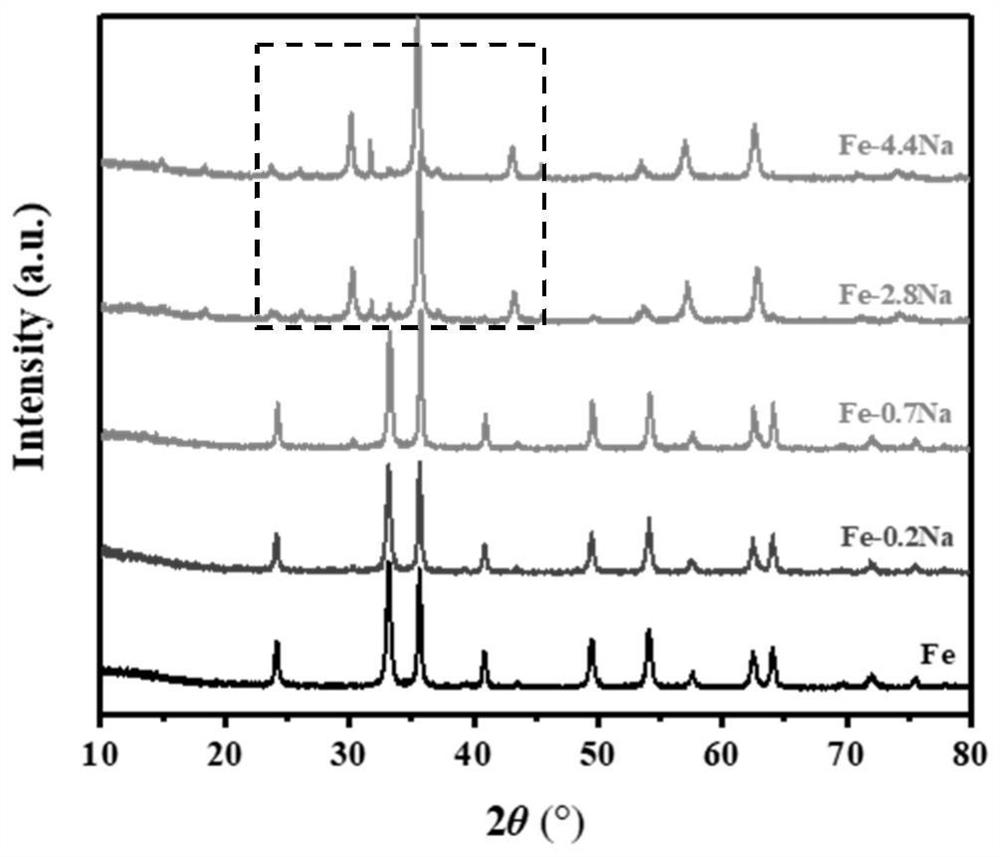
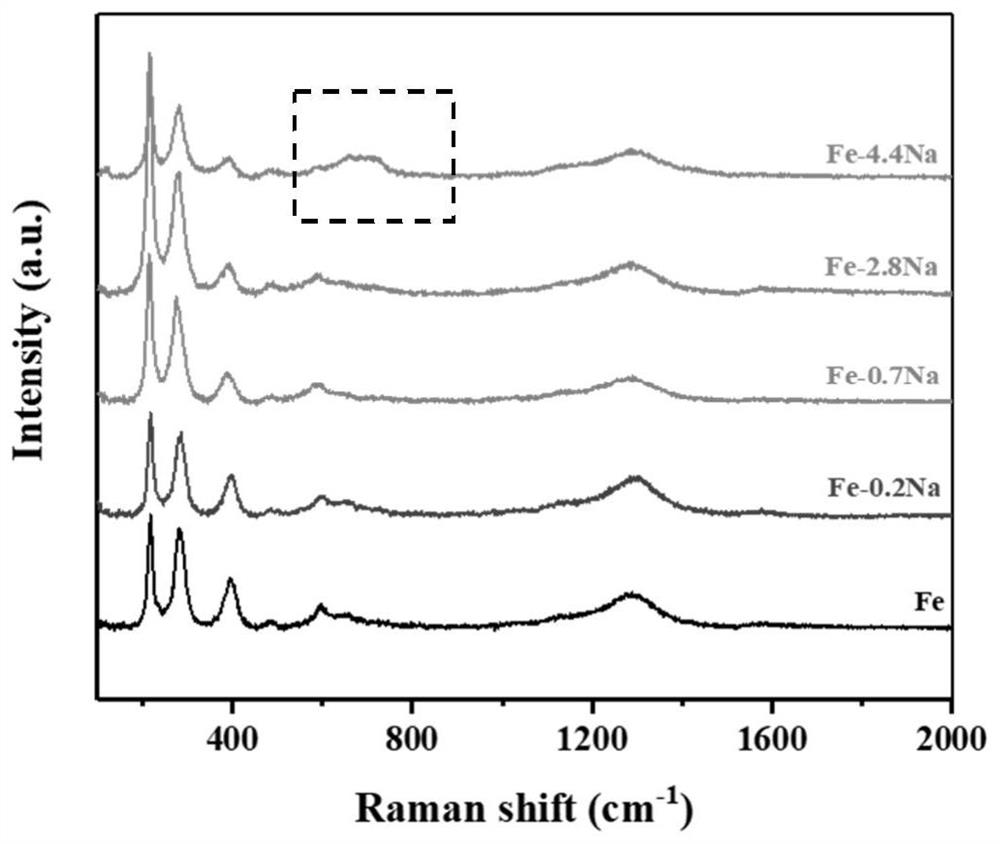
Preparation method of ferric oxide with different crystal forms
A technology of iron oxide, crystal form, applied in the direction of iron oxide, iron oxide/hydroxide, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of controllable regulation, different product morphology and properties, etc. , to achieve the effect of preventing solution coagulation, low equipment requirements, and good antifreeze performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Preparation of α-Fe 2 O 3 The process is as follows:
[0037] First, 2.54g of anhydrous ferrous chloride was weighed and dissolved in the same beaker containing 60ml of ethylene glycol, and ultrasonically stirred for 10 minutes; then, the solution was transferred to a three-necked flask, and the temperature was maintained in an oil bath under magnetic stirring At -20℃, keep for 1h;
[0038] Dissolve 7.52g of ammonium carbonate in 100ml of prepared deionized water, stir ultrasonically for 5min until the sodium carbonate is completely dissolved, and continue to stand for 30min; then add the ammonium carbonate solution dropwise to the ethyl acetate of ferrous chloride at a rate of 1.2ml / min. In the glycol solution, continue to age the precipitate for 2h after the dropwise addition;
[0039]The liquid precipitation mixture was filtered on a suction filter with 1000 mL of deionized water, and the precipitate was separated and transferred to an oven, and dried at 120 °C fo...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Preparation of Alkali-free γ-Fe 2 O 3 The process is as follows:
[0042] First, 2.54g of anhydrous ferrous chloride was weighed and dissolved in the same beaker containing 60ml of ethylene glycol, and ultrasonically stirred for 10 minutes;
[0043] Then, the solution was transferred to a three-necked flask, and the temperature was maintained at -20 °C in an oil bath under magnetic stirring for 1 h; 8.48 g of sodium carbonate was dissolved in 100 ml of prepared deionized water, and ultrasonically stirred for 5 min until the sodium carbonate was completely Dissolve, continue to stand for 30min; then add the sodium carbonate solution dropwise to the ethylene glycol solution of ferrous chloride at a speed of 1.2ml / min, and continue to age the precipitate for 2h after the dropwise addition;
[0044] Distribute the suspension evenly to 6 centrifuge tubes with a range of 50mL, add deionized water to the 35mL mark, centrifuge at 8000r / min for 5 minutes, separate the supernat...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Preparation of γ-Fe by Cellulose Template Impregnation Method 2 O 3 The process is as follows:
[0048] First, cut the cellulose template into a size of 0.5cm×0.5cm, weigh 1g, and add deionized water dropwise to measure its saturated water absorption;
[0049] Next, dissolve 1.875g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate and 0.256g of potassium nitrate in deionized water equal to its saturated water absorption;
[0050] Then, the prepared nitrate solution was added dropwise to the 1 g cellulose template while stirring, and the stirring was continued for 10 min after the dropwise addition;
[0051] Transfer the impregnated cellulose template into an oven at 120 °C for 10 hours until the water evaporates to dryness;
[0052] The dried precipitate was ground and calcined in an air-vented muffle furnace, raised to 900°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min, and held for 4 hours to obtain γ-Fe 2 O 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com