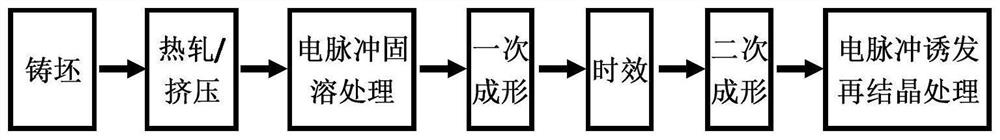
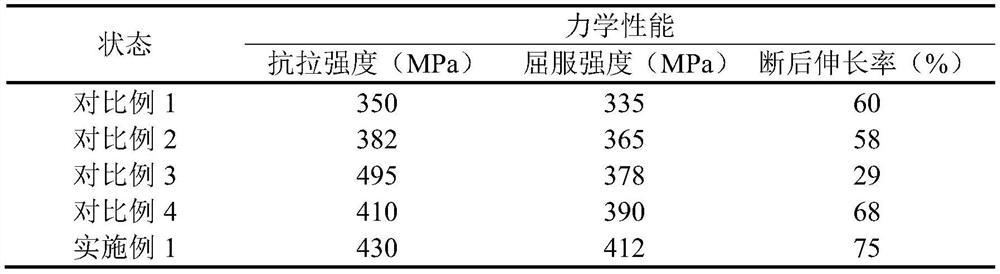
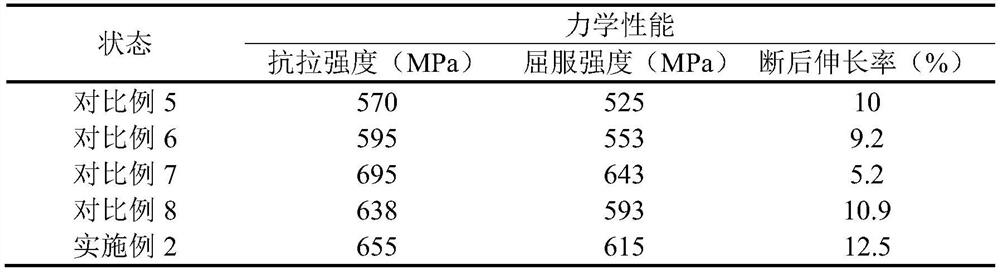
A method for strengthening and toughening non-ferrous metal materials
A non-ferrous metal strengthening and toughening technology, which is applied in the field of strengthening and toughening non-ferrous metal materials, can solve problems such as uneven size distribution, affecting product quality, and demanding processing technology, so as to improve solid solubility and solute atom diffusion ability , Improve the solid solution effect and surface quality, and promote the effect of solute atom diffusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: the preparation of H62 copper alloy strip
[0047] (1) The hot-rolled H62 (Cu-37.5wt% Zn) copper alloy strip blank is subjected to rapid solid solution and water spray cooling and quenching treatment by electric pulse, so that the precipitated phase in the alloy is solid-dissolved in the copper matrix. The electric pulse parameters input to the energized region of the copper alloy strip blank are: frequency 1500Hz, pulse width 100μs, current density amplitude 5000A / mm 2 , effective current density 700A / mm 2 , the maximum heating temperature is 800°C, the heating time is 30s; the cooling water flow rate of spray water is 50L / min.
[0048] (2) Carry out a cold rolling to the copper alloy strip material of electric pulse solution treatment in step (1), pass reduction rate 20%, total reduction rate 80%, rolling speed 50m / min;
[0049] (3) aging treatment is carried out to the primary cold-rolled copper alloy strip in step (2), the aging temperature is 450 DE...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2: Preparation of 7050 aluminum alloy strip
[0064] (1) Rapid solid solution and water spray cooling and quenching are carried out on the hot-rolled 7050 (Al-6.3wt% Zn-2.4wt% Cu-2.1wt% Mg) aluminum alloy strip by electric pulse, so that the precipitated phase in the alloy Soluble in aluminum matrix. The parameters of the electric pulse input to the energized area of the aluminum alloy strip are: frequency 1000Hz, pulse width 120μs, current density amplitude 1500A / mm 2 , effective current density 250A / mm 2 , the maximum heating temperature is 420°C, the heating time is 15s; the flow rate of water spray cooling water is 30L / min.
[0065] (2) Carry out one-time cold rolling to the aluminum alloy strip material treated by electric pulse solution treatment in step (1), the pass reduction rate is 20%, the total reduction rate is 90%, and the rolling speed is 4m / min;
[0066] (3) Aging treatment is carried out to the primary cold-rolled aluminum alloy strip in...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3: the preparation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy strip
[0081] (1) Use electric pulses to perform rapid solution and water spray cooling and quenching treatment on the hot-rolled Ti-6Al-4V (Ti-5.8wt%Al-4.1wt%V) alloy strip, so that the precipitated phase in the alloy is solid-dissolved in a titanium matrix. The parameters of the electric pulse input to the energized region of the titanium alloy strip blank are: frequency 2500Hz, pulse width 100μs, current density amplitude 5500A / mm 2 , effective current density 900A / mm 2 , the maximum heating temperature is 960°C, the heating time is 30s; the cooling water flow rate of spray water is 80L / min.
[0082] (2) Carry out a cold rolling to the titanium alloy strip material of the electric pulse solution treatment in the step (1), the pass reduction rate is 20%, the total reduction rate is 50%, and the rolling speed is 3m / min;
[0083] (3) Aging treatment is carried out to the primary cold-rolled titanium alloy strip in ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com