Method for magnetic field assisted solvothermal synthesis of ferrite and method for regulating and controlling magnetic grain size and morphological characteristics
A magnetic field-assisted, topographical feature technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, inorganic materials, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and complicated process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
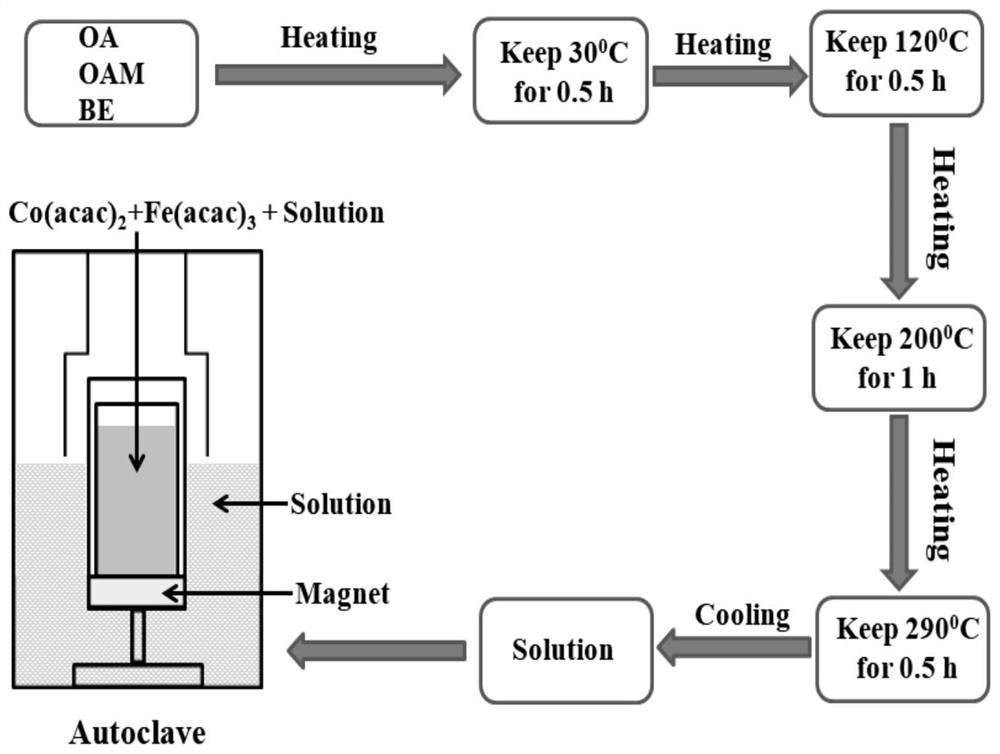
[0045] Please also refer to figure 1 , a method for magnetic field-assisted solvothermal synthesis of ferrite, the steps are as follows:
[0046] ①, solvent pretreatment
[0047] Put oleic acid (OA), oleylamine (OAM) and benzyl ether (BE) into a three-necked flask at a volume ratio of 1:1:4, stir magnetically at 30°C for 0.5h to make the solution evenly mixed, and heat to 120°C Insulate for 0.5h to remove water or alcohol in the solution, and pass high-purity N 2 After protection, heat to 200°C for 1h, and finally heat to 290°C for 0.5h; after the solution is naturally cooled to room temperature, it is used as the preparation of MFe 2 o 4 (M=Co, Ni, Zn) Solvent for ferrite and heat transfer medium.
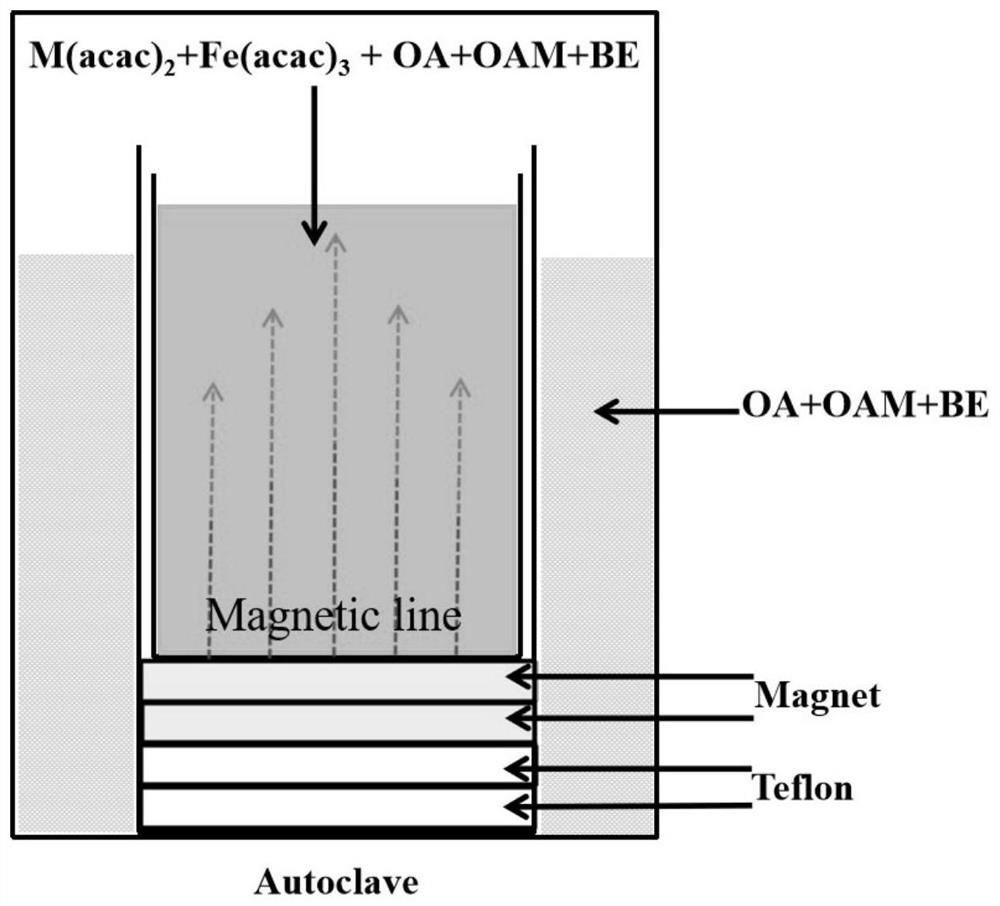
[0048] ②, using iron and metal M (M = Co, Ni, Zn) acetylacetonate as MFe 2 o 4 (M=Co, Ni, Zn) Raw materials for the preparation of ferrite, weigh the acetylacetonate salt of iron and metal M (M=Co, Ni, Zn) according to the stoichiometric ratio, and mix evenly with the solven...
Embodiment 2
[0056] magnetic field on hard magnetic CoFe 2 o 4 Effect of crystal structure\morphology\magnetic properties
[0057] 1. CoFe 2 o 4 Crystal structure and morphology analysis of
[0058] CoFe synthesized in different magnetic fields 2 o 4 XRD results of samples Co0, Co1, Co2, Co3, Co4 and CoFe 2 o 4 Comparison of standard powder diffraction cards (NO.22-1086) reveals that all samples are single-phase spinel structures with a space group of Fd-3m(227). Figure 5 (a) The XRD patterns of Co0 samples are given only representatively. Figure 5 (b) is the enlarged XRD pattern (open circle) of Co0~Co4 samples around 2θ=35.57°. In order to more clearly determine the 2θ angle corresponding to the diffraction peak, we fit the experimental curve with a Gaussian function (solid line). From Figure 5 From the results of (b), it can be seen that the strongest peak of the Co0 sample is located at the position of 2θ=35.57°; the position of the strongest peak of the sample synthesize...
Embodiment 3
[0073] magnetic field on soft magnetic NiFe 2 o 4 Effect of crystal structure\morphology\magnetic properties
[0074] 1. NiFe 2 o 4 Crystal structure and morphology analysis of
[0075] Figure 10 (a) shows the XRD pattern of Ni0 sample and NiFe 2 o 4 Standard powder diffraction card (NO.54-0964). The position of the strongest peak in the figure is 2θ=35.68°, which corresponds to the diffraction of the (311) crystal plane. By comparison with the standard PDF card, it can be seen that the Ni0 sample is NiFe with a single-phase spinel structure 2 o 4 , the space group is Fd-3m(227).
[0076] Figure 11 SEM (a, d), TEM (b, e) and HRTEM (c, f) images of Ni0 and Ni4 samples are given. From Figure 11(a) It can be seen that the Ni0 sample synthesized without an external magnetic field is mainly composed of spherical particles with non-uniform size, and the diameter of the largest spherical particle is about 1.4 μm. The Ni4 sample synthesized under the condition of an e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com