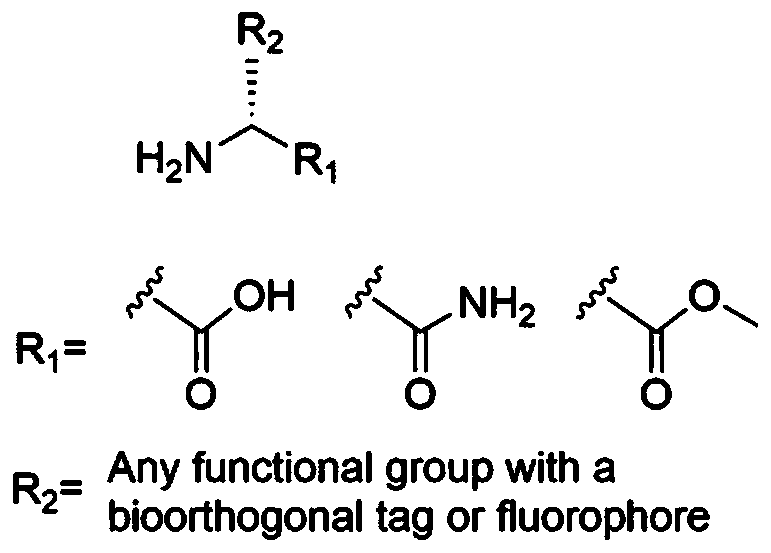
Antibacterial drug sensitivity test detection method based on fluorescent D-type amino acid metabolism marker
A detection method, amino acid technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, microbial determination/inspection, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as high equipment cost, high technical threshold, and wrong judgment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
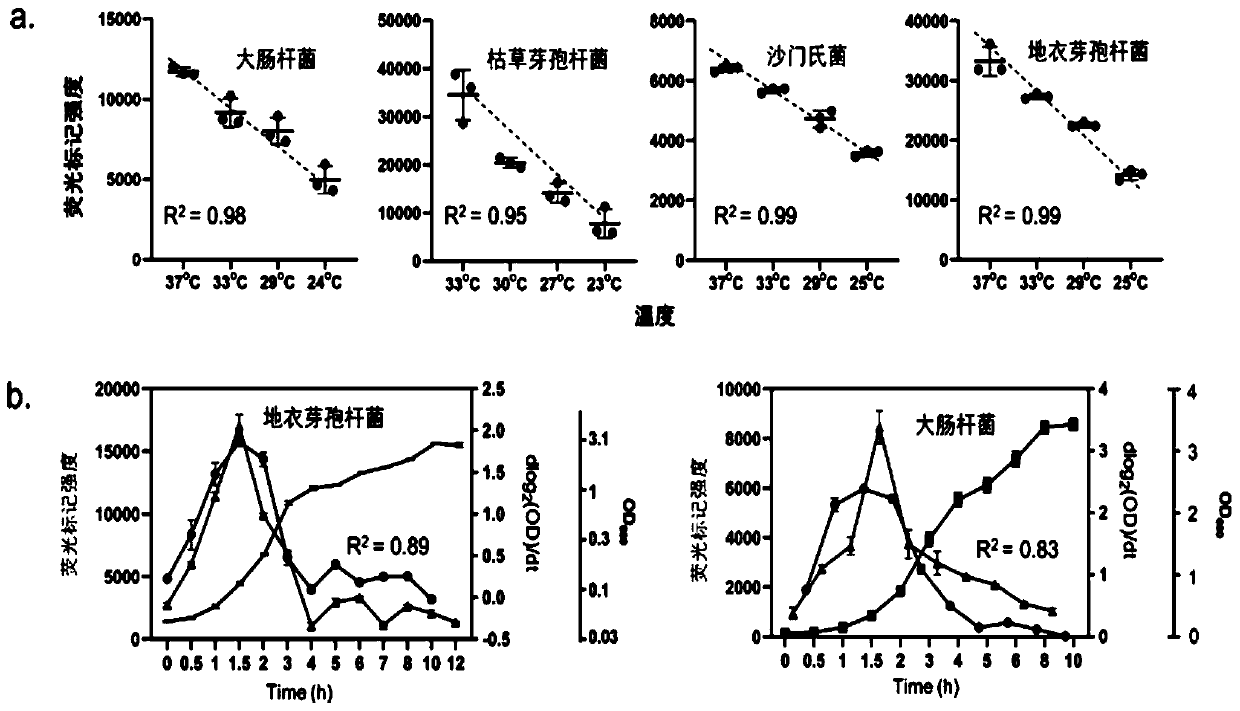
[0028] Detection of oxacillin (OX), vancomycin (VA), and erythromycin (E) against Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus) with high levels of OX-resistant strain ST5, Effects of low-level OX-resistant strain ST59 and OX-sensitive strain ST398.
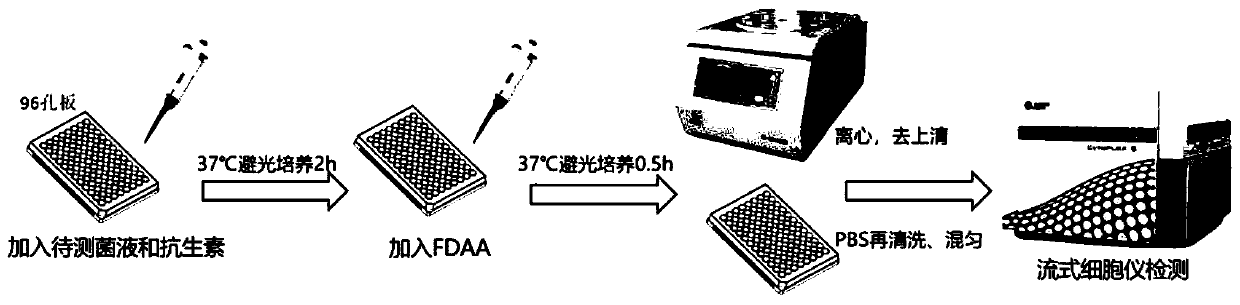
[0029] as attached image 3 The flow chart of the rapid detection method for antimicrobial susceptibility testing based on FDAA metabolic markers is shown, and the specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0030] 1. Pick the colony to be tested that was cultured on the plate overnight and mix it well in normal saline to make a uniform bacterial solution, dilute it into cation-adjusted broth medium (CAMHB) to make a bacterial solution with a concentration of OD600=0.2.
[0031] 2. Add 45 μl of different concentrations of the antibiotic solution to be tested to the 96-well plate (see Table 1 for the antibiotic concentration gradient setting).
[0032] 3. Add 50 μl of the bacterial solution prepared in step 1 to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Using FDAA metabolic labeling method to detect the effects of cefepime (FEP), imipenem (IPM), levofloxacin (LEV) and tigecycline (TGC) on Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli) drug-resistant strain 1113 and sensitive strain 1146.
[0048] The specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0049] 1. Pick the colony to be tested that was cultured on the plate overnight and mix well in normal saline to make a uniform bacterial solution, dilute it into cation-adjusted broth medium (CAMHB) to make a bacterial solution with a concentration of OD600=0.2.
[0050] 2. Add 45 μl of different concentrations of antibiotic solutions to be tested to the 96-well plate (see Table 3 for antibiotic concentration gradient settings).
[0051] 3. Add 50 μl of the bacterial solution prepared in step 1 to the 96-well plate, mix well, and incubate at 37°C in the dark for 2 hours.
[0052] 4. Add 5 μl of 10 mM Cy5-DAA probe (final concentration 0.5 mM, see attached image 3 ), aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com