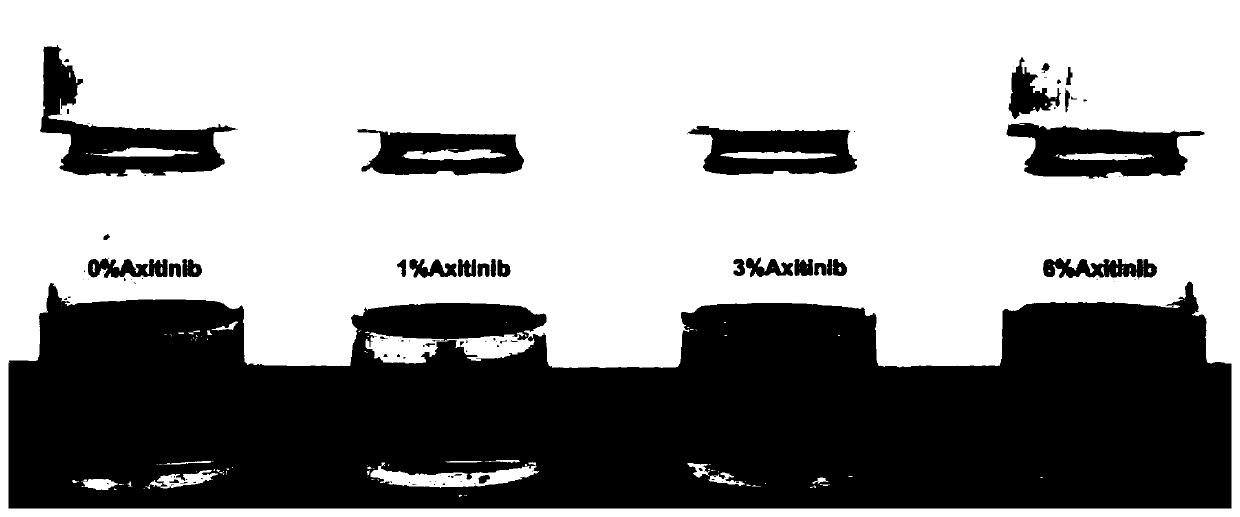
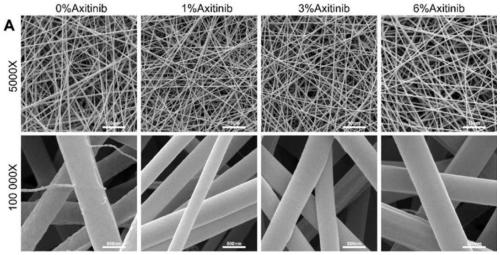
Axitinib-contained nanofiber electrospun membrane and preparation method and application thereof
A nanofiber and axitinib technology, which is applied in the field of nanofiber electrospun membrane containing axitinib and its preparation, can solve the problems of easy ossification of cartilage and achieve ossification prevention, stable structure and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: Preparation of collagen / polycaprolactone nanofiber membrane loaded with Axitinib
[0040] 0 mg, 12 mg, 36 mg, and 72 mg of Axitinib were weighed and dissolved in 10 ml of hexafluoroisopropanol, and 20-30 microliters of acetic acid was added to the solution, and stirred until uniformly mixed. Then add 0.48 gram of collagen and 0.72 gram of polycaprolactone to be made into the spinning solution (collagen and polycaprolactone total mass and hexafluoroethylene) of 12% g / ml in the Axitinib solution of above-mentioned four kinds of different concentrations to be made into mass volume percentage then respectively volume percent of isopropanol solution). A 10ml syringe and a needle with an inner diameter of 1.2mm were selected to extract the collagen / polycaprolactone spinning solution, which was fixed on an electrospinning device for spinning. Electrospinning parameters are: voltage 8-15kv, receiving distance 10-15cm, injection rate 1-3ml / h, temperature 15-30°C, ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2: Study on in vitro biocompatibility and in vitro activity of collagen / polycaprolactone nanofiber membrane loaded with Axitinib
[0043] Rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and rabbit auricle chondrocytes were isolated, cultured and expanded in vitro. The collagen / polycaprolactone nanofiber membranes loaded with 0%, 1%, 3% and 6% Axitinib were sterilized and placed at the bottom of a 24-well plate for use. The second-generation BMSCs and second-generation chondrocytes were seeded on four different amounts of Axitinib-loaded nanofiber materials. On the 1st, 4th and 7th day after inoculation, add CCK8 solution to the culture medium for incubation, and detect the absorbance of the supernatant to judge the proliferation efficiency of the cells on the material. On day 1 and day 7 after inoculation, the cells were fixed, and the nuclei and cytoskeleton were fluorescently stained and photographed.
[0044] The result is as Figure 4 As shown, compared...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Construction of tissue engineered cartilage blocks derived from stem cells in vitro
[0048] Use cylindrical PGLA non-woven scaffolds, such as Figure 6 As shown in A. Observation of the scaffold with a scanning electron microscope, such as Figure 6 B-C, it can be seen that the fiber thickness is uniform, and the fiber diameter distribution is measured, such as Figure 6 D, PGLA fiber diameter is 12.7±1.8um. The second-generation BMSCs were seeded on PGLA scaffolds, such as Figure 6 E, in vitro chondrogenic induction culture, at intervals, SEM observation of cell attachment growth on the scaffold, such as Figure 6 F-H( Figure 6 F is the first day of cell inoculation, Figure 6 G is the 7th day of inoculation, Figure 6 H is the 14th day of inoculation). It can be seen that with the increase of culture time, the secretion of cell matrix increases and gradually fills the gaps between PGLA fibers. After 4 weeks of chondrogenic induction, the tissue-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com