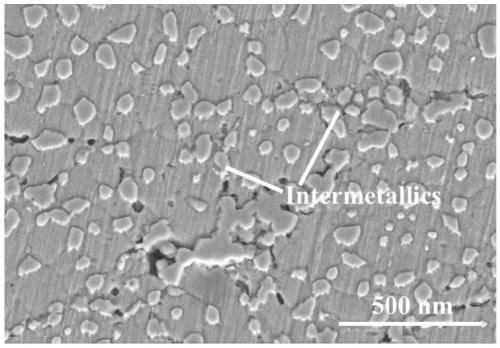
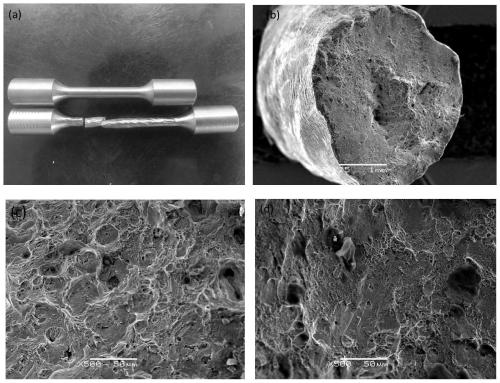
Nano intermetallic compound dispersion strengthened high-conductivity wear-resistant copper alloy and manufacturing method and application thereof
A dispersion-strengthening, nano-metal technology, applied in mechanical equipment, friction linings, etc., can solve the problem that the quality is difficult to meet the requirements of high-speed operation of standard EMUs, the uniformity of structure and properties and casting shrinkage, which affect the quality reliability and stability. and other problems, to achieve the effects of fine grain size, enlarged equiaxed grain area, and improved hardness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1. Test equipment and drugs
[0040] 1.1. Test equipment and test instruments
[0041] 1) JBW-300H instrumented impact testing machine;
[0042] 2) CMT5015 microcomputer-controlled universal testing machine;
[0043] 3) Vickers hardness tester;
[0044] 4) Metallographic microscope;
[0045] 5) scanning electron microscope;
[0046] 6) X-ray diffractometer;
[0047] 7) AztecX-Max50 energy spectrometer;
[0048] 8) Beaker, alcohol cotton, tweezers, sandpaper, polishing machine, ultrasonic cleaning machine;
[0049] 9) MFT-3000 friction and wear testing machine
[0050] 1.2. Test drugs
[0051] 1) Ethanol cleaning agent
[0052] 2) Concentrated hydrochloric acid, concentrated nitric acid (mixed into aqua regia at a volume of 3:1)
[0053] 2. Characterization and test methods
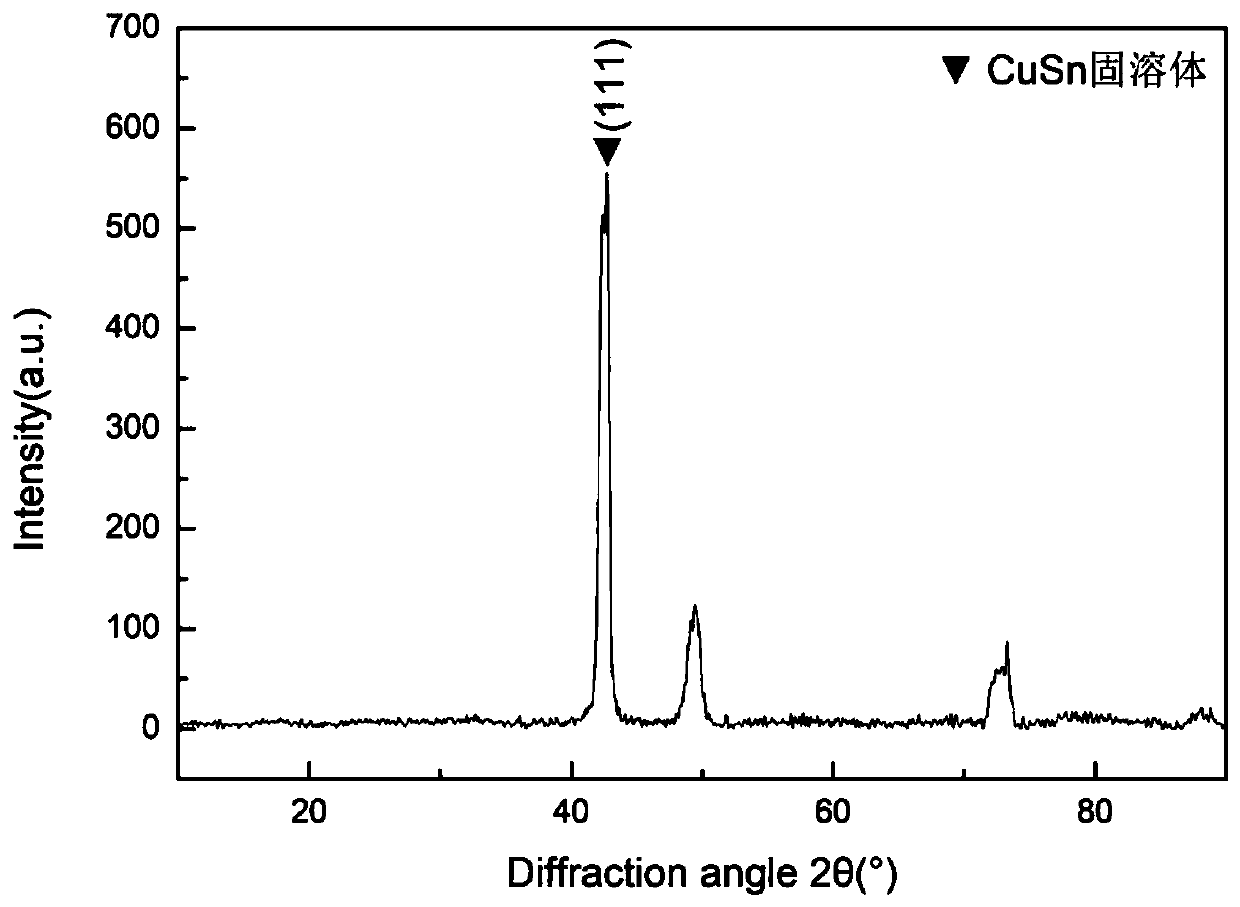
[0054] 2.1. X-ray diffraction analysis
[0055] The surface of the sample is flattened and measured with a Bruker AXS D8-Advance X-ray diffractometer (Cu target, Kα λ=0.154nm. German Bruke...
Embodiment 2
[0128] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that a nano-intermetallic compound dispersion strengthened high-conductivity wear-resistant copper alloy is provided, the composition and mass percentage are as follows: Sn: 4%, Ni: 4%, Ag: 0.05%, Rare earth elements: 0.07%, Zn: 2.43%, Al: 4%, Mn: 3.5%, Sc: 0.05; B: 0.02%; rare earth elements include Ce, La and Y; Ce: 0.019%, La: 0.038%, Y : 0.013%, the balance is Cu.
[0129] A kind of manufacture method of nanometer intermetallic compound dispersion strengthened high conductivity wear-resistant copper alloy, comprises the following steps:
[0130] Step 1: Use a power frequency melting furnace to smelt copper alloys: preheat the power frequency melting furnace at 600°C. After the preheating is complete, put Zn into the bottom of the power frequency melting furnace, then cover the Zn with Cu, and raise the temperature to 750°C within 30 minutes After melting, the temperature is raised to 2300°C within 4 hours, ...
Embodiment 3
[0137]The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that a nano-intermetallic compound dispersion strengthened high-conductivity wear-resistant copper alloy is provided, the composition and mass percentage are as follows: Sn: 6%, Ni: 2%, Ag: 0.3%, Rare earth elements: 0.12%, Zn: 2%, Mn: 3.5%, Sc: 0.02%; B: 0.02%; rare earth elements include Ce, La, Y and Pr; Ce: 0.019%, La: 0.038%, Y: 0.013 %, Pr: 0.05%, and the balance is Cu.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com