Xanthomonas axonopodis as well as composition, kit and application thereof
A technology of monocysts and phages, applied in the field of research and development of Xanthomonas rugosa, can solve the problem of no relevant research and reports on citrus canker, and achieve the effect of a wide host range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Isolation, preparation and purification of phage
[0040] In the present invention, the source sample of Xanthomonas rugosa bacteriophage YHC5 is collected from domestic sewage near University City, Jiangning District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province. After filtering through double-layer filter paper, it is centrifuged at low speed at normal temperature, and then filters the supernatant with a 0.22 μm filter membrane.
[0041] Isolation of bacteriophage: add 10 mL of 2 times TSB medium to 10 mL of the filtered sample supernatant, and add 1 mL of Xanthomonas rugosa host bacteria logarithmic phase bacterial liquid at the same time, shake and culture at 150 r at 25 ° C for 12 h. The above-mentioned culture was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and stored at 4°C for future use. Take 0.5mL of Xanthomonas rugosa host bacteria in the logarithmic phase, add 5mL of semi-solid TSB medium not higher than 4...
Embodiment 2
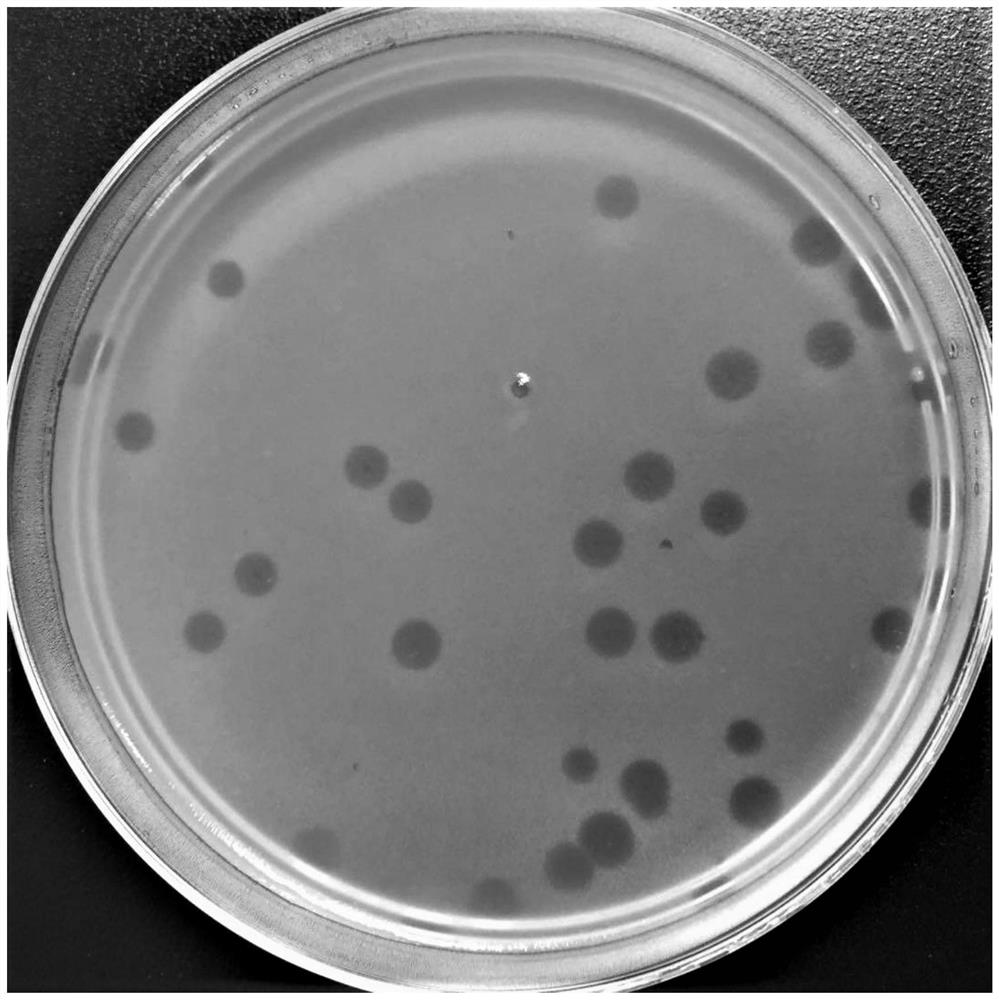
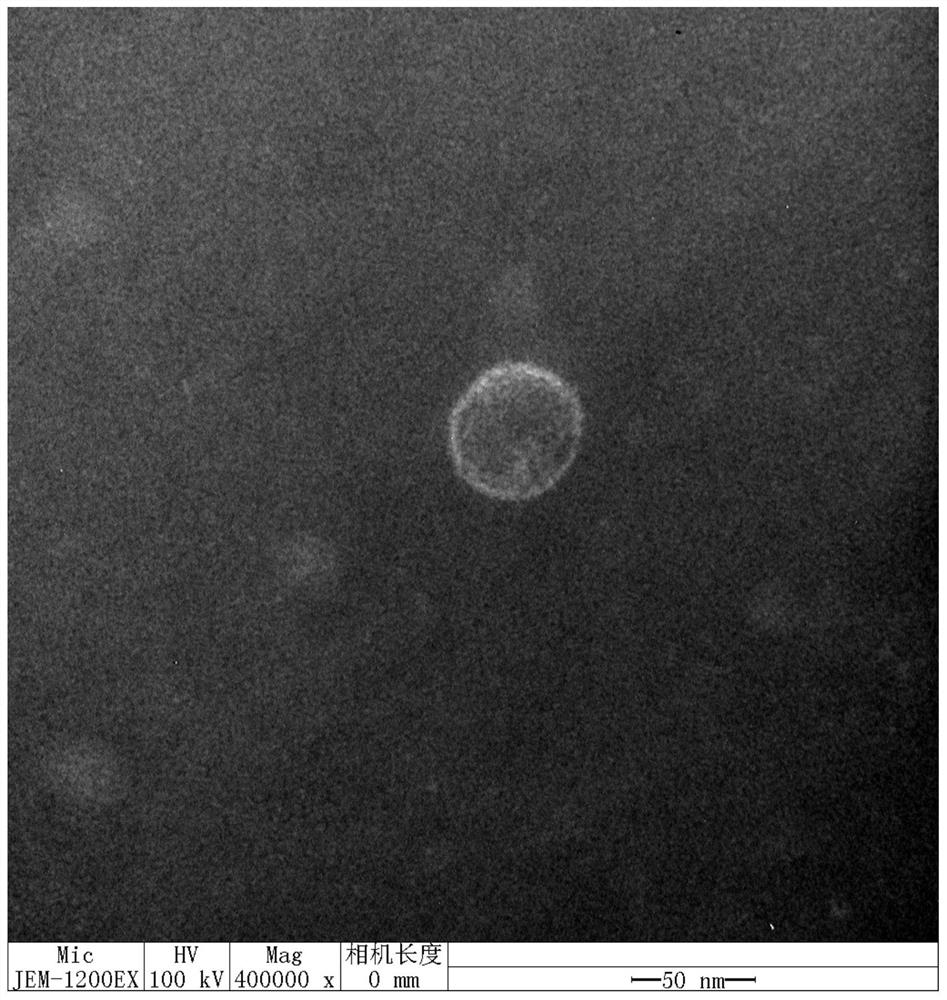
[0044] Embodiment 2: Electron microscope observation of phage
[0045] Take the filtrate of Xanthomonas axonopodis phageYHC5 (Xanthomonas axonopodis phageYHC5) obtained in Example 1 respectively for electron microscope observation: get 20 μ L of sample and drop it on the copper grid, wait for its natural precipitation for 15 minutes, absorb excess liquid from the side with filter paper, add 1 Drop 2% phosphotungstic acid (PTA) on the copper grid, stain for 10 minutes, use filter paper to absorb the dye solution from the side, and observe it with a transmission electron microscope after drying, and observe it with a transmission electron microscope The result is as figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: Extraction and sequencing of phage genome
[0047] Get Xanthomonas axonopodis phageYHC5 (Xanthomonas axonopodis phageYHC5) phage 100mL that makes in Example 1, add the DNaseI of final concentration 1 μ g / mL, RNaseA, add 5.84g Nacl (final concentration 1mol / L ), and placed in an ice bath for 1 h after dissolving. Centrifuge at 11,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, and transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube. Add solid PEG8000 (final concentration 10%, that is, add 10g to 100mL), and after complete dissolution, keep ice bath for at least 1h. Centrifuge at 11,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C, and resuspend the pellet with a small amount of SM solution. Add an equal volume of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol for extraction, gently shake for 30s, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 1min, absorb the supernatant, and repeat the extraction until clarification. Add DNaseI and RNase A again to a final concentration of 1 μg / mL, and react at 37°C for 30-60 minutes. Add EDTA to a fina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com